
The Vienna Central Cemetery is one of the largest cemeteries in the world by number of interred, and is the most well-known cemetery among Vienna's nearly 50 cemeteries. The cemetery's name is descriptive of its significance as Vienna's biggest cemetery, not of its geographic location, as it is not in the city center of the Austrian capital, but on the southern outskirts, in the outer city district of Simmering.

Karl Maria Wiligut was an Austrian Völkisch occultist and soldier. He served in the Austro-Hungarian Army during World War I and was a leading figure in the Irminism movement, eventually joining the SS after being recruited by Heinrich Himmler.

Guido Karl Anton List, better known as Guido von List, was an Austrian occultist, journalist, playwright, and novelist. He expounded a modern Pagan new religious movement known as Wotanism, which he claimed was the revival of the religion of the ancient German race, and which included an inner set of Ariosophical teachings that he termed Armanism.

A rune is a letter in a set of related alphabets known as runic alphabets native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were used to write Germanic languages before they adopted the Latin alphabet, and for specialised purposes thereafter. In addition to representing a sound value, runes can be used to represent the concepts after which they are named (ideographs). Scholars refer to instances of the latter as Begriffsrunen. The Scandinavian variants are also known as fuþark, or futhark; this name is derived from the first six letters of the script, ⟨ᚠ⟩, ⟨ᚢ⟩, ⟨ᚦ⟩, ⟨ᚨ⟩/⟨ᚬ⟩, ⟨ᚱ⟩, and ⟨ᚲ⟩/⟨ᚴ⟩, corresponding to the Latin letters ⟨f⟩, ⟨u⟩, ⟨þ⟩/⟨th⟩, ⟨a⟩, ⟨r⟩, and ⟨k⟩. The Anglo-Saxon variant is known as futhorc, or fuþorc, due to changes in Old English of the sounds represented by the fourth letter, ⟨ᚨ⟩/⟨ᚩ⟩.
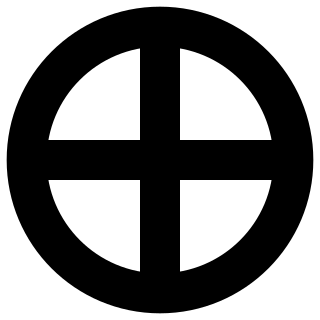
A sun cross, solar cross, or wheel cross is a solar symbol consisting of an equilateral cross inside a circle.

The SS-Ehrenring, unofficially called Totenkopfring, was an award of Heinrich Himmler's Schutzstaffel (SS). It was not a state decoration, but rather a personal gift bestowed by Himmler. It became a highly sought-after award, one which could not be bought or sold. The SS Honour Sword and SS Honour Dagger were similar awards.
Algiz is the name conventionally given to the "z-rune" ᛉ of the Elder Futhark runic alphabet. Its transliteration is z, understood as a phoneme of the Proto-Germanic language, the terminal *z continuing Proto-Indo-European terminal *s via Verner's law.

Armanen runes are 18 pseudo-runes, inspired by the historic Younger Futhark runes, invented by Austrian mysticist and Germanic revivalist Guido von List during a state of temporary blindness in 1902, and described in his Das Geheimnis der Runen, published as a periodical article in 1906, and as a standalone publication in 1908. The name seeks to associate the runes with the postulated Armanen, whom von List saw as ancient Aryan priest-kings. The runes continue in use today in esotericism and in Germanic neopaganism.

Armanism and Ariosophy are esoteric ideological systems that were largely developed by Guido von List and Jörg Lanz von Liebenfels, respectively, in Austria between 1890 and 1930. The term 'Ariosophy', which translates to wisdom of the Aryans, was invented by Lanz von Liebenfels in 1915, and during the 1920s, it became the name of his doctrine. For research on the topic, such as Nicholas Goodrick-Clarke's book The Occult Roots of Nazism, the term 'Ariosophy' is generically used to describe the Aryan/esoteric theories which constituted a subset of the 'Völkische Bewegung'. This broader use of the word is retrospective and it was not generally current among the esotericists themselves. List actually called his doctrine 'Armanism', while Lanz used the terms 'Theozoology' and 'Ario-Christianity' before the First World War.
Karl Spiesberger was a German mystic, occultist, Germanic revivalist and Runosophist. He is most well known for his revivalism and usage of the Sidereal Pendulum for divination and dowsing and for his anti-racialist stance and revivalist usage of the Armanen Futharkh runic system after the second world war, removing its negative connotations. During his involvement with the Fraternitas Saturni Spiesberger was also known as Frater Eratus. Under this name he published several articles in the Blätter für angewandte okkulte Lebenskunst.

Siegfried Adolf Kummer was a German mystic and Germanic revivalist. He is also most well known for his revivalism and use of the Armanen runes row. He, along with Friedrich Bernhard Marby, were imprisoned during the Third Reich for being unauthorised occultists.

Rudolf John Gorsleben was a German Ariosophist, Armanist, journal editor and playwright.

There is some evidence that, in addition to being a writing system, runes historically served purposes of magic. This is the case from the earliest epigraphic evidence of the Roman to the Germanic Iron Age, with non-linguistic inscriptions and the alu word. An erilaz appears to have been a person versed in runes, including their magic applications.
thumb|Hagal rune Hagal is the 7th pseudo-rune of Armanen Futharkh of Guido von List, derived from the Younger Futhark Hagal rune ᚼ.
Germany and Austria have spawned many movements and practices in Western esotericism, including Rosicrucianism, Theosophy, Anthroposophy and Ariosophy, among others.
Sowilo (*sōwilō), meaning "sun", is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic language name of the s-rune.

General of the Infantry is a former rank of the German army. It is currently an appointment or position given to an OF-8 rank officer, who is responsible for particular affairs of training and equipment of the Bundeswehr infantry.

Erwin Guido Kolbenheyer was an Austrian novelist, poet and playwright. Later based in Germany, he belonged to a group of writers that included the likes of Hans Grimm, Rudolf G. Binding, Emil Strauß, Agnes Miegel and Hanns Johst, all of whom found favour under the Nazis.
Members of the Bavarian Maximilian Order for Science and Art, awarded to acknowledge and reward excellent and outstanding achievements in the fields of science and art. It is based in Bavaria, Germany.
Runic alphabets have seen numerous uses since the 18th-century Viking revival, in Scandinavian Romantic nationalism (Gothicismus) and Germanic occultism in the 19th century, and in the context of the Fantasy genre and of Germanic Neopaganism in the 20th century.











