Related Research Articles

Little Turtle was a Sagamore (chief) of the Miami people, who became one of the most famous Native American military leaders. Historian Wiley Sword calls him "perhaps the most capable Indian leader then in the Northwest Territory," although he later signed several treaties ceding land, which caused him to lose his leader status during the battles which became a prelude to the War of 1812. In the 1790s, Mihšihkinaahkwa led a confederation of native warriors to several major victories against U.S. forces in the Northwest Indian Wars, sometimes called "Little Turtle's War", particularly St. Clair's defeat in 1791, wherein the confederation defeated General Arthur St. Clair, who lost 900 men in the most decisive loss by the U.S. Army against Native American forces.

The Miami are a Native American nation originally speaking one of the Algonquian languages. Among the peoples known as the Great Lakes tribes, they occupied territory that is now identified as north-central Indiana, southwest Michigan, and western Ohio. The Miami were historically made up of several prominent subgroups, including the Piankeshaw, Wea, Pepikokia, Kilatika, Mengakonkia, and Atchakangouen. In modern times, Miami is used more specifically to refer to the Atchakangouen. By 1846, most of the Miami had been forcefully displaced to Indian Territory. The Miami Tribe of Oklahoma are the federally recognized tribe of Miami Indians in the United States. The Miami Nation of Indiana, a nonprofit organization of descendants of Miamis who were exempted from removal, have unsuccessfully sought separate recognition.
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolutionary War. Established in 1787 by the Congress of the Confederation through the Northwest Ordinance, it was the nation's first post-colonial organized incorporated territory.

The Battle of Fallen Timbers was the final battle of the Northwest Indian War, a struggle between Native American tribes affiliated with the Northwestern Confederacy and their British allies, against the nascent United States for control of the Northwest Territory. The battle took place amid trees toppled by a tornado near the Maumee River in northwestern Ohio at the site of the present-day city of Maumee, Ohio.

The Treaty of Greenville, formally titled Treaty with the Wyandots, etc., was a 1795 treaty between the United States and indigenous nations of the Northwest Territory, including the Wyandot and Delaware peoples, that redefined the boundary between indigenous peoples' lands and territory for European American community settlement.

The Northwest Indian War (1785–1795), also known by other names, was an armed conflict for control of the Northwest Territory fought between the United States and a united group of Native American nations known today as the Northwestern Confederacy. The United States Army considers it the first of the American Indian Wars.

Jean Baptiste de Richardville, also known as Pinšiwa or Peshewa in the Miami-Illinois language or John Richardville in English, was the last akima 'civil chief' of the Miami people. He began his career in the 1790s as a fur trader who controlled an important portage connecting the Maumee River to the Little River in what became the present-day state of Indiana. Richardville emerged a principal chief in 1816 and remained a leader of the Miamis until his death in 1841. He was a signatory to the Treaty of Greenville (1795), as well as several later treaties between the U.S. government and the Miami people, most notably the Treaty of Fort Wayne (1803), the Treaty of Fort Wayne (1809), the Treaty of Saint Mary's (1818), the Treaty of Mississinewas (1826), the treaty signed at the Forks of the Wabash (1838), and the Treaty of the Wabash (1840).

William Wells, also known as Apekonit, was the son-in-law of Chief Little Turtle of the Miami. He fought for the Miami in the Northwest Indian War. During the course of that war, he became a United States Army officer, and also served in the War of 1812.

Fort Recovery was a United States Army fort ordered built by General "Mad" Anthony Wayne during what is now termed the Northwest Indian War. Constructed from late 1793 and completed in March 1794, the fort was built along the Wabash River, within two miles of what became the Ohio state border with Indiana. A detachment of Wayne's Legion of the United States held off an attack from combined Indian forces on June 30, 1794. The fort was used as a reference in drawing treaty lines for the 1795 Treaty of Greenville, and for later settlement. The fort was abandoned in 1796.

