
Warren Henry Tucker CNZM (born 18 August 1950) is a retired New Zealand intelligence officer. He was the director of the Security Intelligence Service from 2006 to 2014.

Warren Henry Tucker CNZM (born 18 August 1950) is a retired New Zealand intelligence officer. He was the director of the Security Intelligence Service from 2006 to 2014.
Born in 1950, Tucker was educated at Nelson College from 1964 to 1968. [1] He went on to become an officer in the New Zealand Army, holding the rank of Major in the Royal New Zealand Signals Corps. [2]
He has a doctorate in electrical engineering from the University of Canterbury, and later joined the Government Communications Security Bureau (GCSB), New Zealand's primary signals intelligence agency. He became head of communications security in 1982, and in 1983, he was appointed Director of Policy and Plans. From 1984 to 1989, he was the GCSB's liaison officer to the NSA in Washington. On his return, he became Director of Operations (effectively deputy director of the GCSB), and in 1996, he became the Intelligence Co-ordinator in the office of the Prime Minister. He became the third director of the GCSB in 1999, replacing Ray Parker. In 2006, it was announced that he would succeed Richard Woods as director of another New Zealand intelligence agency, the Security Intelligence Service, on 1 November. [3]
On 1 November 2010, Tucker was reappointed for a further two-year term as Director. [4] He retired in May 2014 with Rebecca Kitteridge taking over his role. In the 2014 Queen's Birthday Honours, Tucker was appointed a Companion of the New Zealand Order of Merit, for services to the State. [5]
In November 2014 the Gwyn Report on the SIS criticised the actions in 2011 of the SIS and retired director Tucker over whether opposition leader Phil Goff had received a SIS briefing. [6]

The New Zealand Security Intelligence Service is New Zealand's primary national intelligence agency. It is responsible for providing information and advising on matters including national security and foreign intelligence. It is headquartered in Wellington and overseen by a Director-General, the Minister of New Zealand Security Intelligence Service, and the parliamentary intelligence and security committee; independent oversight is provided by the Inspector-General of Intelligence and Security.

The Government Communications Security Bureau is the public-service department of New Zealand charged with promoting New Zealand's national security by collecting and analysing information of an intelligence nature. The GCSB is considered to be New Zealand's most powerful intelligence agency, and has been alleged to have conducted more espionage and data collection than the country's primary intelligence agency, the less funded NZSIS. This has at times proven controversial, although the GCSB does not have the baggage of criticism attached to it for a perceived failure to be effective like the NZSIS does. The GCSB is considered an equivalent of GCHQ in the United Kingdom or the NSA in the United States.

The United Kingdom – United States of America Agreement is a multilateral agreement for cooperation in signals intelligence between Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The alliance of intelligence operations is also known as the Five Eyes. In classification markings this is abbreviated as FVEY, with the individual countries being abbreviated as AUS, CAN, NZL, GBR, and USA, respectively.

Nicolas Alfred Hager is a New Zealand investigative journalist. He has produced seven books since 1996, covering topics such as intelligence networks, environmental issues and politics. He is one of two New Zealand members of the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists.

The Inspector-General of Intelligence and Security (IGIS) is the official responsible for supervising New Zealand's two main intelligence agencies: the Security Intelligence Service (SIS) and the Government Communications Security Bureau (GCSB).

Lieutenant General Sir Jeremiah Mateparae is a former New Zealand soldier who served as the 20th governor-general of New Zealand between 2011 and 2016, the second Māori person to hold the office, after Sir Paul Reeves. A former officer in the New Zealand Army, he was the chief of the Defence Force from 2006 to 2011, and then served as the director of the New Zealand Government Communications Security Bureau for five months in 2011. Following his term as governor-general, Mateparae was the high commissioner of New Zealand to the United Kingdom between 2017 and 2020.
New Zealand's intelligence agencies and units have existed, with some interruption, since World War II. At present, New Zealand's intelligence community has approximately 550 employees, and has a combined budget of around NZ$145 million.
The National Assessments Bureau (NAB), previously known as the External Assessments Bureau (EAB), is a New Zealand intelligence analysis agency within the Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet (DPMC). The NAB along with the Government Communications Security Bureau and the New Zealand Security Intelligence Service is one of the three core members of New Zealand's intelligence community. It provides assessments to the Prime Minister, other Ministers, senior officials and New Zealand's diplomatic missions abroad, on events and developments that bear on New Zealand's interests, especially in regard to matters of national security.

