
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in soil desalination, which is an issue for agriculture. Saltwater is desalinated to produce water suitable for human consumption or irrigation. The by-product of the desalination process is brine. Desalination is used on many seagoing ships and submarines. Most of the modern interest in desalination is focused on cost-effective provision of fresh water for human use. Along with recycled wastewater, it is one of the few rainfall-independent water resources.

Greywater refers to domestic wastewater generated in households or office buildings from streams without fecal contamination, i.e., all streams except for the wastewater from toilets. Sources of greywater include sinks, showers, baths, washing machines or dishwashers. As greywater contains fewer pathogens than domestic wastewater, it is generally safer to handle and easier to treat and reuse onsite for toilet flushing, landscape or crop irrigation, and other non-potable uses. Greywater may still have some pathogen content from laundering soiled clothing or cleaning the anal area in the shower or bath.

Water conservation includes all the policies, strategies and activities to sustainably manage the natural resource of fresh water, to protect the hydrosphere, and to meet the current and future human demand. Population, household size and growth and affluence all affect how much water is used. Factors such as climate change have increased pressures on natural water resources especially in manufacturing and agricultural irrigation. Many countries have already implemented policies aimed at water conservation, with much success. The key activities to conserve water are as follows: any beneficial reduction in water loss, use and waste of resources, avoiding any damage to water quality; and improving water management practices that reduce the use or enhance the beneficial use of water. Technology solutions exist for households, commercial and agricultural applications. Water conservation programs involved in social solutions are typically initiated at the local level, by either municipal water utilities or regional governments. Common strategies include public outreach campaigns, tiered water rates, or restrictions on outdoor water use such as lawn watering and car washing.

Water reclamation is the process of converting municipal wastewater (sewage) or industrial wastewater into water that can be reused for a variety of purposes. Types of reuse include: urban reuse, agricultural reuse (irrigation), environmental reuse, industrial reuse, planned potable reuse, de facto wastewater reuse. For example, reuse may include irrigation of gardens and agricultural fields or replenishing surface water and groundwater. Reused water may also be directed toward fulfilling certain needs in residences, businesses, and industry, and could even be treated to reach drinking water standards. Treated municipal wastewater reuse for irrigation is a long-established practice, especially in arid countries. Reusing wastewater as part of sustainable water management allows water to remain as an alternative water source for human activities. This can reduce scarcity and alleviate pressures on groundwater and other natural water bodies.

Air Products and Chemicals, Inc. is an American international corporation whose principal business is selling gases and chemicals for industrial uses. Air Products' headquarters is in Allentown, Pennsylvania, in the Lehigh Valley region of Pennsylvania, in the United States.
Water supply and sanitation in Singapore are intricately linked to the historical development of Singapore. It is characterised by a number of challenging environments that have been accomplished despite its geographical limitations. Access to water in Singapore is universal, affordable, efficient and of high quality.

Desert farming is the practice of developing agriculture in deserts. As agriculture depends upon irrigation and water supply, farming in arid regions where water is scarce is a challenge. However, desert farming has been practiced by humans for thousands of years. In the Negev Desert, there is evidence to suggest agriculture as far back as 5000 BC. Today, the Imperial Valley in southern California, Australia, Saudi Arabia, Israel and Palestine are examples of modern desert agriculture. Water efficiency has been important to the growth of desert agriculture. Water reuse, desalination, and drip irrigation are all modern ways that regions and countries have expanded their agriculture despite being in an arid climate.

Water Corporation is the principal supplier of water, wastewater and drainage services throughout the state of Western Australia. It is the seventh successive agency to deal with the services in Perth, Western Australia.
Water supply and sanitation in the United States involves a number of issues including water scarcity, pollution, a backlog of investment, concerns about the affordability of water for the poorest, and a rapidly retiring workforce. Increased variability and intensity of rainfall as a result of climate change is expected to produce both more severe droughts and flooding, with potentially serious consequences for water supply and for pollution from combined sewer overflows. Droughts are likely to particularly affect the 66 percent of Americans whose communities depend on surface water. As for drinking water quality, there are concerns about disinfection by-products, lead, perchlorates, PFAS and pharmaceutical substances, but generally drinking water quality in the U.S. is good.

