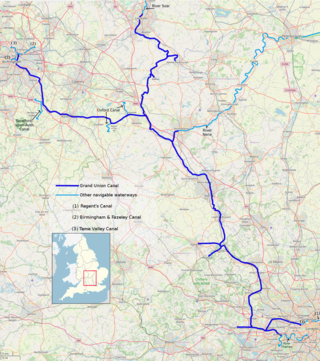
The Grand Union Canal in England is part of the British canal system. It is the principal navigable waterway between London and the Midlands. Starting in London, one arm runs to Leicester and another ends in Birmingham, with the latter stretching for 137 miles (220 km) with 166 locks from London. The Birmingham line has a number of short branches to places including Slough, Aylesbury, Wendover, and Northampton. The Leicester line has two short arms of its own, to Market Harborough and Welford.

A lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water level can be varied; whereas in a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself that rises and falls.

Foxton Locks are ten canal locks consisting of two "staircases" each of five locks, located on the Leicester line of the Grand Union Canal about 3 miles (5 km) west of the Leicestershire town of Market Harborough. They are named after the nearby village of Foxton.

The canal network of the United Kingdom played a vital role in the Industrial Revolution. The UK was the first country to develop a nationwide canal network which, at its peak, expanded to nearly 4,000 miles in length. The canals allowed raw materials to be transported to a place of manufacture, and finished goods to be transported to consumers, more quickly and cheaply than by a land based route. The canal network was extensive and included feats of civil engineering such as the Anderton Boat Lift, the Manchester Ship Canal, the Worsley Navigable Levels and the Pontcysyllte Aqueduct.

An inclined plane is a type of cable railway used on some canals for raising boats between different water levels. Boats may be conveyed afloat, in caissons, or may be carried in cradles or slings.

The Foxton Inclined Plane is a canal inclined plane on the Leicester line of the Grand Union Canal about 5 km (3.1 mi) west of the Leicestershire town of Market Harborough, named after the nearby village of Foxton. The plane was built in 1900 as a solution to various operational restrictions imposed by the Foxton Lock flight. However, it was not a commercial success and only remained in full-time operation for ten years. The plane was dismantled in 1926. A project to re-create the plane commenced in the 2000s because the narrowbeam locks remain a bottleneck for leisure boat traffic.

Bingley Five-Rise Locks is a staircase lock on the Leeds and Liverpool Canal at Bingley. As the name implies, a boat passing through the lock is lifted or lowered in five stages.

The canals of the United Kingdom are a major part of the network of inland waterways in the United Kingdom. They have a varied history, from use for irrigation and transport, through becoming the focus of the Industrial Revolution, to today's role of recreational boating. Despite a period of abandonment, today the canal system in the United Kingdom is again increasing in use, with abandoned and derelict canals being reopened, and the construction of some new routes. Canals in England and Wales are maintained by navigation authorities. The biggest navigation authorities are the Canal & River Trust and the Environment Agency, but other canals are managed by companies, local authorities or charitable trusts.
The Grand Junction Canal is a canal in England from Braunston in Northamptonshire to the River Thames at Brentford, with a number of branches. The mainline was built between 1793 and 1805, to improve the route from the Midlands to London, by-passing the upper reaches of the River Thames near Oxford, thus shortening the journey.

A canal pound, reach, or level, is the stretch of level water impounded between two canal locks. Canal pounds can vary in length from the non-existent, where two or more immediately adjacent locks form a lock staircase, to many kilometres/miles.

Bingley Three Rise Locks is a staircase of three locks on the Leeds and Liverpool Canal at Bingley, West Yorkshire, England. The locks are a Grade II* listed building.

The Grand Union Canal was a canal in England from Foxton, Leicestershire on the Leicestershire and Northamptonshire Union Canal to Norton Junction, close to Long Buckby Wharf on the Grand Junction Canal. It now forms the first 23 miles (37 km) of the Leicester line of the Grand Union Canal.

Foxton is a village and civil parish in the Harborough district, in the county of Leicestershire, England, to the north-west of Market Harborough. The village is on the Grand Union Canal and is a short walk to the site of the Foxton Locks and Foxton Inclined Plane. Swingbridge Street still has a working swing bridge that allows people and vehicles to pass over the canal, which can be opened to allow canal boats to pass. There are two public houses in the village, a village hall, and a primary school. Foxton is serviced by Market Harborough train station which is approximately 3 miles away. London and Birmingham can each be reached by train in approximately 50 minutes.

Fonseranes Locks are a flight of staircase locks on the Canal du Midi near Béziers.

Tardebigge Locks or the Tardebigge Flight is the longest flight of locks in the UK, comprising 30 narrow locks on a two-and-a-quarter-mile (3.6 km) stretch of the Worcester and Birmingham Canal at Tardebigge, Worcestershire. It raises the waterway 220 feet (67 m), and lies between the Tardebigge tunnel to the North and the Stoke Prior flight of six narrow locks to the South. The Tardebigge Engine House is also on this stretch.

The Foxton Inclined Plane Trust is a waterway society and a registered charity on the Grand Union Canal in Foxton, Leicestershire, England, UK. It was founded in 1980 to promote the restoration of the Victorian boat lift or inclined plane, a unique and famous piece of canal history.
The Seven Wonders of the Waterways is a list of landmarks on the navigable waterways of the United Kingdom. The list was originally compiled in 1946 by Robert Aickman, co-founder of the Inland Waterways Association (IWA), at a time when the waterways network was largely derelict. Today, the Canal & River Trust—formerly British Waterways—has jurisdiction over all of the sites except for the Barton Swing Aqueduct, which is owned and operated by the Bridgewater Canal Company.















