Crime and legal history
Furman was convicted of murdering William Micke during a home invasion in Savannah, Georgia on August 11, 1967, and subsequently sentenced to death on September 26, 1968, after a one-day trial. [2]
The sentence was overturned by the Supreme Court on the basis of the Eighth and Fourteenth Amendments. The decision struck down death penalty schemes in the whole country. Four years after the landmark decision, the Supreme Court reaffirmed the constitutionality of the death penalty when it approved the statutory changes made by three states in Gregg v. Georgia (1976).
Furman was paroled in April 1984.
In 2004, Furman pleaded guilty to a 2004 burglary charge in Bibb County Superior Court, and was sentenced to 20 years in prison. He was paroled twelve years later, in April 2016. [3]

The Eighth Amendment to the United States Constitution protects against imposing excessive bail, excessive fines, or cruel and unusual punishments. This amendment was adopted on December 15, 1791, along with the rest of the United States Bill of Rights. The amendment serves as a limitation upon the state or federal government to impose unduly harsh penalties on criminal defendants before and after a conviction. This limitation applies equally to the price for obtaining pretrial release and the punishment for crime after conviction. The phrases in this amendment originated in the English Bill of Rights of 1689.
Furman v. Georgia, 408 U.S. 238 (1972), was a landmark criminal case in which the United States Supreme Court invalidated all then existing legal constructions for the death penalty in the United States. It was a 5–4 decision, with each member of the majority writing a separate opinion. Following Furman, in order to reinstate the death penalty, states had to at least remove arbitrary and discriminatory effects in order to satisfy the Eighth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.
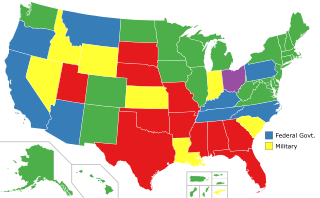
In the United States, capital punishment is a legal penalty throughout the country at the federal level, in 27 states, and in American Samoa. It is also a legal penalty for some military offenses. Capital punishment has been abolished in 23 states and in the federal capital, Washington, D.C. It is usually applied for only the most serious crimes, such as aggravated murder. Although it is a legal penalty in 27 states, 20 states have the ability to execute death sentences, with the other seven, as well as the federal government, being subject to different types of moratoriums. The existence of capital punishment in the United States can be traced to early colonial Virginia. Along with Japan, Singapore, and Taiwan, the United States is one of four advanced democracies and the only Western nation that applies the death penalty regularly. It is one of 54 countries worldwide applying it, and was the first to develop lethal injection as a method of execution, which has since been adopted by five other countries. The Philippines has since abolished executions, and Guatemala has done so for civil offenses, leaving the United States as one of four countries to still use this method. It is common practice for the condemned to be administered sedatives prior to execution, regardless of the method used.

