| Westerhof syndrome | |
|---|---|
 | |
| This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Westerhof syndrome is a cutaneous condition inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion, characterized by congenital hypopigmented macules. [1]
| Westerhof syndrome | |
|---|---|
 | |
| This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
Westerhof syndrome is a cutaneous condition inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion, characterized by congenital hypopigmented macules. [1]

Sézary disease, or Sézary syndrome, is a type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma that was first described by Albert Sézary. The affected T cells, known as Sézary's cells or Lutzner cells, have pathological quantities of mucopolysaccharides. Sézary disease is sometimes considered a late stage of mycosis fungoides with lymphadenopathy.

Kindler syndrome is a rare congenital disease of the skin caused by a mutation in the KIND1 gene.
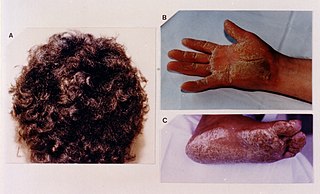
Naxos disease is a cutaneous condition characterized by a palmoplantar keratoderma. The prevalence of the syndrome is up to 1 in every 1000 people in the Greek islands.
Schöpf–Schulz–Passarge syndrome is an autosomal recessive condition with punctate symmetric palmoplantar keratoderma, with the keratoderma and fragility of the nails beginning around age 12. In addition to palmoplantar keratoderma, other symptoms include hypodontia, hypotrichosis, nail dystrophies, and eyelid cysts. Patients may also develop syringofibroadenoma and squamous cell carcinomas.
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, or Bazex syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by psoriasiform changes of hands, feet, ears, and nose, with involvement of the nails and periungual tissues being characteristic and indistinguishable from psoriatic nails. The condition is associated with carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.

Pilomatricoma is a benign skin tumor derived from the hair matrix. These neoplasms are relatively uncommon and typically occur on the scalp, face, and upper extremities. Clinically, pilomatricomas present as a subcutaneous nodule or cyst with unremarkable overlying epidermis that can range in size from 0.5 to 3.0 cm, but the largest reported case was 24 cm.

Trichilemmoma is a benign cutaneous neoplasm that shows differentiation toward cells of the outer root sheath. The lesion is often seen in the face and neck region. Multifocal occurrence is associated with Cowden syndrome, in which hamartomatous intestinal polyposis is seen in conjunction with multiple tricholemmoma lesions.
A trichodiscoma is a cutaneous condition, a benign, usually skin-colored tumor most often affecting the face and upper trunk.
Wende–Bauckus syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by tiny white macules on the trunk with confluence within flexures.

UV-sensitive syndrome is a cutaneous condition inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion, characterized by photosensitivity and solar lentigines. Recent research identified that mutations of the KIAA1530 (UVSSA) gene as cause for the development of UV-sensitive syndrome. Furthermore, this protein was identified as a new player in the Transcription-coupled repair (TC-NER).

Hystrix-like ichthyosis–deafness syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by a keratoderma.

Arthrogryposis–renal dysfunction–cholestasis syndrome is a cutaneous condition caused by a mutation in the VPS33B gene.

Neonatal ichthyosis–sclerosing cholangitis syndrome is a cutaneous condition which is characterized by hypotrichosis of the scalp, alopecia, ichthyosis and sclerosing cholangitis. Only 5 cases from 3 families worldwide have been described in medical literature. It caused by mutations in the Claudin 1 gene.
Sebaceous nevus syndrome is a cutaneous condition and may resemble CHILD syndrome.
Seboacanthoma is a cutaneous condition, and a specific type of sebaceous adenoma which may be specific to Muir–Torre syndrome.

Laryngo-onycho-cutaneous syndrome is a rare epithelial disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. It is characterized by abnormalities in the larynx, nails, and skin ("cutaneous"). The disorder is only found in Punjabi Muslims and only a few cases have been reported.
Pseudomonas hot-foot syndrome is a self-limited cutaneous condition that occurs on the plantar surface of children after swimming in pool water that has high concentrations of P. aeruginosa. The condition typically presents as plantar purple-red nodules.

Autosomal dominant multiple pterygium syndrome is a cutaneous condition inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion.
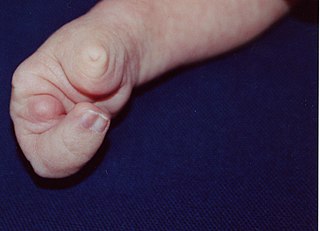
Limb–mammary syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by p63 mutations.