
A web hosting service is a type of Internet hosting service that hosts websites for clients, i.e. it offers the facilities required for them to create and maintain a site and makes it accessible on the World Wide Web. Companies providing web hosting services are sometimes called web hosts.
Teradata Corporation is an American software company that provides cloud database and analytics-related software, products, and services. The company was formed in 1979 in Brentwood, California, as a collaboration between researchers at Caltech and Citibank's advanced technology group.

Dell EMC is an American multinational corporation headquartered in Hopkinton, Massachusetts, and Round Rock, Texas, and is a subsidiary of Dell Technologies. Dell EMC sells data storage, information security, virtualization, analytics, cloud computing and other products and services that enable organizations to store, manage, protect, and analyze data. Dell EMC's target markets include large companies and small- and medium-sized businesses across various vertical markets.
DreamHost is a Los Angeles-based web hosting provider and domain name registrar. It is owned by New Dream Network, LLC, founded in 1996 by Dallas Bethune, Josh Jones, Michael Rodriguez and Sage Weil, undergraduate students at Harvey Mudd College in Claremont, California, and registered in 1997 by Michael Rodriguez. DreamHost began hosting customers' sites in 1997. In May 2012, DreamHost spun off Inktank. Inktank is a professional services and support company for the open source Ceph file system. In November 2014, DreamHost spun off Akanda, an open source network virtualization project. As of February 2016, Dreamhost employs about 200 people and has close to 400,000 customers.
Intertrust Technologies Corporation is a software technology company specializing in trusted distributed computing. Intertrust’s product lines consist of a DataOps platform, Application protection and Content protection solutions. Much of Intertrust's digital rights management (DRM) business is based on the Marlin DRM technology, which Intertrust founded along with four consumer electronics companies: Sony, Panasonic, Philips, and Samsung.

Xunlei Limited is a Chinese multinational technology company and an online service provider founded in 2003. The subsidiary of Xunlei Limited, Shenzhen Xunlei Networking Technologies, Co., Ltd. was formerly known as Sandai Technologies (Shenzhen) Inc. and changed its name to Shenzhen Xunlei Networking Technologies, Co., Ltd. in May 2005. Its headquarters are in Nanshan District, Shenzhen.

Cloud computing is "a paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand," according to ISO.
Founded in 2004 in New York City, Pando Networks was a managed peer-to-peer (P2P) media distribution company backed by Intel Capital, BRM Capital and Wheatley Partners. The company specialized in cloud distribution of games, video and software for publishers and media distributors and also operated a freemium consumer business for sending large files.
Network intelligence (NI) is a technology that builds on the concepts and capabilities of deep packet inspection (DPI), packet capture and business intelligence (BI). It examines, in real time, IP data packets that cross communications networks by identifying the protocols used and extracting packet content and metadata for rapid analysis of data relationships and communications patterns. Also, sometimes referred to as Network Acceleration or piracy.
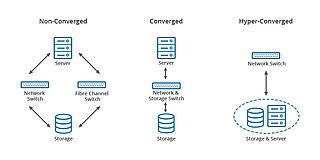
Converged infrastructure is a way of structuring an information technology (IT) system which groups multiple components into a single optimized computing package. Components of a converged infrastructure may include servers, data storage devices, networking equipment and software for IT infrastructure management, automation and orchestration.
Christopher P. Lynch is an American venture capitalist. He invested in sqrrl, DataRobot, Threat Stack, Nutonian and Hadapt. He co-founded hack/reduce, a Boston-based Big Data incubator in May 2012. Lynch was a founding member of ArrowPoint communications and Acopia Networks where he was CEO. Additionally, he was CEO at Vertica System.

Converged storage is a storage architecture that combines storage and computing resources into a single entity. This can result in the development of platforms for server centric, storage centric or hybrid workloads where applications and data come together to improve application performance and delivery. The combination of storage and compute differs to the traditional IT model in which computation and storage take place in separate or siloed computer equipment. The traditional model requires discrete provisioning changes, such as upgrades and planned migrations, in the face of server load changes, which are increasingly dynamic with virtualization, where converged storage increases the supply of resources along with new VM demands in parallel.

HP Cloud was a set of cloud computing services available from Hewlett-Packard. It was the combination of the previous HP Converged Cloud business unit and HP Cloud Services, an OpenStack-based public cloud. It was marketed to enterprise organizations to combine public cloud services with internal IT resources to create hybrid clouds, or a mix of private and public cloud environments, from around 2011 to 2016.
Aerospike is the company behind the Aerospike NoSQL distributed database management system. Citrusleaf, a Mountain View, California based company which rebranded to Aerospike in August 2012, announced the product in 2011. The software is used by developers to deploy real-time big data applications.

Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) is a not-for-profit organization with the mission to “promote the use of best practices for providing security assurance within cloud computing, and to provide education on the uses of cloud computing to help secure all other forms of computing.”

An Internet area network (IAN) is a concept for a communications network that connects voice and data endpoints within a cloud environment over IP, replacing an existing local area network (LAN), wide area network (WAN) or the public switched telephone network (PSTN).
Tresorit is a cloud storage platform that offers functions for administration, storage, synchronization, and transfer of data using end-to-end encryption.

Hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) is a software-defined IT infrastructure that virtualizes all of the elements of conventional "hardware-defined" systems. HCI includes, at a minimum, virtualized computing, software-defined storage, and virtualized networking. HCI typically runs on commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) servers.
Alibaba Cloud, also known as Aliyun, is a cloud computing company, a subsidiary of Alibaba Group. Alibaba Cloud provides cloud computing services to online businesses and Alibaba's own e-commerce ecosystem. Its international operations are registered and headquartered in Singapore.

SAP Converged Cloud is a private managed cloud developed and marketed by SAP.









