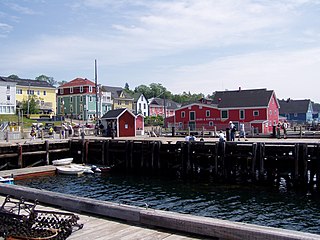Colchester County is a county in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. With a population of 51,476 the county is the fourth largest in Nova Scotia. Colchester County is located in north central Nova Scotia.
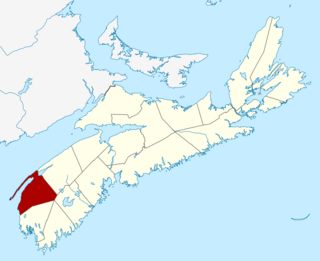
Digby County is a county in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.
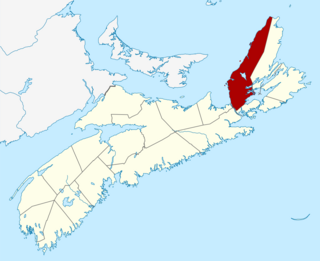
Inverness County is an historical county and census division of Nova Scotia, Canada. Local government is provided by the Municipality of the County of Inverness, the town of Port Hawkesbury and the Whycocomagh 2 Waycobah First Nation reserve.

Kings County is a county in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. With a population of 62,914 in the 2021 Census, Kings County is the third most populous county in the province. It is located in central Nova Scotia on the shore of the Bay of Fundy, with its northeastern part forming the western shore of the Minas Basin.
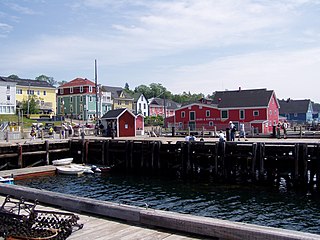
Lunenburg County is a historical county and census division on the South Shore of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. Major settlements include Bridgewater, Lunenburg, and Mahone Bay.
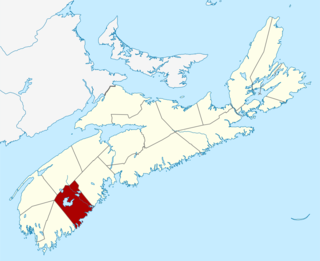
Queens County is a county in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.
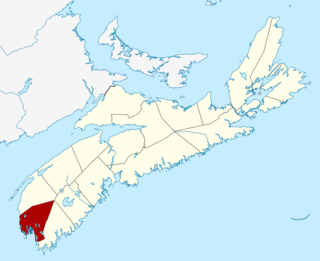
Yarmouth County is a rural county in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. It has both traditional Anglo-Scottish and Acadian French culture as well as significant inland wilderness areas, including over 365 lakes and several major rivers. It comprises three municipalities: the Town of Yarmouth, the Municipality of the District of Yarmouth, and the Municipality of the District of Argyle.

The Mi'kmaq are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the northeastern region of Maine. The traditional national territory of the Mi'kmaq is named Miꞌkmaꞌki.

The Nova Scotia Highlanders is an infantry regiment in the primary reserve of the Canadian Army. It is part of 36 Canadian Brigade Group, 5th Canadian Division.
The Membertou First Nation is a Mi'kmaq First Nation band government in the tribal district of Unama'ki, also known as Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia. As of 2012, the Mi'kmaq population is 814 on-Reserve, and approximately 481 off-Reserve. It operates a community radio station CJIJ-FM. Currently, Membertou has become the most well-off First Nation in Atlantic Canada.
The Congress of Aboriginal Peoples (CAP), founded in 1971, is a national Canadian aboriginal organization, that represents Aboriginal peoples who live off Indian reserves, in either urban or rural areas across Canada. As of 2011, more than 70% of Aboriginal people live off-reserve.

Potlotek First Nation, also known as Chapel Island, is a Mi'kmaw community in northeastern Nova Scotia. The community is situated in Richmond County, Nova Scotia, Canada. As of 2022, the First Nation has approximately 800 band members living on and off reserve.

Bear River First Nation is a Míkmaq First Nations band government located in both Annapolis County and Digby County, Nova Scotia. As of 2012, the Mi'kmaq population is 103 on-Reserve, and approximately 211 off-Reserve.
The Acadia First Nation is composed of five Mi'kmaq First Nation reserves located in southwestern Nova Scotia. As of 2015, the Mi'kmaq population is 223 on-reserve, and 1,288 off-reserve. Acadia First Nation was founded in 1967 and covers the south shore area of Nova Scotia and Yarmouth County. The community runs multiple businesses including five gaming centres, three gas stations and two Rose Purdy centers.
Lawrence Paul was a Canadian Mi'kmaq leader and First Nations activist. Paul served as the chief of the Membertou First Nation of Nova Scotia from 1967 to 1969. Paul also co-founded the Union of Nova Scotia Indians.
Annapolis Valley First Nation is composed of two Mi'kmaq First Nation reserves located in southwestern Nova Scotia. As of 2017, the Mi'kmaq population is 119 on-Reserve, and approximately 173 off-Reserve for a total population of 292. The community has a gas bar, tobacco shop, gaming centre, health centre, and a chapel. It is the second smallest First Nation community in Nova Scotia in terms of population.

The Sipekne'katik First Nation is composed of four Mi'kmaq First Nation reserves located in central Nova Scotia. As of 2012, the Mi'kmaq population is 1,195 on-Reserve, and approximately 1,190 off-Reserve. The First Nation includes Indian Brook 14, Nova Scotia, near Shubenacadie, Nova Scotia. The band was known as the Shubenacadie First Nation until 2014 when the traditional spelling and pronunciation of its name was officially adopted.
Paqtnkek Mi’kmaw Nation is a Mi'kmaq Band in northeastern Nova Scotia. Its populated reserve is Paqtnkek-Niktuek 23. As of December 2019 the total registered population was 598. It is a member of the Confederacy of Mainland Mi'kmaq. The name Paqtnkek means “by the bay” or "Above the water ". The area has long been important to Mi'kmaq for the fishing of eel and other species.
Malagawatch 4 is a Mi'kmaq reserve located in Inverness County, Nova Scotia.