Air Marshal Sir Bruce Reid Ferguson, is a retired Royal New Zealand Air Force officer who served as Chief of the New Zealand Defence Force and Director of the Government Communications Security Bureau. He took up the appointment when the previous director, Warren Tucker, was appointed as Director of the Security Intelligence Service on 1 November 2006. Ferguson's term of appointment was for four years, stepping down from the role in 2011. Following his retirement, in July 2012, he was appointed as a Justice of the Peace for New Zealand.

John Walter McKinnon is a New Zealand diplomat and public servant.

Simon Peter Wallace Murdoch is a New Zealand diplomat and public servant. He was New Zealand's Secretary of Foreign Affairs and Trade and was previously New Zealand High Commissioner to Canberra, and Chief Executive of the Department of Prime Minister and Cabinet.

Roy Neil Ferguson,, is the former New Zealand Ambassador to the United States. He was replaced by former New Zealand Prime Minister and Director-General of the World Trade Organization Mike Moore in 2010. Ferguson replaced John Wood in the role in 2006. He was Director of the Americas Division in the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade from 2002 to 2005, and has served on the Boards of the New Zealand-United States Council, Fulbright New Zealand, the Ian Axford Fellowships, and the New Zealand Centre for Latin American Studies. Ferguson previously served in Washington as Deputy Chief of Mission between 1991 and 1995. From 1999 to 2002 he served as the New Zealand Ambassador to South Korea and concurrently served as Ambassador to North Korea from 2001. He has also served in Manila and Canberra.
Signals intelligence by alliances, nations and industries comprises signals intelligence (SIGINT) gathering activities by national and non-national entities; these entities are commonly responsible for communications security (COMSEC) as well.
New Zealand is committed to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and has ratified the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, both of which contain a right to privacy. Privacy law in New Zealand is dealt with by statute and the common law. The Privacy Act 2020 addresses the collection, storage and handling of information. A general right to privacy has otherwise been created in the tort of privacy. Such a right was recognised in Hosking v Runting [2003] 3 NZLR 385, a case that dealt with publication of private facts. In the subsequent case C v Holland [2012] NZHC 2155 the Court recognised a right to privacy in the sense of seclusion or a right to be free from unwanted intrusion. For a useful summary see: court-recognises-intrusion-on-seclusion-privacy-tort-hugh-tomlinson-qc/
The Tangimoana Station is a radio communications interception facility run by the New Zealand Government Communications Security Bureau. It is located 30 kilometres west of Palmerston North.


The Government Communications Security Bureau Act 2003 is a repealed New Zealand Act of Parliament. It formalised the role of the Government Communications Security Bureau, which had previously existed in various states of secrecy since 1977, as the national authority for signals intelligence and information systems security, and put it on a similar legislative footing to the New Zealand Security Intelligence Service.
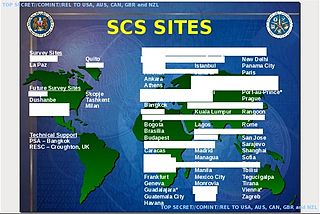
STATEROOM is the code name of a highly secretive signals intelligence collection program involving the interception of international radio, telecommunications and Internet traffic. It is operated out of the diplomatic missions of the signatories to the UKUSA Agreement and the members of the ECHELON network including Australia, New Zealand, United Kingdom, Canada and the United States.

Rebecca Lucy Kitteridge is a New Zealand public servant. Her current position is Deputy Public Service Commissioner.

The Minister of National Security and Intelligence is a minister in the government of New Zealand who is responsible for leading and setting the policies and legislative framework of New Zealand's national security system. The current minister is Chris Hipkins, who is also the current Prime Minister of New Zealand, as by convention, the National Security and Intelligence portfolio is always held by the Prime Minister.