A disk image is a snapshot of a storage device's structure and data typically stored in one or more computer files on another storage device.
Abdulaziz bin Muhammad Al Saud was the second ruler of the Emirate of Diriyah. He was the eldest son of Muhammad bin Saud and the son-in-law of Muhammad bin Abdul Wahhab. Abdulaziz ruled the Emirate from 1765 until 1803. He was nicknamed by his people as the savior of his time due to his fearless activities.

The Emirate of Nejd or Imamate of Nejd, also known as the second Saudi state was existing between 1824 and 1891 in Nejd, the regions of Riyadh and Ha'il of what is now Saudi Arabia. Saudi rule was restored to central and eastern Arabia after the Emirate of Diriyah, the first Saudi state, having previously been brought down by the Ottoman Empire's Egypt Eyalet in the Ottoman–Wahhabi War (1811–1818).
Saud bin Faisal Al Saud, also known as Imam Saud, (1833—1875) was the ruler of the Second Saudi State in 1871 and 1873–75. He joined alliances with foreign tribes and revolted against his half-brother Abdullah. His rule was short-lived and Abdullah overthrew him. Saud gained power again in 1873 but died two years later. His reign was notable for the infighting in the House of Saud which he initiated.

Aircrack-ng is a network software suite consisting of a detector, packet sniffer, WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK cracker and analysis tool for 802.11 wireless LANs. It works with any wireless network interface controller whose driver supports raw monitoring mode and can sniff 802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g traffic. Packages are released for Linux and Windows.
A Sybil attack is a type of attack on a computer network service in which an attacker subverts the service's reputation system by creating a large number of pseudonymous identities and uses them to gain a disproportionately large influence. It is named after the subject of the book Sybil, a case study of a woman diagnosed with dissociative identity disorder. The name was suggested in or before 2002 by Brian Zill at Microsoft Research. The term pseudospoofing had previously been coined by L. Detweiler on the Cypherpunks mailing list and used in the literature on peer-to-peer systems for the same class of attacks prior to 2002, but this term did not gain as much influence as "Sybil attack".
Virgil Dorin Gligor is a Romanian-American professor of electrical and computer engineering who specializes in the research of network security and applied cryptography.
An Inference Attack is a data mining technique performed by analyzing data in order to illegitimately gain knowledge about a subject or database. A subject's sensitive information can be considered as leaked if an adversary can infer its real value with a high confidence. This is an example of breached information security. An Inference attack occurs when a user is able to infer from trivial information more robust information about a database without directly accessing it. The object of Inference attacks is to piece together information at one security level to determine a fact that should be protected at a higher security level.
A device fingerprint or machine fingerprint is information collected about the software and hardware of a remote computing device for the purpose of identification. The information is usually assimilated into a brief identifier using a fingerprinting algorithm. A browser fingerprint is information collected specifically by interaction with the web browser of the device.
MindModeling@Home is an inactive non-profit, volunteer computing research project for the advancement of cognitive science. MindModeling@Home is hosted by Wright State University and the University of Dayton in Dayton, Ohio.

GroupLens Research is a human–computer interaction research lab in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at the University of Minnesota, Twin Cities specializing in recommender systems and online communities. GroupLens also works with mobile and ubiquitous technologies, digital libraries, and local geographic information systems.
ProVerif is a software tool for automated reasoning about the security properties of cryptographic protocols. The tool has been developed by Bruno Blanchet and others.
Value sensitive design (VSD) is a theoretically grounded approach to the design of technology that accounts for human values in a principled and comprehensive manner. VSD originated within the field of information systems design and human-computer interaction to address design issues within the fields by emphasizing the ethical values of direct and indirect stakeholders. It was developed by Batya Friedman and Peter Kahn at the University of Washington starting in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Later, in 2019, Batya Friedman and David Hendry wrote a book on this topic called "Value Sensitive Design: Shaping Technology with Moral Imagination". Value Sensitive Design takes human values into account in a well-defined matter throughout the whole process. Designs are developed using an investigation consisting of three phases: conceptual, empirical and technological. These investigations are intended to be iterative, allowing the designer to modify the design continuously.

Evercookie is an open-source JavaScript application programming interface (API) that identifies and reproduces intentionally deleted cookies on the clients' browser storage. This behavior is known as a Zombie cookie. It was created by Samy Kamkar in 2010 to demonstrate the possible infiltration from the websites that use respawning. Websites that have adopted this mechanism can identify users even if they attempt to delete the previously stored cookies.
Muhammad bin Saud Al Muqrin Al Saud, also known as Ibn Saud, was the emir of Diriyah and is considered the founder of the First Saudi State and the Saud dynasty, named after his father, Saud bin Muhammad Al Muqrin. His reign lasted between 1727 and 1765.
Contextual integrity is a theory of privacy developed by Helen Nissenbaum and presented in her book Privacy In Context: Technology, Policy, and the Integrity of Social Life. It comprises four essential descriptive claims:
Elena Ferrari is a Professor of Computer Science and Director of the STRICT Social Lab at the Università degli Studi dell’Insubria, Varese, Italy. Ferrari was named Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in 2013 for contributions to security and privacy for data and applications. She has been named one of the “50 Most Influential Italian Women in Tech” in 2018. She was elected as an ACM Fellow in 2019 "for contributions to security and privacy of data and social network systems".

Jean-Pierre Hubaux is a Swiss-Belgian computer scientist specialised in security and privacy. He is a professor of computer science at EPFL and is the head of the Laboratory for Data Security at EPFL's School of Computer and Communication Sciences.
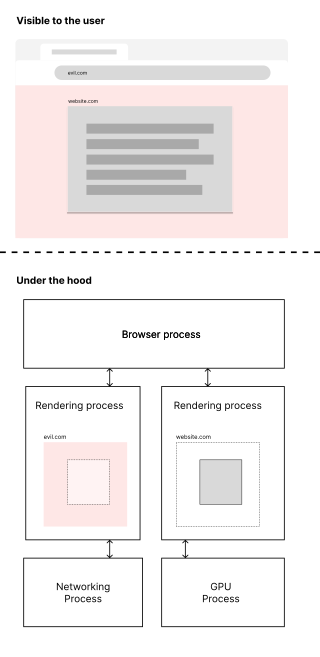
Site isolation is a web browser security feature that groups websites into sandboxed processes by their associated origins. This technique enables the process sandbox to block cross-origin bypasses that would otherwise be exposed by exploitable vulnerabilities in the sandboxed process.
Keystroke inference attacks are a class of privacy-invasive technique that allows attackers to infer what a user is typing on a keyboard.







