Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related to information retrieval, knowledge representation and computational linguistics, a subfield of linguistics. Typically data is collected in text corpora, using either rule-based, statistical or neural-based approaches in machine learning and deep learning.
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also known as automatic speech recognition (ASR), computer speech recognition or speech-to-text (STT). It incorporates knowledge and research in the computer science, linguistics and computer engineering fields. The reverse process is speech synthesis.
In digital transmission, the number of bit errors is the number of received bits of a data stream over a communication channel that have been altered due to noise, interference, distortion or bit synchronization errors.

In information theory, linguistics, and computer science, the Levenshtein distance is a string metric for measuring the difference between two sequences. The Levenshtein distance between two words is the minimum number of single-character edits required to change one word into the other. It is named after Soviet mathematician Vladimir Levenshtein, who defined the metric in 1965.
In computational linguistics and computer science, edit distance is a string metric, i.e. a way of quantifying how dissimilar two strings are to one another, that is measured by counting the minimum number of operations required to transform one string into the other. Edit distances find applications in natural language processing, where automatic spelling correction can determine candidate corrections for a misspelled word by selecting words from a dictionary that have a low distance to the word in question. In bioinformatics, it can be used to quantify the similarity of DNA sequences, which can be viewed as strings of the letters A, C, G and T.

Typing is the process of writing or inputting text by pressing keys on a typewriter, computer keyboard, mobile phone, or calculator. It can be distinguished from other means of text input, such as handwriting and speech recognition. Text can be in the form of letters, numbers and other symbols. The world's first typist was Lillian Sholes from Wisconsin in the United States, the daughter of Christopher Sholes, who invented the first practical typewriter.
Peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) is an engineering term for the ratio between the maximum possible power of a signal and the power of corrupting noise that affects the fidelity of its representation. Because many signals have a very wide dynamic range, PSNR is usually expressed as a logarithmic quantity using the decibel scale.
In statistics, the k-nearest neighbors algorithm (k-NN) is a non-parametric supervised learning method. It was first developed by Evelyn Fix and Joseph Hodges in 1951, and later expanded by Thomas Cover. Most often, it is used for classification, as a k-NN classifier, the output of which is a class membership. An object is classified by a plurality vote of its neighbors, with the object being assigned to the class most common among its k nearest neighbors (k is a positive integer, typically small). If k = 1, then the object is simply assigned to the class of that single nearest neighbor.
Speech analytics is the process of analyzing recorded calls to gather customer information to improve communication and future interaction. The process is primarily used by customer contact centers to extract information buried in client interactions with an enterprise. Although speech analytics includes elements of automatic speech recognition, it is known for analyzing the topic being discussed, which is weighed against the emotional character of the speech and the amount and locations of speech versus non-speech during the interaction. Speech analytics in contact centers can be used to mine recorded customer interactions to surface the intelligence essential for building effective cost containment and customer service strategies. The technology can pinpoint cost drivers, trend analysis, identify strengths and weaknesses with processes and products, and help understand how the marketplace perceives offerings.
In information theory and computer science, the Damerau–Levenshtein distance is a string metric for measuring the edit distance between two sequences. Informally, the Damerau–Levenshtein distance between two words is the minimum number of operations required to change one word into the other.
BLEU is an algorithm for evaluating the quality of text which has been machine-translated from one natural language to another. Quality is considered to be the correspondence between a machine's output and that of a human: "the closer a machine translation is to a professional human translation, the better it is" – this is the central idea behind BLEU. Invented at IBM in 2001, BLEU was one of the first metrics to claim a high correlation with human judgements of quality, and remains one of the most popular automated and inexpensive metrics.

In statistical analysis of binary classification and information retrieval systems, the F-score or F-measure is a measure of predictive performance. It is calculated from the precision and recall of the test, where the precision is the number of true positive results divided by the number of all samples predicted to be positive, including those not identified correctly, and the recall is the number of true positive results divided by the number of all samples that should have been identified as positive. Precision is also known as positive predictive value, and recall is also known as sensitivity in diagnostic binary classification.
In information theory, perplexity is a measure of uncertainty in the value of a sample from a discrete probability distribution. The larger the perplexity, the less likely it is that an observer can guess the value which will be drawn from the distribution. Perplexity was originally introduced in 1977 in the context of speech recognition by Frederick Jelinek, Robert Leroy Mercer, Lalit R. Bahl, and James K. Baker.
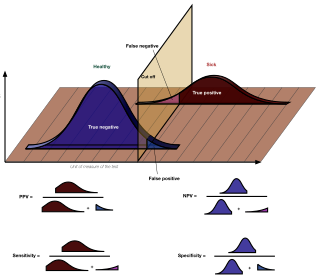
In medicine and statistics, sensitivity and specificity mathematically describe the accuracy of a test that reports the presence or absence of a medical condition. If individuals who have the condition are considered "positive" and those who do not are considered "negative", then sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives:
In computer science and statistics, the Jaro–Winkler similarity is a string metric measuring an edit distance between two sequences. It is a variant of the Jaro distance metric proposed in 1990 by William E. Winkler.

In pattern recognition, information retrieval, object detection and classification, precision and recall are performance metrics that apply to data retrieved from a collection, corpus or sample space.
In finance, the T-model is a formula that states the returns earned by holders of a company's stock in terms of accounting variables obtainable from its financial statements. The T-model connects fundamentals with investment return, allowing an analyst to make projections of financial performance and turn those projections into a required return that can be used in investment selection.
In statistics, the phi coefficient is a measure of association for two binary variables.
The NER model is one of a number of methods for determining the accuracy of live subtitles in television broadcasts and events that are produced using speech recognition. The three letters stand for number, edition error and recognition error. It is an alternative to the WER model used in several countries.
P4 metric (also known as FS or Symmetric F ) enables performance evaluation of the binary classifier. It is calculated from precision, recall, specificity and NPV (negative predictive value). P4 is designed in similar way to F1 metric, however addressing the criticisms leveled against F1. It may be perceived as its extension.






