
The Canadian Pacific Railway, also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), was a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway was owned by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001.

SkyTrain is the medium-capacity rapid transit system serving the Metro Vancouver region in British Columbia, Canada. SkyTrain has 79.6 km (49.5 mi) of track and uses fully automated trains on grade-separated tracks running on underground and elevated guideways, allowing SkyTrain to hold consistently high on-time reliability. In 2022, the system had a ridership of 116,569,000, or about 426,900 per weekday as of the second quarter of 2023.
Whistler is a resort municipality in Squamish-Lillooet Regional District, British Columbia, Canada. It is located in the southern Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains, approximately 125 km (78 mi) north of Vancouver and 36 km (22 mi) south of Pemberton. It has a permanent population of approximately 13,982 (2021), as well as a larger but rotating population of seasonal workers.

The Kettle Valley Railway was a subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) that operated across southern British Columbia, west of Midway running to Rock Creek, then north to Myra Canyon, down to Penticton over to Princeton, Coalmont, Brookmere, Coquihalla and finally Hope where it connected to the main CPR line.

BC Rail is a railway in the Canadian province of British Columbia.

The British Columbia Electric Railway (BCER) was an historic railway which operated in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Originally the parent company for, and later a division of, BC Electric Company, the BCER assumed control of existing streetcar and interurban lines in southwestern British Columbia in 1897, and operated the electric railway systems in the region until the last interurban service was discontinued in 1958. During and after the streetcar era, BC Electric also ran bus and trolleybus systems in Greater Vancouver and bus service in Greater Victoria; these systems subsequently became part of BC Transit, and the routes in Greater Vancouver eventually came under the control of TransLink. Trolley buses still run in the City of Vancouver with one line extending into Burnaby.

The Canada Line is a rapid transit line in Greater Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, that is part of the SkyTrain system. The line is owned by TransLink and InTransitBC and is operated by ProTrans BC. Coloured turquoise on route maps, it operates as an airport rail link between Vancouver, Richmond, and the Vancouver International Airport (YVR). The line comprises 16 stations and 19.2 kilometres (11.9 mi) of track; the main line runs from Vancouver to Richmond while a 4-kilometre (2.5 mi) spur line from Bridgeport station connects to the airport. It opened on August 17, 2009, ahead of the 2010 Winter Olympics.

Waterfront station is a major intermodal public transportation facility and the main transit terminus in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It is located on West Cordova Street in Downtown Vancouver, between Granville and Seymour Street. The station is also accessible via two other street-level entrances, one on Howe Street to the west for direct access to the Expo Line and another on Granville Street to the south for direct access to the Canada Line.
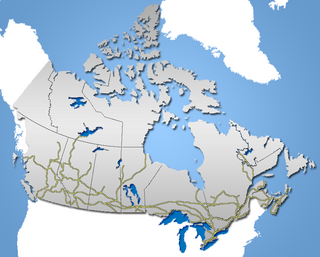
Canada has a large and well-developed railway system that primarily transports freight. There are two major publicly traded transcontinental freight railway systems, Canadian National (CN) and Canadian Pacific Kansas City (CPKC). Nationwide passenger services are provided by the federal crown corporation Via Rail, and three international services to the US by Amtrak. Three Canadian cities have commuter train services: in the Montreal area by Exo, in the Toronto area by GO Transit, and in the Vancouver area by West Coast Express. These cities and several others are also served by light rail or metro systems. Only one (Toronto) has an extensive streetcar (tram) system. Smaller railways such as Ontario Northland Railway also run passenger trains to remote rural areas. The Rocky Mountaineer and Royal Canadian Pacific provide luxury rail tours for viewing scenery in the Canadian Rockies as well as other mountainous areas of British Columbia and Alberta.

The Canadian is a transcontinental passenger train operated by Via Rail with service between Union Station in Toronto, Ontario, and Pacific Central Station in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada.

