Related Research Articles

Health informatics is the field of science and engineering that aims at developing methods and technologies for the acquisition, processing, and study of patient data, which can come from different sources and modalities, such as electronic health records, diagnostic test results, medical scans. The health domain provides an extremely wide variety of problems that can be tackled using computational techniques.
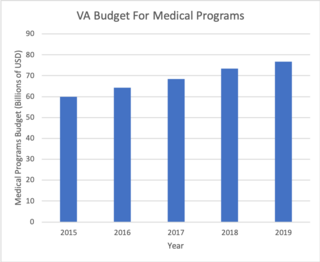
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the component of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) led by the Under Secretary of Veterans Affairs for Health that implements the healthcare program of the VA through a nationalized healthcare service in the United States, providing healthcare and healthcare-adjacent services to Veterans through the administration and operation of 146 VA Medical Centers (VAMC) with integrated outpatient clinics, 772 Community Based Outpatient Clinics (CBOC), and 134 VA Community Living Centers Programs. It is the largest division in the Department, and second largest in the entire federal government, employing over 350,000 employees. All VA hospitals, clinics and medical centers are owned by and operated by the Department of Veterans Affairs as opposed to private companies, and all of the staff employed in VA hospitals are government employees. Because of this, Veterans that qualify for VHA healthcare do not pay premiums or deductibles for their healthcare but may have to make copayments depending on what procedure they are having. VHA is distinct from the U.S. Department of Defense Military Health System of which it is not a part.

Westmead Hospital is a major tertiary hospital in Sydney, Australia. Opened on 10 November 1978, the 975-bed hospital forms part of the Western Sydney Local Health District, and is a teaching hospital of Sydney Medical School at the University of Sydney.

UConn Health is the branch of the University of Connecticut that oversees clinical care, advanced biomedical research, and academic education in medicine. The main branch is located in Farmington, Connecticut, in the US. It includes a teaching hospital, the UConn School of Medicine, School of Dental Medicine, and Graduate School. Other community care satellite locations exist in Avon, Canton, East Hartford, Putnam, Simsbury, Southington, Storrs, Torrington, West Hartford, and Willimantic, including two urgent cares in both Storrs and Canton. The university owns and operates many smaller clinics around the state that contain UConn Medical Group, UConn Health Partners, University Dentists and research facilities. Andrew Agwunobi stepped down as the CEO of UConn Health in February 2022 after serving since 2014 for a private-sector job. Bruce Liang is UConn Heath's interim CEO and remains dean of the UConn School of Medicine.
The Lions Eye Institute (LEI) is an Australian medical research institute affiliated with the University of Western Australia. It was established in 1983 with support of the Lions Clubs of Western Australia and headquartered in the Perth suburb of Nedlands, Western Australia. The LEI is a not-for-profit centre of excellence that combines an ophthalmic clinic with scientific discovery developing techniques for the prevention of blindness and the reduction of pain from blinding eye conditions.

Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital (SCGH) is a teaching hospital in Nedlands, Western Australia.

Los Angeles County Department of Health Services operates the public hospitals and clinics in Los Angeles County, and is the United States' second largest municipal health system, after NYC Health + Hospitals.
A Patient Safety Organization (PSO) is a group, institution, or association that improves medical care by reducing medical errors. Common functions of patient safety organizations are data collection and analysis, reporting, education, funding, and advocacy. A PSO differs from a Federally designed Patient Safety Organization (PSO), which provides health care providers in the U.S. privilege and confidentiality protections for efforts to improve patient safety and the quality of patient care delivery
MedStar Health is a not-for-profit healthcare organization. It operates more than 120 entities, including ten hospitals in the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area of the United States. In 2011 it was ranked as the employer with the largest number of local employees in the region.

Nationwide Children's Hospital is a nationally ranked pediatric acute care teaching hospital located in the Southern Orchards neighborhood of Columbus, Ohio. The hospital has 673 pediatric beds and is affiliated with the Ohio State University College of Medicine. The hospital provides comprehensive pediatric specialties and subspecialties to infants, children, teens, and young adults aged 0–21 throughout Ohio and surrounding regions. Nationwide Children's Hospital also sometimes treats adults that require pediatric care. Nationwide Children's Hospital also features an ACS designated Level 1 Pediatric Trauma Center, 1 of 4 in the state. The hospital has affiliations with the nearby Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. Nationwide Children's Hospital is located on its own campus and has more than 1,379 medical staff members and over 11,909 total employees.
University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (UCLH) is an NHS foundation trust based in London, United Kingdom. It comprises University College Hospital, University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street, the UCH Macmillan Cancer Centre, the Royal National ENT and Eastman Dental Hospitals, the Hospital for Tropical Diseases, the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, the Royal London Hospital for Integrated Medicine and the Royal National Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital.

