
Exmoor is loosely defined as an area of hilly open moorland in west Somerset and north Devon in South West England. It is named after the River Exe, the source of which is situated in the centre of the area, two miles north-west of Simonsbath. Exmoor is more precisely defined as the area of the former ancient royal hunting forest, also called Exmoor, which was officially surveyed 1815–1818 as 18,810 acres (7,610 ha) in extent. The moor has given its name to a National Park, which includes the Brendon Hills, the East Lyn Valley, the Vale of Porlock and 55 km (34 mi) of the Bristol Channel coast. The total area of the Exmoor National Park is 692.8 km2 (267.5 sq mi), of which 71% is in Somerset and 29% in Devon.

Dunkery Beacon at the summit of Dunkery Hill is the highest point on Exmoor and in Somerset, England. It is also the highest point in southern England outside of Dartmoor.

The Brendon Hills are a range of hills in west Somerset, England. The hills merge level into the eastern side of Exmoor and are included within the Exmoor National Park. The highest point of the range is Lype Hill at 1,388 feet (423 m) above sea level with a secondary summit several kilometres to the southeast at 1,350 feet (411 m). Both points are marked by Ordnance Survey trig points and are located within enclosed farmland. Early versions of the name include Brunedun and Brundon reflecting an original name of Bruna or Brune, meaning 'brown one'. Dun is a common Old English word for a fairly flat and extensive hill. This name is not connected with the village of Brendon in Devon, the name of which has a different origin.
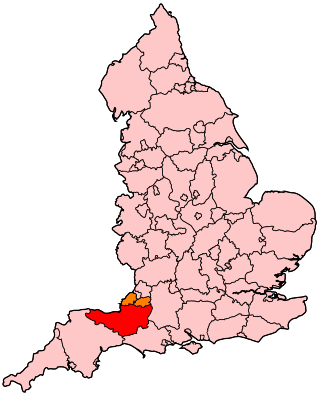
Somerset is a rural county in the southwest of England, covering 4,171 square kilometres (1,610 sq mi). It is bounded on the north-west by the Bristol Channel, on the north by Bristol and Gloucestershire, on the north-east by Wiltshire, on the south-east by Dorset, and on the south west and west by Devon. It has broad central plains with several ranges of low hills. The landscape divides into four main geological sections from the Silurian through the Devonian and Carboniferous to the Permian which influence the landscape, together with water-related features.

The River Heddon is a river in Devon, in the south of England. Running along the western edges of Exmoor, the river reaches the North Devon coast at Heddon's Mouth. The nearest road access to the beach is at Hunter's Inn, approximately 1.6-kilometre (1 mi) south of sea-fall. The named river flows for 8.8 kilometres (5.5 mi) and drains an area of 17.07 square kilometres (6.59 sq mi).

The mountains and hills of England comprise very different kinds of terrain, from a mountain range which reaches almost 1,000 metres high, to several smaller areas of lower mountains, foothills and sea cliffs. Most of the major upland areas have been designated as Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) or national parks. The highest and most extensive areas are in the north and west, while the midlands, south-east and east of the country tend to be low-lying.

Hoar Oak Water is a moorland tributary of the East Lyn River in Exmoor, Somerset, England.

Shoulsbury Castle is an Iron Age hill fort close to Challacombe in Devon, England. It takes the form of a multi-ditch and rampart enclosure close to the top of a hill on the shoulder of Shoulsbarrow Common at an elevation of 472 metres (1,549 ft) above sea level.
Voley Castle is an Iron Age hill fort situated close to Parracombe in north Devon, England. The fort is situated on a promontory on the eastern side of Heale Down, approximately 230 metres (750 ft) above sea level. It is close to another Iron Age hill fort at Beacon Castle. Voley Castle is a slight univallate hillfort, a rare type of hill fort found mainly in Devon, and is unusual for its type because it has an outer earthwork.

Roborough Castle is an Iron Age enclosure or hill fort situated close to Lynton in Devon, England. The fort is situated on the North East edge of a Hillside forming a promontory above a tributary to the East Lyn River known as Hoaroak Water at approx 320 Metres above Sea Level.

