Related Research Articles

The Group of Eight (G8) was an inter-governmental political forum from 1997 until 2014. It had formed from incorporating Russia into the Group of Seven, or G7, and returned to its previous name after Russia was expelled in 2014.

Interfaith dialogue refers to cooperative, constructive, and positive interaction between people of different religious traditions and/or spiritual or humanistic beliefs, at both the individual and institutional levels.

The Group of Seven (G7) is an intergovernmental political forum consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States; additionally, the European Union (EU) is a "non-enumerated member". It is organized around shared values of pluralism, liberal democracy, and representative government. As of 2020, G7 members are the major IMF advanced economies and account for over half of global net wealth, 30 to 43 percent of global gross domestic product, and 10 percent of the world's population. Its members maintain mutually close political, economic, diplomatic, and military relations in global affairs.

The Canadian Council of Churches is a broad and inclusive ecumenical body, now representing 26 member churches including Anglican; Eastern and Roman Catholic; Evangelical; Free Church; Eastern and Oriental Orthodox; and Historic Protestant traditions. Together these member churches represent 13,500 worshiping communities and comprise 85% of the Christians in Canada.

The G20 or Group of 20 is an intergovernmental forum comprising 19 sovereign countries, the European Union (EU), and the African Union (AU). It works to address major issues related to the global economy, such as international financial stability, climate change mitigation and sustainable development.

John James Kirton is professor emeritus of political science and the director and founder of the G7 Research Group, director and founder of the G20 Research Group, founder and co-director of the Global Health Diplomacy Program, and founder and co-founder of the BRICS Research Group, based at University of Trinity College in the University of Toronto.
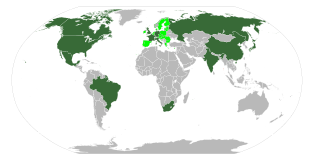
The Group of Eight + Five (G8+5) was an international group that consisted of the leaders of the heads of government from the G8 nations, plus the heads of government of the five leading emerging economies. In March 2014, Russia was cast out of the Group of 8 due to its involvement in the 2014 Crimea crisis in Ukraine, so the G8+5 in its original form is unlikely to reconvene with Russia present.

Yehuda Stolov, an Israeli, is a founder and the executive director of the Interfaith Encounter Association (IEA). He currently resides in Jerusalem with his wife, Lia and his three kids.

The 35th G8 summit was held in L'Aquila, Abruzzo, Italy, on 8–10 July 2009. It was originally to be held at Sardinian seaside city of La Maddalena, but it was moved to L'Aquila as part of an attempt to redistribute disaster funds after the devastating earthquake that April.

The 36th G8 summit was held in Muskoka, Ontario, Canada, on June 25–26, 2010. In this year's meeting, the G8 leaders agreed in reaffirming the group's essential and continuing role in international affairs and "assertions of new-found relevance". The form and function of the G8 was reevaluated as the G20 summits evolved into the premier forum for discussing, planning and monitoring international economic cooperation.

The 37th G8 summit was held on 26–27 May 2011 in Deauville, France.

The 2011 G20 Cannes Summit was the sixth meeting of the G20 heads of government/heads of state in a series of on-going discussions about financial markets and the world economy.

The 2012 G20 Los Cabos Summit was the seventh meeting of the G20 heads of government/heads of state.
The Canadian Centre For Ecumenism (CCE) is a non-profit organization whose main focus is interfaith dialogues and is established in Montreal, Québec, Canada. The centre is supported by the Canadian Conference of Catholic Bishops. It promotes conversations, interfaith dialogues and ecumenical dialogues.

The 41st G7 summit was held in Schloss Elmau, Krün, Bavaria, Germany on 7–8 June 2015. In March 2014 the remaining members of the G8 declared that a meaningful discussion was currently not possible with Russia, and since then meetings have continued under the G7 name.

Yoshinobu Miyake is a Japanese Shinto priest and scholar. Rev. Miyake was appointed the Superior General of Konko Church of Izuo in 2006 and appointed chair of the Board of International Shinto Studies Association in 2013.

Sayyid Ibraheem Khaleel Al Bukhari is founder and chairman of Ma'din Academy and adviser of World Interfaith Harmony Week. He is a sunni Islamic scholar, Joint Secretary of Samastha Kerala Jamiyyathul Ulama, General Secretary of Kerala Muslim Jamaat, a body of various Muslim organisations in Kerala and he is listed in The Muslim 500.

The Millennium Peace Summit of Religious and Spiritual Leaders was held in New York City between August 28–31, 2000. The meeting recognized the importance of religion to world peace and faith leaders’ commitment to peacekeeping, poverty relief, and environmental conservation. It preceded the Millennium Summit, which commemorated the 50th anniversary of the United Nations (UN).

Interfaith studies, or Interreligious studies, is a new and primarily evidence-based education interdisciplinary academic discipline that uses scientific methods to access social sciences and humanities in the development of rule of law nonviolence humanitarian aid social services cultural diplomacy, mainly through policymaking, multi-religious literacy, and interfaith education, always aiming at the common good in interpersonal relationships and communities organizing.