Saint Boniface Hospital is Manitoba's second-largest hospital, located in the Saint Boniface neighbourhood of Winnipeg. Founded by the Sisters of Charity of Montreal in 1871, it was the first hospital in Western Canada. The hospital was incorporated in 1960, and as of 2003 has 554 beds and 78 bassinets.
CareFlight is an air medical service headquartered in Westmead, New South Wales, Australia.
Health care in the United States far outspends that of any other nation, measured both in per capita spending and as a percentage of GDP. Despite this, the country has significantly worse healthcare outcomes when compared to peer nations. The United States is the only developed nation without a system of universal health care, with a large proportion of its population not carrying health insurance, a substantial factor in the country's excess mortality.

The UCLH/UCL Biomedical Research Centre is a biomedical research centre based in London. It is a partnership between University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (UCLH), University College London (UCL) and the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) and was one of the original five Comprehensive Biomedical Research Centres established by the NIHR in April 2007.

Gujarat Cancer & Research Institute (GCRI) is a state owned cancer research institute in Gujarat, India. It was established in 1972. It is one of the 25 government funded Regional Cancer Centres in India.

EMMS International is a non-denominational christian Non-governmental Organization (NGO) that provides medical aid to countries around the world and operates field offices in the UK, Malawi, India, Israel, and Nepal. Founded to provide clinical education to missionaries and medical aid to people in need in Scotland, it later expanded to the Middle East, South Asia, and Africa through sponsoring the construction of dispensaries and hospitals. Its educational mission expanded from training missionary physicians in Edinburgh to training local nurses and physicians in the countries where it works. EMMS continues to provide resource assistance at all its sites. Based in Scotland, its vision is "health for today, hope for tomorrow."

Telepharmacy is the delivery of pharmaceutical care via telecommunications to patients in locations where they may not have direct contact with a pharmacist. It is an instance of the wider phenomenon of telemedicine, as implemented in the field of pharmacy. Telepharmacy services include drug therapy monitoring, patient counseling, prior authorization and refill authorization for prescription drugs, and monitoring of formulary compliance with the aid of teleconferencing or videoconferencing. Remote dispensing of medications by automated packaging and labeling systems can also be thought of as an instance of telepharmacy. Telepharmacy services can be delivered at retail pharmacy sites or through hospitals, nursing homes, or other medical care facilities.

The Binaytara Foundation (BTF) was established in 2007 by Dr. Binay Shah and wife Tara Shah with the goal of promoting health and education in underprivileged societies. The BTF is a Washington State nonprofit organization exempt from taxation pursuant to Section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code. At the 37th plenary meeting held July 18, 2013, the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) decided to grant special consultative status to the BTF. The ECOSOC grants special consultative status to NGOs that are concerned specifically with only a few of the fields of activity covered in ECOSOC and bears special competence in that field. BTF has founded multiple programs in underdeveloped and developing countries to improve access to healthcare. Recent accomplishments include developing home hospice and palliative care in India and Nepal, and the first bone marrow transplant center in Nepal.

Voluntary Health Services, popularly known as the VHS Hospital, is a multispecialty tertiary care referral hospital in the south Indian state of Tamil Nadu, reportedly serving the economically weaker sections of the society. It was founded in 1958 by Krishnaswami Srinivas Sanjivi, an Indian physician, social worker and a winner of Padma Shri and Padma Bhushan awards and is run by a charitable non governmental organization of the same name. The hospital is situated along Rajiv Gandhi Salai at Taramani, in Chennai.
References
This article may contain excessive or inappropriate references to self-published sources .(May 2017) |
- 1 2 "Annual Report" (PDF). Westmead Medical Research Foundation. 2016. Retrieved 5 May 2017.
- ↑ "How we help". Westmead Hospital Foundation webpage. Retrieved 16 October 2013.
- 1 2 3 "Annual Report" (PDF). Westmead Medical Research Foundation. 2012. Retrieved 16 October 2013.
- ↑ "Annual Report" (PDF). Westmead Medical Research Foundation. 2007. Retrieved 16 October 2013.
- ↑ "Annual Review" (PDF). Westmead Medical Research Foundation. 2008. Retrieved 16 October 2013.
- ↑ "Annual Report" (PDF). Westmead Medical Research Foundation. 2010. Retrieved 16 October 2013.