Bremridge Wood formerly part of the Domesday Book estate of Bremridge near South Molton, Devon, England, is the site of an Iron Age enclosure or hill fort. The earthwork is situated in woodland on a Hillside forming a promontory above the River Bray to the West of the Town at approx 175 Metres above Sea Level.
Myrtlebury is an Iron Age enclosure or 'spur' hill fort situated close to Lynmouth in Devon, England. The fort is effectively the north east of a hillside forming a spur or promontory above the steep valley of the East Lyn River to the east of the village, at approximately 150 metres above sea level.
The Macmillan Way West is a long-distance footpath in Somerset and Devon, England. It runs for 102 miles (164 km) from Castle Cary in Somerset to Barnstaple in Devon. It is one of the Macmillan Ways and connects with the main Macmillan Way at Castle Cary.
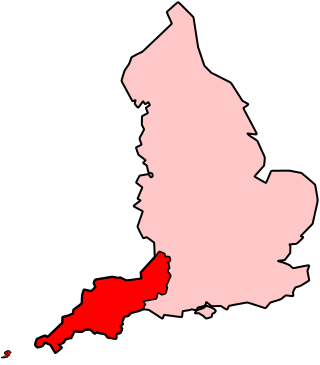
The climate of south-west England is classed as oceanic (Cfb) according to the Köppen climate classification. The oceanic climate is typified by frequent cloudy skies, cool winters with cool summers and precipitation all year round, with more experienced in winter. Annual rainfall is about 1,000 millimetres (39 in) and up to 2,000 millimetres (79 in) on higher ground. Exceptions include areas to the east of high ground ( e.g. Exeter / parts of West Somerset that are subject to a rain shadow effect and annual rainfall is closer to 30 inches.
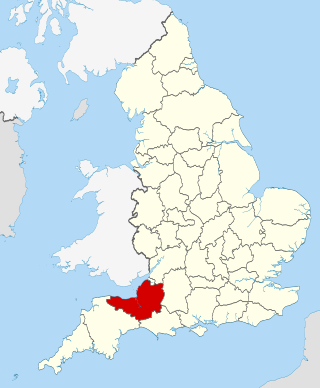
The county of Somerset is in South West England, bordered by the Bristol Channel and the counties of Bristol and Gloucestershire to the north, and Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south, and Devon to the west. The climate, influenced by its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean and the prevailing westerly winds, tends to be mild, damp and windy.

The Vale of Taunton and Quantock Fringes form a natural region in the southwest of England in the county of Somerset. Natural England have designated the Vale of Taunton and Quantock Fringes as National Character Area 146.

Haddon Hill is a prominent east–west aligned ridge in west Somerset, England, close to Hartford within the civil parish of Brompton Regis. It lies on the south-eastern fringe of Exmoor National Park though is separated from the Exmoor massif itself by the valleys of the rivers Haddeo and Exe The highest point of the ridge at OS grid reference SS 962286 is crowned by a trig point at 1,164 feet (355 m) above sea level. Much of the upper part of the hill is mapped as open access under the Countryside and Rights of Way Act 2000 and hence available for public access on foot. A couple of public footpaths traverse the hill north–south whilst numerous tracks run along its length. The larger part of the hill is within the national park, the boundary of which runs along the B3190 road which runs diagonally across the eastern end of the ridge en route from Watchet to Bampton. Vehicular access is available off this road. The hill affords views across Wimbleball Reservoir which occupies the Haddeo valley immediately to its north.

Countisbury is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Brendon and Countisbury, in the North Devon district, in the county of Devon, England. It is on Exmoor, roughly two miles east of Lynmouth along the A39. It has a church and pub. The National Trust owns the other buildings. In 2001 the parish had a population of 66.

Withypool Stone Circle, also known as Withypool Hill Stone Circle, is a stone circle located on the Exmoor moorland, near the village of Withypool in the southwestern English county of Somerset. The ring is part of a tradition of stone circle construction that spread throughout much of Britain, Ireland, and Brittany during the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, over a period between 3300 and 900 BCE. The purpose of such monuments is unknown, although archaeologists speculate that the stones represented supernatural entities for the circle's builders.
The geology of Exmoor National Park in south-west England contributes significantly to the character of Exmoor, a landscape which was designated as a national park in 1954. The bedrock of the area consists almost wholly of a suite of sedimentary rocks deposited during the Devonian, a period named for the English county of Devon in which the western half of the park sits. The eastern part lies within Somerset and it is within this part of the park that limited outcrops of Triassic and Jurassic age rocks are to be found.