The Legion of the United States was a reorganization and extension of the United States Army from 1792 to 1796 under the command of Major General Anthony Wayne. It represented a political shift in the new United States, which had recently adopted the United States Constitution. The new Congressional and Executive branches authorized a standing army composed of professional soldiers rather than relying on state militias.

The Battle of Fort Recovery, 30 June – 1 July 1794, was a battle of the Northwest Indian War, fought at the present-day village of Fort Recovery, Ohio. A large force of warriors in the Western Confederacy attacked a fort held by United States soldiers deep in Ohio Country. The United States suffered heavy losses, but maintained control of the fort. The battle exposed a division in the Western Confederacy's military strategy at a time when they seemed to hold the advantage, and the United States pressed farther into the Northwest Territory.
Charles Beaubien was a French Canadian trader in the 18th century who became British Agent to the Miami Nation.

Pacanne was a leading Miami chief during the late 18th and early 19th centuries. Son of The Turtle (Aquenackqua), he was the brother of Tacumwah, who was the mother of Chief Jean Baptiste Richardville. Their family owned and controlled the Long Portage, an 8-mile strip of land between the Maumee and Wabash Rivers used by traders travelling between Canada and Louisiana. As such, they were one of the most influential families of Kekionga.
Snake was the English language name of two Shawnee leaders prominent in the history of the Ohio Country: Peteusha and Shemanetoo. They were both commonly referred to as "Snake" in historical records, or by variations such as "Black Snake" or "Captain Snake," so it is often difficult to determine which individual was being referred to. On a number of occasions, the two Snakes both signed a letter or appeared together, so it is clear they were two different people. There may have been additional Shawnees called "Snake," further complicating the matter. According to historian John Sugden, "it is unlikely if the biographies of these chiefs will ever be completely disentangled."
Nagohquangogh, was a chief of the Pepikokia band of the Miami tribe in the 18th century. Also known as The Gray, he was one of three important Miami leaders during the Northwest Indian War, along with Pacanne and Little Turtle.
In 1802, during a trip to Washington, DC, Miami Chief Little Turtle extended an invitation to the Baltimore area Quakers to visit Fort Wayne and teach the Miami about white civilization and European cultivation methods. The Quakers sent farm implements in 1803. Little Turtle, by way of William Wells, sent a letter thanking them for the tools, but expressed uncertainty of how they should be used.
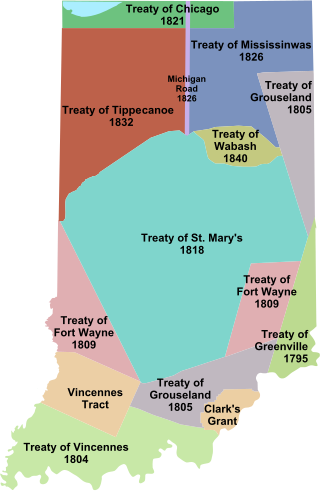
The Treaty of Fort Wayne was a treaty between the United States and several groups of Native Americans. The treaty was signed on June 7, 1803 and proclaimed December 26, 1803. It more precisely defined the boundaries of the Vincennes tract ceded to the United States by the Treaty of Greenville, 1795.

St. Clair's defeat, also known as the Battle of the Wabash, the Battle of Wabash River or the Battle of a Thousand Slain, was a battle fought on 4 November 1791 in the Northwest Territory of the United States. The U.S. Army faced the Western Confederacy of Native Americans, as part of the Northwest Indian War. It was "the most decisive defeat in the history of the American military" and its largest defeat ever by Native Americans.
Asa Hartshorne was a United States Army officer who died in 1794 during the Northwest Indian War. He was among the signers of the Treaty with the Six Nations and the Treaty with the Wyandot at Fort Harmar on January 9, 1789. Hartshorne became the namesake of a 1790 frontier skirmish near Maysville, Kentucky.
References
- Carter, Harvey Lewis. The Life and Times of Little Turtle: First Sagamore of the Wabash. Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1987. ISBN 0-252-01318-2.