
The Cotswolds is a region in central-southwest England, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper Thames to an escarpment above the Severn Valley and Evesham Vale.

Gloucestershire is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.

The Battle of Deorham is claimed as a decisive military encounter between the West Saxons and the Britons of the West Country in 577. The battle, which was a major victory for Wessex's forces led by Ceawlin and his son, Cuthwine, resulted in the capture of the Brythonic cities of Glevum (Gloucester), Corinium Dobunnorum (Cirencester), and Aquae Sulis (Bath). It also led to the permanent cultural and ethnic separation of Dumnonia from Wales.

Cirencester is a market town in Gloucestershire, England, 80 miles (130 km) west of London. Cirencester lies on the River Churn, a tributary of the River Thames, and is the largest town in the Cotswolds. It is the home of the Royal Agricultural University, the oldest agricultural college in the English-speaking world, founded in 1840. The town had a population of 20,229 in 2021.

Chedworth is a village and civil parish in Gloucestershire, southwest England, in the Cotswolds. It is known as the location of Chedworth Roman Villa, administered since 1924 by the National Trust.
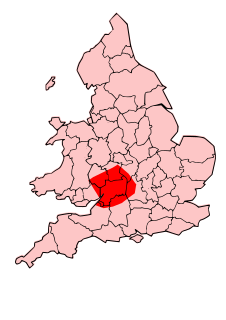
The Dobunni were one of the Iron Age tribes living in the British Isles prior to the Roman conquest of Britain. There are seven known references to the tribe in Roman histories and inscriptions.

The region now known as Gloucestershire was originally inhabited by Brythonic peoples in the Iron Age and Roman periods. After the Romans left Britain in the early 5th century, the Brythons re-established control but the territorial divisions for the post-Roman period are uncertain. The city of Caerloyw was one centre and Cirencester may have continued as a tribal centre as well. The only reliably attested kingdom is the minor south-east Wales kingdom of Ergyng, which may have included a portion of the area. In the final quarter of the 6th century, the Saxons of Wessex began to establish control over the area.

Bibury is a village and civil parish in Gloucestershire, England. It is on the River Coln, a Thames tributary that rises in the same (Cotswold) District. The village centre is 6+1⁄2 miles northeast of Cirencester. Arlington Row is a nationally notable architectural conservation area depicted on the inside cover of all British passports. It is a major destination for tourists visiting the traditional rural villages, tea houses and many historic buildings of the Cotswold District; it is one of six places in the country featured in Mini-Europe, Brussels.

Kemble is a village in the civil parish of Kemble and Ewen, in the Cotswold district of Gloucestershire, England. Historically part of Wiltshire, it lies 4 miles (6.4 km) from Cirencester and is the settlement closest to Thames Head, the source of the River Thames. In 2020 it had an estimated population of 940. At the 2011 census the parish had a population of 1,036.

Charlton Kings is a contiguous village adjoining Cheltenham in Gloucestershire, England. The area constitutes a civil parish of 10,396 residents (2011).

Barnsley is a village and civil parish in the Cotswold district of Gloucestershire, England, 3.7 miles (6.0 km) northeast of Cirencester. It is 125 kilometres (78 mi) (geodesically) west of London.

Coln Rogers is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Coln St. Dennis, in the Cotswold district of the county of Gloucestershire, England. In 1931 the parish had a population of 95.

Daglingworth is a Gloucestershire village in the valley of the River Dunt, near the A417 road connecting Gloucester and Cirencester. As with many smaller villages in the Cotswolds, most of the buildings are now private houses. Other properties are the church, the village hall, a stable & horse riding centre and Bridge Farm. The Church of the Holy Rood in the village is an Anglo-Saxon church with well-preserved stone carvings, including an Anglo-Saxon crucifixion tablet dating to 1015. There is also a canonical sundial on the south wall.
Cirencester Abbey or St Mary's Abbey, Cirencester in Gloucestershire was founded as an Augustinian monastery in 1117 on the site of an earlier church, the oldest-known Saxon church in England, which had itself been built on the site of a Roman structure. The church was greatly enlarged in the 14th century with addition of an ambulatory to the east end. The abbot became mitred 1416. The monastery was suppressed in 1539 and presented to Roger Bassinge.

Siddington is a village and civil parish in Gloucestershire, England. It is located immediately south of Cirencester. At the 2011 United Kingdom Census, the parish had a population of 1,249.

The Church of St. John Baptist, Cirencester is a parish church in the Church of England in Cirencester, Gloucestershire, England. It is a Grade I listed building.

Coates is a village and civil parish situated in Cotswold District,Gloucestershire, England. It is around 3 miles (4.8 km) west of Cirencester and close to Cirencester Park, part of the Bathurst Estate. It is the nearest village to the source of the river Thames at Thames Head, and it is close to the course of the Foss Way or Fosse Way, the ancient Roman road. The nearest railway station is Kemble. The village population taken at the 2011 census was 507.
An Anglo-Saxon multiple estate was a large landholding controlled from a central location with surrounding subsidiary settlements. These estates were present in the early Anglo-Saxon period, but fragmented into smaller units in the late Anglo-Saxon period. Despite some academic criticism, the concept has been widely used and a large number of possible examples have been proposed.

Elkstone is a village and civil parish in the English county of Gloucestershire. In the 2001 United Kingdom census, the parish had a population of 203, increasing to 248 at the 2011 census

Colesbourne is a village and civil parish in the Cotswold district of Gloucestershire, England. The village and parish lies within the Cotswolds, a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.


















