
The kilogram is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), having the unit symbol kg. 'Kilogram' means 'one thousand grams' and is colloquially abbreviated to kilo.

The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. It is the only system of measurement with official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI system is coordinated by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures which is abbreviated BIPM from French: Bureau international des poids et mesures.

The SI base units are the standard units of measurement defined by the International System of Units (SI) for the seven base quantities of what is now known as the International System of Quantities: they are notably a basic set from which all other SI units can be derived. The units and their physical quantities are the second for time, the metre for length or distance, the kilogram for mass, the ampere for electric current, the kelvin for thermodynamic temperature, the mole for amount of substance, and the candela for luminous intensity. The SI base units are a fundamental part of modern metrology, and thus part of the foundation of modern science and technology.
A metric prefix is a unit prefix that precedes a basic unit of measure to indicate a multiple or submultiple of the unit. All metric prefixes used today are decadic. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is prepended to any unit symbol. The prefix kilo-, for example, may be added to gram to indicate multiplication by one thousand: one kilogram is equal to one thousand grams. The prefix milli-, likewise, may be added to metre to indicate division by one thousand; one millimetre is equal to one thousandth of a metre.

The tonne is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton and the long ton. It is equivalent to approximately 2,204.6 pounds, 1.102 short tons, and 0.984 long tons. The official SI unit is the megagram (Mg), a less common way to express the same amount.

The metric system is a decimal-based system of measurement. The current international standard for the metric system is the International System of Units, in which all units can be expressed in terms of seven base units: the metre (m), kilogram (kg), second (s), ampere (A), kelvin (K), mole (mol), and candela (cd). These can be made into larger or smaller units with the use of metric prefixes.
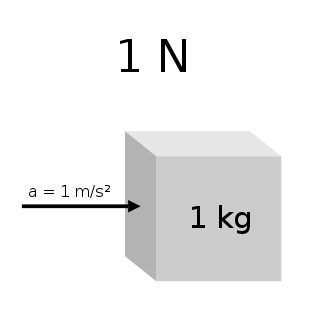
The newton is the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI). Expressed in terms of SI base units, it is 1 kg⋅m/s2, the force that accelerates a mass of one kilogram at one metre per second squared.
The kilogram-force, or kilopond, is a non-standard gravitational metric unit of force. It is not accepted for use with the International System of Units (SI) and is deprecated for most uses. The kilogram-force is equal to the magnitude of the force exerted on one kilogram of mass in a 9.80665 m/s2 gravitational field. That is, it is the weight of a kilogram under standard gravity. One kilogram-force is defined as 9.80665 N. Similarly, a gram-force is 9.80665 mN, and a milligram-force is 9.80665 μN.

STS-103, the 96th launch of the Space Shuttle and the 27th launch of Space Shuttle Discovery, was a Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission. It launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on 19 December 1999 and returned on 27 December 1999 and was the last Shuttle mission of the 1990s. It was the only mission to span through Christmas after being delayed by 13 days for technical and weather reasons.
Nameirakpam Kunjarani Devi is an Indian weightlifter. She is among the most decorated Indian sportswoman in weightlifting.

Mesosiderites are a class of stony–iron meteorites consisting of about equal parts of metallic nickel-iron and silicate. They are breccias with an irregular texture; silicates and metal occur often in lumps or pebbles as well as in fine-grained intergrowths. The silicate part contains olivine, pyroxenes, and Ca-rich feldspar and is similar in composition to eucrites and diogenites.

Esquel is a meteorite found near Esquel, a Patagonian town in the northwest part of the province of Chubut in Argentina. It is a pallasite, a type of stony–iron meteorite that when cut and polished shows yellowish olivine (peridot) crystals.

Homestead is a L5 meteorite fallen in 1875 in Iowa, United States.

The 13th Pan American Games were held in Havana, Cuba, from August 2 to August 18, 1991.

Jon Brower Minnoch was an American man who is the heaviest recorded human in history, weighing approximately 1,400 lb at his peak. Obese since childhood, Minnoch normally weighed 800–900 lb during his adult years. He owned a taxi company and worked as a driver around his home in Bainbridge Island, Washington.

The Orbital Maneuvering System (OMS) is a system of hypergolic liquid-propellant rocket engines used on the Space Shuttle and the Orion spacecraft. Designed and manufactured in the United States by Aerojet, the system allowed the orbiter to perform various orbital maneuvers according to requirements of each mission profile: orbital injection after main engine cutoff, orbital corrections during flight, and the final deorbit burn for reentry. From STS-90 onwards the OMS were typically ignited part-way into the Shuttle's ascent for a few minutes to aid acceleration to orbital insertion. Notable exceptions were particularly high-altitude missions such as those supporting the Hubble Space Telescope (STS-31) or those with unusually heavy payloads such as Chandra (STS-93). An OMS dump burn also occurred on STS-51-F, as part of the Abort to Orbit procedure.

Jamaica competed at the 13th Pan American Games, which were held in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada from July 23 to August 8, 1999.
Cannabis in Senegal is illegal; the drug is locally referred to as yamba.
This is a list of world records progression in men's weightlifting from 1998 to 2018. These records are maintained in each weight class for the snatch lift, clean and jerk lift, and the total for both lifts.
The men's freestyle 63 kilograms is a competition featured at the 1998 World Wrestling Championships, and was held at the Azadi Indoor Stadium in Tehran, Iran from 8 to 10 September 1998.














