Related Research Articles

The BBC World Service is an international broadcaster, owned and operated by the BBC. It is the world's largest of any kind. It broadcasts radio news, speech and discussions in more than 40 languages to many parts of the world on analogue and digital shortwave platforms, internet streaming, podcasting, satellite, DAB, FM and MW relays. In 2015, The World Service reached an average of 210 million people a week. In November 2016, the BBC announced that it would start broadcasting in additional languages including Amharic and Igbo, in its biggest expansion since the 1940s.

Shortwave radio is radio transmission using shortwave radio frequencies. There is no official definition of the band, but the range always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), and generally extends from 3–30 MHz ; above the medium frequency band (MF), to the end of the HF band.

Voice of America (VOA) is a U.S. multimedia agency which serves as the United States government institution for non-military, external broadcasting. It is the largest U.S. international broadcaster. VOA produces digital, TV, and radio content in 47 languages which it distributes to affiliate stations around the globe. It is primarily viewed by foreign audiences, so VOA programming has an influence on public opinion abroad regarding the United States and its people.
International broadcasting is broadcasting that is deliberately aimed at a foreign, rather than a domestic, audience. It usually is broadcast by means of longwave, mediumwave, or shortwave radio, but in recent years has also used direct satellite broadcasting and the internet as means of reaching audiences.
A numbers station is a shortwave radio station characterized by broadcasts of formatted numbers, which are believed to be addressed to intelligence officers operating in foreign countries. Most identified stations use speech synthesis to vocalize numbers, although digital modes such as phase-shift keying and frequency-shift keying, as well as Morse code transmissions, are not uncommon. Most stations have set time schedules, or schedule patterns; however, other stations appear to broadcast at random times. Stations may or may not have set frequencies in the HF band.
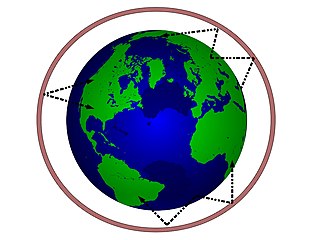
In radio communication, skywave or skip refers to the propagation of radio waves reflected or refracted back toward Earth from the ionosphere, an electrically charged layer of the upper atmosphere. Since it is not limited by the curvature of the Earth, skywave propagation can be used to communicate beyond the horizon, at intercontinental distances. It is mostly used in the shortwave frequency bands.
Radio Netherlands Worldwide was a public radio and television network based in Hilversum, producing and transmitting programmes for international audiences outside the Netherlands. Radio Netherlands Worldwide also distributed content via web and e-mail technology from as early as 1992.

Shortwave listening, or SWLing, is the hobby of listening to shortwave radio broadcasts located on frequencies between 1700 kHz and 30 MHz. Listeners range from casual users seeking international news and entertainment programming, to hobbyists immersed in the technical aspects of radio reception and collecting official confirmations that document their reception of distant broadcasts (DXing). In some developing countries, shortwave listening enables remote communities to obtain regional programming traditionally provided by local medium wave AM broadcasters. In 2002, the number of households that were capable of shortwave listening was estimated to be in the hundreds of millions.
Shortwave broadcasting in the United States allows private ownership of commercial and non-commercial shortwave stations that are not relays of existing AM/MW or FM radio stations, as are common in Africa, Europe, Asia, Oceania except Australia and Latin America. In addition to private broadcasters, the United States also has government broadcasters and relay stations for international public broadcasters. Most privately owned shortwave stations have been religious broadcasters, either wholly owned and programmed by Roman Catholic and evangelical Protestant charities or offering brokered programming consisting primarily of religious broadcasters. To better reach other continents of the world, several stations are located in far-flung US territories. Shortwave stations in the USA are not permitted to operate exclusively for a domestic audience; they are subject to antenna and power requirements to reach an international audience.
HCJB, "The Voice of the Andes", was the first radio station with daily programming in Ecuador and the first Christian missionary radio station in the world. The station was founded in 1931 by Clarence W. Jones, Reuben Larson, and D. Stuart Clark. HCJB now focuses on Ecuador with unified programming on FM at 89.3 MHz in Pichincha, at 92.5 MHz in Manabí, at 96.1 MHz in Tungurahua and Cotopaxi, at 98.3 MHz in Esmeraldas and with separate programming on AM at 690 kHz. Broadcasts in Spanish and indigenous languages on 6050 kHz (1 kW), continue on an intermittent basis with a new solid state transmitter which in 2017 replaced an older (5 kW) transmitter. These broadcasts were not listed on the HCJB English website as of February 2016.