Capital punishment is a legal punishment under the criminal justice system of the United States federal government. It is the most serious punishment that could be imposed under federal law. The serious crimes that warrant this punishment include treason, espionage, murder, large-scale drug trafficking, or attempted murder of a witness, juror, or court officer in certain cases.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in the U.S. state of Indiana. The last man executed in the state, excluding federal executions at Terre Haute, was the murderer Matthew Wrinkles in 2009.
Gregg v. Georgia, Proffitt v. Florida, Jurek v. Texas, Woodson v. North Carolina, and Roberts v. Louisiana, 428 U.S. 153 (1976), is a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court. It reaffirmed the Court's acceptance of the use of the death penalty in the United States, upholding, in particular, the death sentence imposed on Troy Leon Gregg. The set of cases is referred to by a leading scholar as the July 2 Cases, and elsewhere referred to by the lead case Gregg. The court set forth the two main features that capital sentencing procedures must employ in order to comply with the Eighth Amendment ban on "cruel and unusual punishments". The decision essentially ended the de facto moratorium on the death penalty imposed by the Court in its 1972 decision in Furman v. Georgia 408 U.S. 238 (1972).
Roper v. Simmons, 543 U.S. 551 (2005), is a landmark decision by the Supreme Court of the United States in which the Court held that it is unconstitutional to impose capital punishment for crimes committed while under the age of 18. The 5–4 decision overruled Stanford v. Kentucky, in which the court had upheld execution of offenders at or above age 16, and overturned statutes in 25 states.
The People of the State of California v. Robert Page Anderson, 493 P.2d 880, 6 Cal. 3d 628, was a landmark case in the state of California that outlawed capital punishment for nine months until the enactment of a constitutional amendment reinstating it, Proposition 17.
McCleskey v. Kemp, 481 U.S. 279 (1987), is a United States Supreme Court case, in which the death sentence of Warren McCleskey for armed robbery and murder was upheld. The Court said the "racially disproportionate impact" in the Georgia death penalty indicated by a comprehensive scientific study was not enough to mitigate a death penalty determination without showing a "racially discriminatory purpose." McCleskey has been described as the "most far-reaching post-Gregg challenge to capital sentencing."
Coker v. Georgia, 433 U.S. 584 (1977), held that the death penalty for rape of an adult woman was grossly disproportionate and excessive punishment, and therefore unconstitutional under the Eighth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution. A few states continued to have child rape statutes that authorized the death penalty. In Kennedy v. Louisiana (2008), the court expanded Coker, ruling that the death penalty is unconstitutional in all cases that do not involve intentional homicide or crimes against the State.
Aikens v. California, 406 U.S. 813 (1972), was a decision of the United States Supreme Court where a petitioner was appealing his conviction and death sentence. After oral argument had been made on the case, but before the court decided on it, the Supreme Court of California in People v. Anderson, declared the death penalty unconstitutional under the state constitution. This made his appeal unnecessary because the decision in Anderson
declared capital punishment in California unconstitutional under Art. 1, 6, of the state constitution... The California Supreme Court declared in the Anderson case that its decision was fully retroactive and stated that any prisoner currently under sentence of death could petition a superior court to modify its judgment. [Aikens] thus no longer faces a realistic threat of execution... [emphasis added]
Witherspoon v. Illinois, 391 U.S. 510 (1968), was a U.S. Supreme Court case where the court ruled that a state statute providing the state unlimited challenge for cause of jurors who might have any objection to the death penalty gave too much bias in favor of the prosecution.
Kennedy v. Louisiana, 554 U.S. 407 (2008), is a landmark decision by the Supreme Court of the United States which held that the Eighth Amendment's Cruel and Unusual Punishments Clause prohibits the imposition of the death penalty for a crime in which the victim did not die and the victim's death was not intended.
In the United States, life imprisonment is amongst the most severe punishments provided by law, depending on the state, and second only to the death penalty. According to a 2013 study, 1 of every 2,000 inhabitants of the U.S. were imprisoned for life as of 2012.
Capital punishment was abolished in Colorado in 2020. It was legal from 1974 until 2020 prior to it being abolished in all future cases.

William Henry Hance was an American serial killer and soldier who is believed to have murdered four women and molested 3 of the woman in and around military bases before his arrest in 1978. He was convicted of murdering three of them, and not brought to trial on the fourth. He was executed by the state of Georgia in the electric chair.

Luis José Monge was a convicted mass murderer who was executed in the gas chamber at Colorado State Penitentiary in 1967. Monge was the last inmate to be executed before an unofficial moratorium on execution that lasted for more than four years while most death penalty cases were on appeal, culminating in the U.S. Supreme Court decision in Furman v. Georgia in 1972, invalidating all existing death penalty statutes as written.
Capital punishment is currently a legal penalty in the U.S. state of Kansas, although it has not been used since 1965.
Montgomery v. Louisiana, 577 U.S. 190 (2016), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court held that its previous ruling in Miller v. Alabama (2012), that a mandatory life sentence without parole should not apply to persons convicted of murder committed as juveniles, should be applied retroactively. This decision potentially affects up to 2,300 cases nationwide.




