Berlin is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.6 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constituent states, Berlin is surrounded by the State of Brandenburg and contiguous with Potsdam, Brandenburg's capital. Berlin's urban area, which has a population of around 4.5 million, is the second most populous urban area in Germany after the Ruhr. The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's third-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr and Rhine-Main regions.

Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of 357,022 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi), with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr.
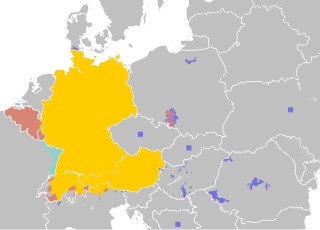
German is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a co-official language of Luxembourg and Belgium, as well as a national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France (Bas-Rhin), Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia and Hungary (Sopron).

The German Empire, also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Kaiserreich, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a republic.

East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic, was a country in Central Europe that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the country was a part of the Eastern Bloc in the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state". With the Potsdam Agreement on 1 August 1945, its territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II in Europe—the Soviet occupation zone, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR. Most scholars and academics describe the GDR as a totalitarian dictatorship.

The Holy Roman Empire since 1512 also the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation, was a political entity in Western, Central and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.

Nazi Germany was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a dictatorship. Under Hitler's rule, Germany quickly became a totalitarian state where nearly all aspects of life were controlled by the government. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", alluded to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which Hitler and the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945 after just 12 years when the Allies defeated Germany, ending World War II in Europe.

The Treaty of Versailles was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919 in the Palace of Versailles, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, which led to the war. The other Central Powers on the German side signed separate treaties. Although the armistice of 11 November 1918 ended the actual fighting, it took six months of Allied negotiations at the Paris Peace Conference to conclude the peace treaty. The treaty was registered by the Secretariat of the League of Nations on 21 October 1919.

World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries.

West Germany is the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 October 1990. During the Cold War, the western portion of Germany and the associated territory of West Berlin were parts of the Western Bloc. West Germany was formed as a political entity during the Allied occupation of Germany after World War II, established from eleven states formed in the three Allied zones of occupation/Trizone held by the United States, the United Kingdom, and France. The FRG's provisional capital was the city of Bonn, and the Cold War era country is retrospectively designated as the Bonn Republic.

The Weimar Republic, officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclaimed itself, as the German Republic. The state's informal name is derived from the city of Weimar, which hosted the constituent assembly that established its government. In English, the state was usually simply called "Germany", with "Weimar Republic" not commonly used until the 1930s.

Wilhelm II was the last German Emperor and King of Prussia, reigning from 15 June 1888 until his abdication on 9 November 1918. Despite strengthening the German Empire's position as a great power by building a powerful navy, his tactless public statements and erratic foreign policy greatly antagonized the international community and are considered by many to be one of the underlying causes of World War I. When the German war effort collapsed after a series of crushing defeats on the Western Front in 1918, he was forced to abdicate, thereby marking the end of the German Empire and the House of Hohenzollern's 300-year reign in Prussia and 500-year reign in Brandenburg.

The 2006 FIFA World Cup, also branded as Germany 2006, was the 18th FIFA World Cup, the quadrennial international association football world championship tournament. It was held from 9 June to 9 July 2006 in Germany, which had won the right to host the event in July 2000. Teams representing 198 national football associations from all six populated continents participated in the qualification process which began in September 2003. Thirty-one teams qualified from this process along with hosts Germany for the finals tournament. It was the second time that Germany staged the competition and the first as a unified country along with the former East Germany with Leipzig as a host city, and the 10th time that the tournament was held in Europe.

The Germany national football team represents Germany in men's international football and played its first match in 1908. The team is governed by the German Football Association, founded in 1900. Between 1949 and 1990, separate German national teams were recognised by FIFA due to Allied occupation and division: the DFB's team representing the Federal Republic of Germany, the Saarland team representing the Saar Protectorate (1950–1956) and the East Germany team representing the German Democratic Republic (1952–1990). The latter two were absorbed along with their records; the present team represents the reunified Federal Republic. The official name and code "Germany FR (FRG)" was shortened to "Germany (GER)" following reunification in 1990.

Prussia was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was de facto dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and de jure by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany.

Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of Führer und Reichskanzler in 1934. During his dictatorship, he initiated World War II in Europe by invading Poland on 1 September 1939. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust, the genocide of about six million Jews and millions of other victims.

World War I or the First World War, often abbreviated as WWI or WW1, and referred to by some Anglophone authors as the "Great War" or "War to End All Wars", was a global conflict which lasted from 1914 to 1918, and is considered one of the deadliest conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war.

The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; around two-thirds of Europe's Jewish population. The murders were carried out in pogroms and mass shootings; by a policy of extermination through labor in concentration camps; and in gas chambers and gas vans in German extermination camps, chiefly Auschwitz-Birkenau, Bełżec, Chełmno, Majdanek, Sobibór, and Treblinka in occupied Poland.

The Republic of Austria, commonly just Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and state. A landlocked country, Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of 83,871 km2 (32,383 sq mi) and has a population of 9 million.
Nazism, the common name in English for National Socialism, is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Nazi Germany. During Hitler's rise to power in 1930s Europe, it was frequently referred to as Hitlerism. The later related term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideas which formed after the Second World War.