Radio Australia is the international broadcasting and online service operated by the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC), Australia's public broadcaster. Most programming is in English, with some in Tok Pisin and French.
WYFR was a shortwave radio station located in Okeechobee, Florida, United States. The station was owned by Family Stations, Inc., as part of the Family Radio network, and used to broadcast traditional Christian radio programming to international audiences. WYFR ceased all shortwave transmissions July 1, 2013. In December 2013, another shortwave broadcaster, WRMI of Miami, purchased the WYFR transmission complex.

The Woofferton transmitting station is owned and operated by Encompass Digital Media, as one of the BBC’s assets which were handed over as part of the privatization of World Service distribution and transmission in 1997. It is the last remaining UK shortwave broadcasting site, located at Woofferton, south of Ludlow, Shropshire, England. The large site spreads across into neighbouring Herefordshire.
Radio France Internationale, usually referred to as RFI, is a French public radio service that broadcasts in Paris and all over the world. With 35.6 million listeners in 2008, it is one of the most listened to international radio stations in the world, along with BBC World Service, Voice of America and China Radio International.
WRNO is a commercial shortwave radio station which began international broadcasting on February 18, 1982 and continued regular broadcasting through the early 1990s from Metairie, Louisiana, with a continuation of periodic broadcasts starting in 2009. These call letters are still in use by the New Orleans station WRNO-FM; both were founded and originally owned by Joseph Costello III.
Radio México Internacional is a Mexican government-run radio service based in Mexico City. It broadcast as a shortwave radio station with the broadcast callsign XERMX-OC from 1969 to 2004, and was relaunched as an Internet-only radio service in 2011. Since 1983 it has been under the control of the Instituto Mexicano de la Radio (IMER). The -OC suffix is from onda corta, Spanish for "short wave", equivalent to the -SW suffix in Canada.
WGEO-LP is a low-power radio station licensed to Georgetown, South Carolina, United States. Currently owned by the Georgetown City Fire Department, the station broadcasts emergency messages when necessary, as well as visitors' information for Georgetown-area attractions all other times.

DZRP - Radyo Pilipinas Worldwide is a short-wave radio station broadcasting outside the Philippines. Owned by the Philippine Broadcasting Service under the Presidential Communications Group, the station is operated from Mondays to Sundays 11:30 PM to 12:00 NN PST on various shortwave frequencies, with internet live streaming across all schedules. It broadcasts in Filipino and English languages. Radyo Pilipinas uses the relay transmitter tower of Voice of America in Tinang, Concepcion, Tarlac for its broadcast purposes.
WINB is a brokered Christian shortwave radio station licensed to Red Lion, Pennsylvania, in the United States. WINB began broadcasting in October 1962, making it the oldest private shortwave radio station in the United States that is still in operation. In the 1960s, the station was notable for its criticism of American domestic and foreign policy, leading to the government freezing the expansion of private shortwave radio transmission schedules for several years.
KGEI was a privately owned shortwave radio station based originally in San Francisco, then in nearby Belmont, California and finally in San Carlos, California in the San Francisco Bay Area. Founded and originally owned and operated by General Electric (GE). The station was popular during World War II with Allied servicemen serving in the Pacific Theater.
References
- ↑ "Wavescan". On The shortwaves.com. Retrieved 2020-02-19.
| This article about a radio station in New York is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |