
Lowell is a village in Washington County, Ohio, United States, along the Muskingum River. The population was 549 at the 2020 census. The village is located about 7.6 miles (12.2 km) north of Marietta, Ohio.

The Muskingum River is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately 111 miles (179 km) long, in southeastern Ohio in the United States. An important commercial route in the 19th century, it flows generally southward through the eastern hill country of Ohio. Via the Ohio, it is part of the Mississippi River watershed. The river is navigable for much of its length through a series of locks and dams.

The Little Muskingum River is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately 65 mi (105 km) long, in southeast Ohio in the United States.
Fleming is a small unincorporated community in rural eastern Barlow Township, Washington County, Ohio, United States.

The Big South Fork of the Cumberland River is a 76-mile-long (122 km) river in the U.S. states of Tennessee and Kentucky. It is a major drainage feature of the Cumberland Plateau, a major tributary of the Cumberland River system, and the major feature of the Big South Fork National River and Recreation Area.

The Licking River is a tributary of the Muskingum River, about 40 mi (65 km) long, in central Ohio in the United States. Via the Muskingum and Ohio Rivers, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River.

Wills Creek is a tributary of the Muskingum River, 92.2 mi (148.4 km) long, in eastern Ohio in the United States. Via the Muskingum and Ohio Rivers, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River. It drains an area of 853 mi2 (2,209 km2).

Moxahala Creek is a tributary of the Muskingum River, 29.2 miles (47.0 km) long, in southeastern Ohio in the United States. Via the Muskingum and Ohio Rivers, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River, draining an area of 301 square miles (780 km2)

Wakatomika Creek is a tributary of the Muskingum River, 42.6 mi (68.6 km) long, in central Ohio in the United States. Via the Muskingum and Ohio Rivers, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River, draining an area of 234 mi² (606 km²)
Little Wakatomika Creek is a stream which flows through Coshocton and Muskingum counties in Ohio, US. The stream originates north of Tunnel Hill in Coshocton County and flows south through the villages of Tunnel Hill and Wakatomika before entering Muskingum County. Here, it empties into Wakatomika Creek just west of the village of Trinway, near the intersection of State Routes 60 and 16. The stream is part of the Mississippi River catchment via Wakatomika Creek, the Muskingum River and the Ohio River.

Beargrass Creek is the name given to several forks of a creek in Jefferson County, Kentucky. The Beargrass Creek watershed is one of the largest in the county, draining over 60 square miles (160 km2). It is fairly small, with an average discharge of 103 cubic feet per second at River Road in Louisville.

The Mohican River is a principal tributary of the Walhonding River, about 40 miles (64 km) long, in north-central Ohio in the United States. Via the Walhonding, Muskingum and Ohio Rivers, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River, draining an area of 999 square miles (2,590 km2).

The Clear Fork is a principal tributary of the Mohican River, 36.6 miles (58.9 km) long, in north central Ohio in the United States. Via the Mohican, Walhonding, Muskingum and Ohio Rivers, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River, draining an area of 219 square miles (570 km2). According to the Geographic Names Information System, it has also been known historically as "Clear Creek" and as "Clear Fork Mohecan Creek".

Bartlett is an unincorporated community in southwestern Wesley Township, Washington County, Ohio, United States. It has a post office with the ZIP code 45713. It sits at the intersection of State Routes 550 and 555 near Coal Run, a subsidiary of Wolf Creek, which meets the Muskingum River at Waterford to the north. Near Bartlett is located the Shinn Covered Bridge, which spans Wolf Creek.

Barlow is an unincorporated community in western Barlow Township, Washington County, Ohio, United States. Although it is unincorporated, it has a ZIP code 45712. It lies at the intersection of State Routes 339 and 550 near the South Fork of Wolf Creek, which meets the Muskingum River at Waterford to the north.
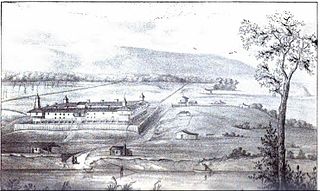
Campus Martius was a defensive fortification at the Marietta, Ohio settlement, and was home to Rufus Putnam, Benjamin Tupper, Arthur St. Clair, and other pioneers from the Ohio Company of Associates during the Northwest Indian War. Major Anselm Tupper was commander of the Campus Martius during the war. Construction began in 1788 and was fully completed in 1791. The Campus Martius was located on the east side of the Muskingum River, and upriver from its confluence with the Ohio River. A firsthand description of the fort is provided in Hildreth's Pioneer History,
Campus Martius is the handsomest pile of buildings on this side of the Alleghany mountains, and in a few days will be the strongest fortification in the territory of the United States. It stands on the margin of the elevated plain on which are the remains of the ancient works [mounds], mentioned in my letter of May last, thirty feet above the high bank of the Muskingum, twenty-nine perches distant from the river, and two hundred and seventy-six from the Ohio. It consists of a regular square, having a block house at each angle, eighteen feet square on the ground, and two stories high; the upper story on the outside or face, jutting over the lower one, eighteen inches. These block houses serve as bastions to a regular fortification of four sides. The curtains are composed of dwelling houses two stories high, eighteen feet wide, and of different lengths.

Picketed Point Stockade was the last of three fortifications built at Marietta, Ohio. This defensive stockade was built by pioneers during the Northwest Indian War in 1791 on the east side of the mouth of the Muskingum River at its confluence with the Ohio River, and directly across the Muskingum from Fort Harmar. Colonel William Stacy superintended the construction of the stockade under direction of Colonel Ebenezer Sproat. Palisades or pickets were set from the Muskingum River eastward, meeting in the northeast corner of the fortification with another line of pickets built from the Ohio River northward, enclosing about four acres.
Three block houses were immediately built: one on the Muskingum bank, at the western termination of the pickets; one in the northeast corner of the inclosure; and one on the Ohio bank. Near to the latter, and by that on the Muskingum, were strong gates, of a size to admit teams, the approaches to which were commanded by the block houses. These block houses were surmounted by sentry boxes, or turrets, the sides of which were secured with thick planks for the defense of the men when on guard.

Conotton Creek is a tributary of the Tuscarawas River, 38.7 miles (62.3 km) long, in eastern Ohio in the United States. Via the Tuscarawas, Muskingum and Ohio Rivers, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River, draining an area of 286 square miles (741 km²) in Carroll, Harrison and Tuscarawas County, Ohio. The source is at 1240 feet and the mouth is at 874 feet. Dover Dam, downstream on the Tuscarawas river, is normally dry, but can impound a reservoir on Conotton and tributaries to a pool elevation of 916 feet for downstream flood control by the Corps of Engineers. From its source in eastern Harrison County, Ohio the creek flows west northwest through Jewitt, Scio, Conotton, Bowerston, Leesville, Sherrodsville, New Cumberland and Somerdale before reaching its mouth in central Tuscarawas County, Ohio. The Wheeling and Lake Erie Railway is situated in the valley. Ohio State Route 151 runs in the valley from near the source to Bowerston. Ohio State Route 212 run along the valley from Bowerston to the mouth. The Conotton Creek Trail runs from Bowerston to Jewett.
Archers Fork is a stream located entirely within Washington County, Ohio. It is a tributary of the Little Muskingum River, which it enters near the community of Dart.
















