Related Research Articles

Morrison County is a county in the U.S. state of Minnesota. As of the 2020 census, the population was 34,010. Its county seat is Little Falls. Camp Ripley Military Reservation occupies a significant area in north-central Morrison County.

Lac qui Parle County is a county in the southwestern part of the U.S. state of Minnesota. As of the 2020 census, the population was 6,719. Its county seat is Madison. The largest city in the county is Dawson.

The Wisconsin River is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. At approximately 430 miles long, it is the state's longest river. The river's name was first recorded in 1673 by Jacques Marquette as "Meskousing", which is rooted in the Algonquian languages used by the area's Native American tribes. The river's original meaning is obscure, but French explorers who followed in the wake of Marquette later modified the name to "Ouisconsin", and so it appears on Guillaume de L'Isle's map. This was simplified to "Wisconsin" in the early 19th century, before being applied to Wisconsin Territory and finally the state of Wisconsin.

The Assiniboine River is a 1,070-kilometre (660 mi) river that runs through the prairies of Western Canada in Saskatchewan and Manitoba. It is a tributary of the Red River. The Assiniboine is a typical meandering river with a single main channel embanked within a flat, shallow valley in some places and a steep valley in others. Its main tributaries are the Qu'Appelle, Souris, and Whitesand Rivers. For early history and exploration see Assiniboine River fur trade.

The Feather River is the principal tributary of the Sacramento River, in the Sacramento Valley of Northern California. The river's main stem is about 73 miles (117 km) long. Its length to its most distant headwater tributary is just over 210 miles (340 km). The main stem Feather River begins in Lake Oroville, where its four long tributary forks join—the South Fork, Middle Fork, North Fork, and West Branch Feather Rivers. These and other tributaries drain part of the northern Sierra Nevada, and the extreme southern Cascades, as well as a small portion of the Sacramento Valley. The total drainage basin is about 6,200 square miles (16,000 km2), with approximately 3,604 square miles (9,330 km2) above Lake Oroville.

The Little Don River also known as the Porter, is a tributary of the River Don in South Yorkshire, England. Arising on the Langsett Moors in the northern Peak District, the Little Don River feeds the Langsett and Underbank Reservoirs. It runs through the town of Stocksbridge before joining the River Don.
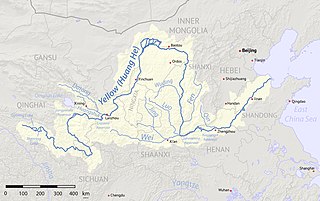
The Fen River drains the center of Shanxi Province, China. It originates in the Guancen Mountains of Ningwu County in northeast Shanxi, flows southeast into the basin of Taiyuan, and then south through the central valley of Shanxi before turning west to join the Yellow River west of Hejin. The Fen and the Wei Rivers are the two largest tributaries of the Yellow River. The river is 694 kilometers (431 mi) long and drains an area of 39,417 km2 (15,219 sq mi), 25.3% of Shanxi's area. The Fen River is the longest in Shanxi. It is also the second-longest tributary of the Yellow River. Within Taiyuan, the Fen runs from north to south; the prefecture includes one-seventh of the river's course.

The Iskar is a right tributary of the Danube. With a length of 368 km, it is the longest river that runs entirely within Bulgaria. Originating as three forks in Balkan's highest mountain range Rila, the Iskar flows in a northern direction until its confluence with the Danube. As it flows northwards it fuels the largest artificial lake in the country, the Iskar Reservoir, forms the divide between the Vitosha and Plana Mountains in the west and the Sredna Gora mountain range in the east before entering the Sofia Valley, which contains the nation's capital Sofia. From there the Iskar runs through the Balkan Mountains, forming the spectacular 84 km long Iskar Gorge. As it crosses the mountains, its water course turns in a north-eastern direction at Lakatnik. North of the Balkan Mountains, the river crosses the Danubian Plain and finally flows into the Danube between the villages of Baykal and Gigen. Geologically, Iskar is the oldest river in the Balkan Peninsula.

Big Wapwallopen Creek is a tributary of the Susquehanna River in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is approximately 23 miles (37 km) long and flows through Bear Creek Township, Fairview Township, Rice Township, Wright Township, Dorrance Township, Hollenback Township, Nescopeck Township, and Conyngham Township. The watershed of the creek has an area of 53.2 square miles (138 km2). The creek has three named tributaries: Balliet Run, Watering Run, and Bow Creek. The creek is designated as a Coldwater Fishery and a Migratory Fishery and is also Class A Wild Trout Waters for part of its length. However, a portion is considered to be impaired by organic enrichment and/or low levels of dissolved oxygen and its pH ranges from moderately acidic to slightly alkaline.
The Croton Falls Reservoir is a reservoir in the New York City water supply system in the Putnam County, New York townships of Carmel, and Southeast, roughly 50 miles (80 km) north of New York City. Part of the system's Croton Watershed, it was formed by impounding the West Branch and Middle Branch of the Croton River, tributaries of the Croton River, which flows into the Hudson River.

Black Creek is a long source tributary of Nescopeck Creek so part of the Susquehanna River drainage basin. It is also the second & longer stream of the same name recognized by the USGS GNIS system in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, in the United States—compared to the Black Creek beyond the ridgeline of the drainage divide, so in the Lehigh River valley and Carbon County. The headwaters of both Black Creeks in Luzerne county are only a few miles apart, and both valleys were traversed by the Lausanne-Nescopeck Turnpike in the first half of the 19th-century.

The Tomahawk River is a river in the U.S. state of Wisconsin.