Northern Alberta Railways was a Canadian railway which served northern Alberta and northeastern British Columbia. Jointly owned by both Canadian National Railway and Canadian Pacific Railway, NAR existed as a separate company from 1929 until 1981.

Rocky Mountaineer is a Canadian rail-tour company based in Vancouver that operates luxury scenic trains on four rail routes in British Columbia, Alberta, Colorado, and Utah.
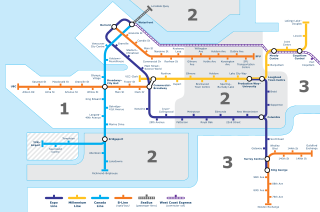
Transportation in Vancouver, British Columbia, has many of the features of modern cities worldwide. Unlike many large metropolises, Vancouver has no freeways into or through the downtown area. A proposed freeway through the downtown was rejected in the 1960s by a coalition of citizens, community leaders and planners. This event "signalled the emergence of a new concept of the urban landscape" and has been a consistent element of the city's planning ever since.
The Whistler Sea to Sky Climb, previously known as the Whistler Mountaineer, was a sight-seeing railway service. It was operated by Rocky Mountaineer Vacations (RMV) tour company, based in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada who operate vintage trains over numerous sightseeing routes in Western Canada. It was established in 2006 and discontinued in 2015 after the retirement of Rocky Mountaineer's RedLeaf service fleet.

Rocky Mountaineer Station in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, is a railway station which acts as the western terminus of the Rocky Mountaineer train service to Jasper, Banff and Calgary. Prior to 2005, the Vancouver terminus for the Rocky Mountaineer was the Pacific Central Station.
Quesnel station in Quesnel, British Columbia, Canada is a railway station which is used by the Rocky Mountaineer train service. The station is used on the Rainforest to Gold Rush route that links Whistler to Quesnel. Service is infrequent and only occurs several days per month.

Tower Centre in Calgary, Alberta, Canada, is an office tower and retail centre connected to the Calgary Tower. It is only three minutes on foot from the CTrain's 1 Street SW station and Centre Street station.
North Vancouver station is a railway station located in the city of North Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada and is serviced by the Rocky Mountaineer tour company. The station is used on the Rainforest to Gold Rush route that goes to Jasper. It was formerly the southern terminus of the Whistler Sea to Sky Climb.
The SkyTrain rapid transit system in Greater Vancouver, Canada, was conceived as a legacy project of Expo 86 and was finished in time to showcase the fair's theme: "Transportation and Communication: World in Motion – World in Touch". Construction was funded by the provincial and federal governments. Vancouver had plans as early as the 1950s to build a monorail system, with modernist architect Wells Coates pencilled in to design it; that project was abandoned. The lack of a rapid transit system was said to be the cause of traffic problems in the 1970s, and the municipal government could not fund the construction of such a system. During the same period, Urban Transportation Development Corporation, then an Ontario crown corporation, was developing a new rapid transit technology known as an "Intermediate Capacity Transit System". In 1980, the need for rapid transit was great, and Ontario needed buyers for its new technology. "Advanced Rapid Transit" was selected to be built in Vancouver to showcase the Ontario project at Expo 86.

The Cariboo Prospector or Cariboo Dayliner or The BC Rail Budd cars was a passenger train service in British Columbia, Canada, which used Budd Rail Diesel Car trains. It was operated by the Pacific Great Eastern, later known as the British Columbia Railway Company and then BC Rail. The train ran from BC Rail's North Vancouver railway station, the one located a few blocks from the current North Vancouver railway station used by the Rocky Mountaineer and ran to Lillooet railway station. From there a section was split from the train that would continue down to Prince George BC Rail station located in BC Rail's Prince George yards. This train service ended along with the other BC Rail passenger services in 2002. A section serving the line between Lillooet, Seton Portage, and D'Arcy was replaced by the Koaham Shuttle.

















