
Saxony-Anhalt is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of 20,451.7 square kilometres (7,896.4 sq mi) and has a population of 2.17 million inhabitants, making it the 8th-largest state in Germany by area and the 11th-largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Magdeburg.

Lüchow-Dannenberg is a district in Lower Saxony, Germany, which is usually referred to as Hanoverian Wendland or Wendland. It is bounded by the districts of Uelzen and Lüneburg and the states of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Brandenburg and Saxony-Anhalt.
Uelzen is a district in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Gifhorn, Celle, Heidekreis, Lüneburg and Lüchow-Dannenberg, and by the state of Saxony-Anhalt. The district capital is the town of Uelzen.

Salzwedel is a town in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is the capital of the district (Kreis) of Altmarkkreis Salzwedel, and has a population of approximately 21,500. Salzwedel is located on the German Timber-Frame Road.

Altmarkkreis Salzwedel is a district in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is bounded by the districts Gifhorn, Uelzen, Lüchow-Dannenberg in Lower Saxony, and the districts of Stendal and Börde (district).

The Altmark is a historic region in Germany, comprising the northern third of Saxony-Anhalt. As the initial territory of the March of Brandenburg, it is sometimes referred to as the "Cradle of Prussia", as by Otto von Bismarck, a native of Schönhausen near Stendal.
The Ohrekreis was a district (Kreis) in the north-east of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Neighboring districts are Altmarkkreis Salzwedel, Stendal, Jerichower Land, the district-free city Magdeburg, Bördekreis, and the districts Helmstedt and Gifhorn in Lower Saxony. Its territory is now incorporated into Börde.
Stendal is a district in the north-east of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Its neighbouring districts are : Jerichower Land, Börde, Altmarkkreis Salzwedel, Lüchow-Dannenberg in Lower Saxony, and the districts of Prignitz, Ostprignitz-Ruppin and Havelland in Brandenburg.

The Province of Saxony, also known as Prussian Saxony, was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1944. Its capital was Magdeburg.
Börde is a district in Saxony-Anhalt in Germany. Its seat is the town Haldensleben. It takes its name from the natural region Magdeburg Börde. It is the site of the Morsleben radioactive waste repository. The disposal of waste into the facility ended in 1998.
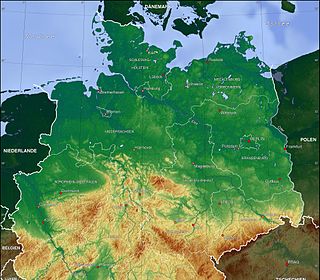
The North German Plain or Northern Lowland is one of the major geographical regions of Germany. It is the German part of the North European Plain. The region is bounded by the coasts of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the north, Germany's Central Uplands to the south, by the Netherlands to the west and Poland to the east.

The river Jeetzel, which begins in the Altmark under the name Jeetze, flows from Saxony-Anhalt through Lower Saxony, in Germany. From its source near the village of Dönitz, it flows north through Beetzendorf, Salzwedel, Wustrow, Lüchow and Dannenberg, before joining the Elbe in Hitzacker. Its total length is 73 kilometres (45 mi).

The Drawehn is a partly wooded and partly agricultural region of hills in the northeastern part of the German state of Lower Saxony, lying between the districts of Lüneburg and Uelzen in the west and Lüchow-Dannenberg in the east.
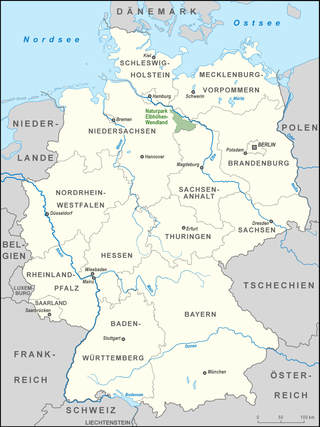
The Elbhöhen-Wendland Nature Park, formerly known as the Elbufer-Drawehn Nature Park is a German nature park east of Lüneburg in Lower Saxony.

The Bundesstraße 71 is one of the longer German federal roads, numbered in the 60s and 70s series. It begins at the B 6 in Bremerhaven by the Unterweser and ends in Könnern near Halle (Saale) in Saxony-Anhalt.

The Magdeburg Börde is the central landscape unit of the state of Saxony-Anhalt and lies to the west and south of the eponymous state capital Magdeburg. Part of a loess belt stretching along the southeastern rim of the North German Plain, it is noted for its very fertile Chernozem soils.
The Magdeburg Region is the name of the central region in the state of Saxony-Anhalt in North Germany. It includes the landscape units of Magdeburg Börde, Jerichow Land, the northern Harz Foreland and the Colbitz-Letzlingen Heath. The centre of the region is the city of Magdeburg; other important towns are Haldensleben, Aschersleben, Staßfurt, Oschersleben, Schönebeck (Elbe) and Burg. Towards the east the Elbe-Börde Heath transitions into the neighbouring region of Anhalt-Wittenberg. To the south lies the Harz and the Saale-Unstrut Region, to the north the Altmark. The regional tourist association uses the name Elbe-Börde-Heide which came originally from regional planning and was first coined in the 1990s. Currently it is used in the fields of tourism or regional marketing.
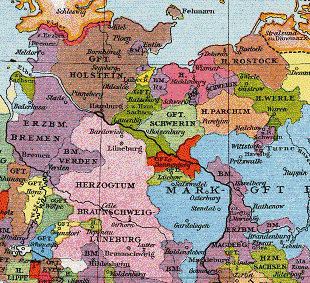
The County of Dannenberg was a fief in the Duchy of Saxony. Its heartland was largely identical with the present-day collective municipality of Elbtalaue in north Germany.

The Salzwedel–Dannenberg railway was a branch line between Salzwedel in the north of Saxony-Anhalt and Dannenberg in eastern Lower Saxony in Germany. It was built in 1891 by the Prussian state railways, initially as a stub line from Salzwedel to Lüchow and extended in 1911 to Dannenberg. Shortly before the end of the Second World War the line between Salzwedel in the Soviet Zone and Lübbow in the British Zone was cut. Passenger services ceased in 1975, goods trains continued tor run until the end of 1997. The section still being worked between Lüchow and the station at Dannenberg Ost has been owned since 2001 by the Deutsche Regionaleisenbahn (DRE) and is called the Jeetzel Valley Railway (Jeetzeltalbahn).

The Wendland is a region in Germany on the borders of the present states of Brandenburg, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Lower Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt. Its heart is the Hanoverian Wendland in the county of Lüchow-Dannenberg in Lower Saxony.