Pelican Lake is a 3,585-acre (14.51 km2) lake located in Oneida County in Wisconsin. It has a maximum depth of 39 ft (12 m). Visitors have access to the lake from five public boat landings. A dam is located on the lake's primary outlet, which feeds into the Pelican River. Pelican Lake serves as one of 21 reservoirs used to regulate and maintain optimal water flow on the Wisconsin and Tomahawk rivers, the process of which is facilitated in part by the Wisconsin Valley Improvement Company.

Glen Brook is a tributary of East Branch Briar Creek in Luzerne County and Columbia County, in Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is approximately 4.7 miles (7.6 km) long and flows through Salem Township in Luzerne County and Briar Creek Township and Berwick in Columbia County. Its watershed has an area of 4.96 square miles (12.8 km2). A number of dams and reservoirs have been built on the creek and two major bridges cross it. The stream lies over mudstone, siltstone, limestone, sandstone and shale.
The Willow Reservoir or Willow Flowage is an artificial lake in Oneida County, Wisconsin formed by a dam on the Tomahawk River. The dam and reservoir level are controlled by the Wisconsin Valley Improvement Company as part of regulating the overall flow of the upper Wisconsin River. When full, Willow Reservoir has a surface area of 6306 acres.

The Jersey City Flowage is an artificial lake on the Tomahawk River, located about one mile above the confluence with the Wisconsin River in Tomahawk, Wisconsin. The dam and the flow are controlled by the Wisconsin Valley Improvement Company. The dam was originally built in 1910 to provide power for a tannery. Jersey City Flowage is a 423 acre lake located in Lincoln County. It has a maximum depth of 20 feet.

Spring Brook is a tributary of the Lackawanna River in Lackawanna County and Luzerne County, in Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is approximately 17 miles (27 km) long and flows through Covington Township, Spring Brook Township, and Moosic in Lackawanna County and Pittston Township in Luzerne County. The watershed of the stream has an area of 57.2 square miles (148 km2). It is designated as a High-Quality Coldwater Fishery and a Migratory Fishery above Interstate 476 and as a Coldwater Fishery and a Migratory Fishery below it. A section is also designated as Class A Wild Trout Waters. The stream's tributaries include Panther Creek, Plank Bridge Creek, Rattlesnake Creek, Green Run, Monument Creek, and Covey Swamp Creek. It has a relatively high level of water quality and is very slightly acidic, with a pH of 6.4 to 6.9.
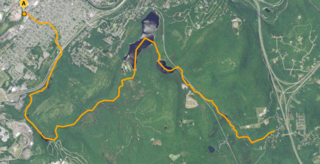
Stafford Meadow Brook is a tributary of the Lackawanna River in Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is approximately 11.2 miles (18.0 km) long and flows through Roaring Brook Township, Scranton, and Moosic. The watershed of the stream has an area of 14.1 square miles (37 km2). Part of it is designated as a High-Quality Coldwater Fishery and a Migratory Fishery. The other part is a Warmwater Fishery and a Migratory Fishery. The stream has one named tributary, which is known as Mountain Lake Run. Stafford Meadow Brook has a very high level of water quality for much of its length and part of it meets the criteria for an Exceptional Value designation. The stream begins on the Pocono Plateau and flows through the Moosic Mountains in a mountainous watershed. Its channel has been substantially altered in its lower reaches.

Roaring Brook is a tributary of the Lackawanna River in Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is approximately 21 miles (34 km) long and flows through Covington Township, Madison Township, Moscow, Roaring Brook Township, Elmhurst Township, Dunmore, and Scranton. The watershed of the stream has an area of 56.3 square miles (146 km2). Its named tributaries include Little Roaring Brook, Rock Bottom Creek, White Oak Run, Van Brunt Creek, Bear Brook, and East Branch Roaring Brook. It has a high level of water quality for much of its length. However, it is affected by abandoned mining land, stormwater, and other impacts in its lower reaches. Reservoirs in the watershed include the Hollister Reservoir, the Elmhurst Reservoir, and others. The stream also flows through the Nay Aug Gorge and passes over the Nay Aug Falls, which are on the National Register of Geologic Landmarks. It flows through a concrete channel in its lower reaches. The topography of the watershed contains rolling hills in its upper reaches and the mountainous land of the Moosic Mountains in its lower reaches.

Leggetts Creek is a tributary of the Lackawanna River in Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is approximately 9.0 miles (14.5 km) long and flows through Scott Township, South Abington Township, and Scranton. The watershed of the creek has an area of 18.5 square miles (48 km2). The creek has three named tributaries: Leach Creek, Clover Hill Creek, and Summit Lake Creek. Leggetts Creek is considered to be impaired due to urban development problems, but is not affected by acid mine drainage. The creek is fairly alkaline and is a perennial stream. Its headwaters are in wetlands outside of the Lackawanna Valley and it flows through a water gap known as Leggetts Gap or The Notch. Major lakes in the watershed include the Griffin Reservoir, Summit Lake, and Maple Lake. The creek is a source of flooding in South Abington Township.
References
- ↑ "Wisconsin Valley Improvement Company". Wisconsin Valley Improvement Company web site. Archived from the original on May 17, 2024. Retrieved September 13, 2014.
- ↑ "Wisconsin River Power Company". Archived from the original on September 13, 2014. Retrieved September 13, 2014.
- ↑ "Expera Specialty Solutions". Archived from the original on September 13, 2014. Retrieved September 13, 2014.
- ↑ Wisconsin Statutes 182.70(2)(a).
- ↑ Wisconsin Statutes 182.70(3)(a)1.
- ↑ Durbin, Richard (1997). The Wisconsin River: And Odyssey Through Time and Space. Cross Plains, Wisconsin: Spring Freshet Press. pp. 8–9. ISBN 0-9658559-0-2.