
Sogdia or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian civilization between the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, and in present-day Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Empire, and listed on the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great. Sogdiana was first conquered by Cyrus the Great, the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, and then was annexed by the Macedonian ruler Alexander the Great in 328 BC. It would continue to change hands under the Seleucid Empire, the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, the Kushan Empire, the Sasanian Empire, the Hephthalite Empire, the Western Turkic Khaganate and the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana.

Parvati, also known as Uma and Gauri, is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism, revered as the goddess of power, energy, nourishment, harmony, love, beauty, devotion, and motherhood. Along with Lakshmi and Sarasvati, she forms the trinity, known as the Tridevi.
The "White Huns", also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the Spet Xyon, and in Sanskrit as the Sveta-huna, were a subgroup of the Huna and/or Xionites. The White Huns are sometimes regarded as synonymous with the Hephthalites but may have included other tribes as well. They are known for their historical conquest and occupation of North India, particularly the Punjab region.

Panjakent or Penjikent is a city in the Sughd province of Tajikistan on the river Zeravshan, with a population of 52,500. It was once an ancient town in Sogdiana. The ruins of the old town are on the outskirts of the modern city. The Sarazm Important Bird Area lies downstream of the city on the tugay-vegetated floodplain of the river.

Huvishka was the emperor of the Kushan Empire from the death of Kanishka until the succession of Vasudeva I about thirty years later.
Boris Ilich Marshak was an archeologist who spent more than fifty years excavating the Sogdian ruins at Panjakent, Tajikistan.

Ganesha is a prominent Hindu god. He is the god of beginnings, wisdom and luck and worshipped as the remover of obstacles. Ganesha is easily recognized from his elephant head. Devotion to Ganesha is widely diffused and extends to Jains and Buddhists and beyond India.

The Afrasiab murals, also called the Paintings of the Ambassadors, is a rare example of Sogdian art. It was discovered in 1965 when the local authorities decided to construct a road in the middle of Afrāsiāb mound, the old site of pre-Mongol Samarkand. It is now preserved in a special museum on the Afrāsiāb mound.

Afrasiyab ,(Persian: افراسيابafrāsiyāb) is an ancient site in Northern Samarkand, present day Uzbekistan, that was occupied from c. 500 BC to 1220 AD prior to the Mongol invasion in the 13th century. The oldest layers date from the middle of the first millennium BC. Today, it is a hilly grass mound located near the Bibi Khanaum Mosque. Excavations uncovered the now famous Afrasiab frescoes exposed in the Afrasiab Museum of Samarkand, located next to the archaeological site.

The Muslim conquest of Transoxiana, also called the Arab conquest of Transoxiana, was part of the early Muslim conquests. It began shortly after the Muslim conquest of Persia enabled the Arabs to enter Central Asia. Relatively small-scale incursions had taken place under the Rashidun Caliphate, but it was not until after the establishment of the Umayyad Caliphate that an organized military effort was made to conquer Transoxiana, a region that today includes all or parts of Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan. The campaign continued under the Abbasid Caliphate, and gradually saw the Islamization of the region.

Alex Battler, known in Russia under the pen name Oleg Alekseyevich Arin, is a Soviet-born Russian-Canadian scholar and political writer. He is a member of the organization «Defend Science» (US).

The Principality of Ushrusana was a local dynasty ruling the Ushrusana region, in the northern area of modern Tajikistan, from an unknown date to 892 CE. Ushrusana, just like Ferghana, did not belong to Sogdia proper, but its inhabitants wrote in Sogdian, and may have spoken the Sogdian language as well. The rulers of the principality were known by their title of Afshin.
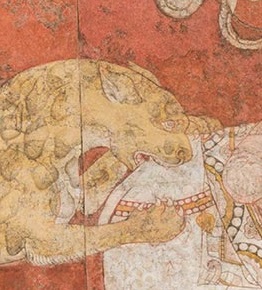
Sogdian art refers to art produced by the Sogdians, an Iranian people living mainly in ancient Sogdia, present-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, who also had a large diaspora living in China. Its apex was between the 5th and 9th centuries, and it consists of a rich body of pre-Muslim Central Asian visual arts. New finds recovered in the past decades allowed scholars to achieve a better understanding of Sogdian art.

Balalyk tepe, in former Bactria, modern Uzbekistan, is a Central Asian archaeological site with many mural paintings. It was the site of a small fortified manor belonging to a princely Hephthalite clan. It is generally dated a bit later than the painting at Dilberjin, from the late 5th century to the early 7th century CE, or from the end of the 6th century to the early 7th century CE. The paintings of Balalyk Tepe are part of a "Tokharistan school", which also includes Adzhina-tepe and Kafyr-kala. They are succeeded chronologically by the Sogdian art of Penjikent.

The murals of Penjikent are among the most famous murals of the pre-Islamic period in Panjakent, ancient Sogdiana, in Tajikistan. Numerous murals were recovered from the site, and many of them are now on display in the Hermitage Museum in Saint Petersburg, and in the National Museum of Antiquities of Tajikistan in Dushanbe. The murals reveal the cosmopolitan nature of the Penjikent society that was mainly composed of Sogdian and Turkic elites and likely other foreign merchant groups of heterogeneous origin. Significant similarities with Old Turkic clothing, weapon items, hairstyles and ritual cups are noted by comparative research.
The Nuydi treasure is a hoard of ancient silver coins discovered near the village of Nuydi in the Agsu district of Azerbaijan. The treasure, consisting of 36 coins dated to the 2nd or 1st century BC, was discovered in grave No. 11 of the female in the Nuydi monument.

Manichaean manuscript fragment number "MIK Ⅲ 4979" is a collection Fragments of Manichaean illuminated manuscript in Germany Berlin Asian Art Museum, painted during the 8th–9th centuries, and were found in the early 20th century. German Turpan expedition team found in Xinjiang Gaochang site. The broken page is 12.4 cm long and 25.2 cm wide, with slender painting illustrations drawn on both sides, written in Sogdian in Manuscript, Turkic and Middle Persian text.

The Ikhshids of Sogdia, or Ikhshids of Samarkand, were a series of rulers of Soghdia in Transoxiana, with their capital at Samarkand, during the pre-Islamic and early Islamic periods.

Oxus was an ancient Eastern Iranian god regarded as the divine representation of the Amu Darya. In Bactria he was also considered the king of the gods. Multiple different depictions of him are known from ancient Central Asian art. On an altar from his temple discovered in Takht-i Sangin he is depicted in the form of the Greek river god Marsyas presumably introduced by soldiers and settlers who arrived in this area during the reigns of Alexander the Great and the Seleucids. In Kushan art he was instead depicted as a Poseidon-like figure holding a staff and a fish. In Sogdian art he might have been depicted either as a horse or as a figure seated on a throne with horse protomes, though this proposal remains a matter of debate.

The Anikova dish or Anikovsky dish is a cast silver dish representing armoured cavalrymen attacking a fortress in the Siege of Jericho, and thought to have been created in Semirechye (Zhetysu) in Central Asia in the 9th–10th century. It was found in 1909 near the village of Bolshe-Anikovskaya, Cherdyn district, Perm province. It is now in the State Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg (S-46).




