The Eastern Municipal Water District of Southern California is a regional water district formed in 1950 to secure additional water for a largely rural area of western Riverside County. In addition to water service, responsibilities include sewage collection, water desalination and water recycling.
The National Water Research Institute (NWRI) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, located in California, was founded in 1991. It is devoted to promoting the protection, maintenance, and restoration of water supplies through collaborative research and outreach activities. It is governed by a Board of Directors consisting of representatives of water and wastewater agencies/districts in Southern California.
Water supply and sanitation in Saudi Arabia is characterized by challenges and achievements. One of the main challenges is water scarcity. In order to overcome water scarcity, substantial investments have been undertaken in seawater desalination, water distribution, sewerage and wastewater treatment. Today about 50% of drinking water comes from desalination, 40% from the mining of non-renewable groundwater and only 10% from surface water in the mountainous southwest of the country. The capital Riyadh, located in the heart of the country, is supplied with desalinated water pumped from the Persian Gulf over a distance of 467 km. Water is provided almost for free to residential users. Despite improvements, service quality remains poor, for example in terms of continuity of supply. Another challenge is weak institutional capacity and governance, reflecting general characteristics of the public sector in Saudi Arabia. Among the achievements is a significant increase in desalination, and in access to water, the expansion of wastewater treatment, as well as the use of treated effluent for the irrigation of urban green spaces, and for agriculture.
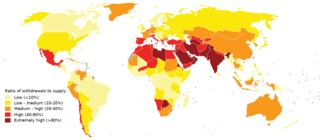
Water scarcity is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity: physical or economic water scarcity. Physical water scarcity is where there is not enough water to meet all demands, including that needed for ecosystems to function effectively. Arid areas often suffer from physical water scarcity. On the other hand, economic water scarcity is caused by a lack of investment in infrastructure or technology to draw water from rivers, aquifers, or other water sources, or insufficient human capacity to satisfy the demand for water. Much of Sub-Saharan Africa has economic water scarcity.

Water resources are natural resources of water that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply or irrigation water. 97% of the water on the Earth is salt water and only three percent is fresh water; slightly over two thirds of this is frozen in glaciers and polar ice caps. The remaining unfrozen freshwater is found mainly as groundwater, with only a small fraction present above ground or in the air. Natural sources of fresh water include surface water, under river flow, groundwater and frozen water. Artificial sources of fresh water can include treated wastewater and desalinated seawater. Human uses of water resources include agricultural, industrial, household, recreational and environmental activities.
Water supply and sanitation in Israel are intricately linked to the historical development of Israel. Because rain falls only in the winter, and largely in the northern part of the country, irrigation and water engineering are considered vital to the country's economic survival and growth. Large scale projects to desalinate seawater, direct water from rivers and reservoirs in the north, make optimal use of groundwater, and reclaim flood overflow and sewage have been undertaken. Among them is the National Water Carrier, carrying water from the country's biggest freshwater lake, the Sea of Galilee, to the northern part of the Negev desert through channels, pipes and tunnels. Israel's water demand today outstrips available conventional water resources. Thus, in an average year, Israel relies for about half of its water supply on unconventional water resources, including reclaimed water and desalination. A particularly long drought in 1998–2002 had prompted the government to promote large-scale seawater desalination.
As Australia's supply of freshwater is increasingly vulnerable to droughts, possibly as a result of climate change, there is an emphasis on water conservation and various regions have imposed restrictions on the use of water.
Water supply and sanitation in Jordan is characterized by severe water scarcity, which has been exacerbated by forced immigration as a result of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, the Six-Day War in 1967, the Gulf War of 1990, the Iraq War of 2003 and the Syrian Civil War since 2011. Jordan is considered one of the ten most water scarce countries in the world. High population growth, the depletion of groundwater reserves and the impacts of climate change are likely to aggravate the situation in the future.
The three cities of Abu Dhabi Emirate within the United Arab Emirates – the coastal city Abu Dhabi itself as well as the inland oases Al Ain and Liwa – receive their drinking water supply entirely from desalinated seawater.
Beijing, the capital of China, is characterized by intense water scarcity during the long dry season as well as heavy flooding during the brief wet season. Beijing is one of the most water-scarce cities in the world. Total water use is 3.6 billion cubic meters, compared to renewable fresh water resources of about 3 billion cubic meters. The difference is made up by the overexploitation of groundwater. Two-thirds of the water supply comes from groundwater, one third from surface water. Average rainfall has substantially declined since the 1950s. Furthermore, one of the two main rivers supplying the city, the Yongding River, had to be abandoned as a source of drinking water because of pollution. Water savings in industry and agriculture have compensated for these losses and freed up water for residential uses.

Water reuse in California is the use of reclaimed water for beneficial use. As a heavily populated state in the drought-prone arid west, water reuse is developing as an integral part of water in California enabling both the economy and population to grow. Reclaimed water is treated wastewater that comes from homes and businesses, such as sink water, shower water, and toilet water including everything dumped into wastewater drains from laundry soap to bleach to oil to human waste. Wastewater can divided into greywater and blackwater, with the first being defined as water that had been used for laundry, bathing, sink washing, and dishwashers. Blackwater is defined as sewage that includes feces from toilets. Due to the low amounts of physical pollutants in greywater, most of its contaminants are dissolved organic matter, which can be physically filtered and cleaned through various membranes, as well as through biological treatment methods.










