
The Gengshi Emperor, born Liu Xuan, was an emperor of the Han dynasty that had been restored following the downfall of Wang Mang's short-lived Xin dynasty. He was also known by his courtesy name Shenggong and as the King or Prince of Huaiyang, a posthumous title bestowed upon him by Emperor Guangwu of the Eastern Han. The Gengshi Emperor was viewed as a weak and incompetent ruler, who briefly ruled over an empire willing to let him rule over them, but was unable to keep that empire together. He was eventually deposed by the Red Eyebrows and strangled a few months after his defeat.

Emperor Guangwu of Han, born Liu Xiu (劉秀), courtesy name Wenshu (文叔), was a Chinese monarch. He served as an emperor of the Han dynasty by restoring the dynasty in AD 25, thus founding the Eastern Han dynasty. He ruled over parts of China at first since his dynasty was formed through rebellion against the short-lived Xin dynasty, and through suppression and conquest of regional warlords, the whole of China proper was consolidated by the time of his death in AD 57. During his reign, Taoism was made the official religion of China, and the Chinese folk religion began to decline.
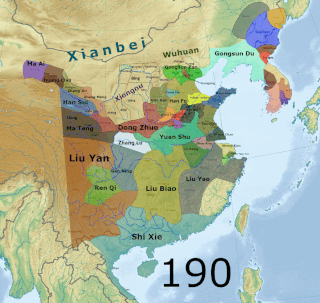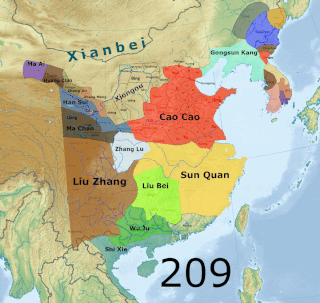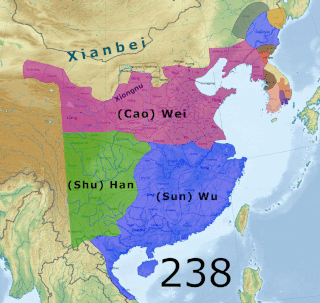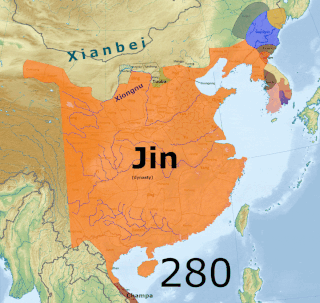
The military history of the Three Kingdoms period encompasses roughly a century's worth of prolonged warfare and disorder in Chinese history. After the assassination of General-in-chief He Jin in September 189, the administrative structures of the Han government became increasingly irrelevant. By the time of death of Cao Cao, the most successful warlord of North China, in 220, the Han empire was divided between the three rival states of Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu. Due to the ensuing turmoil, the competing powers of the Three Kingdoms era found no shortage of willing recruits for their armies, although press-ganging as well as forcible enlistment of prisoners from defeated armies still occurred. Following four centuries of rule under the Han dynasty, the Three Kingdoms brought about a new era of conflict in China that shifted institutions in favor of a more permanent and selective system of military recruitment. This ultimately included the creation of a hereditary military class as well as increasing reliance on non-Chinese cavalry forces and the end of universal conscription.

Lulin was one of two major agrarian rebellion movements against Wang Mang's short-lived Xin dynasty in the modern southern Henan and northern Hubei regions. These two regions banded together to pool their strengths, their collective strength eventually leading to the downfall of the Xin and a temporary reinstatement of the Han dynasty with Liu Xuan as the emperor.

The Red Eyebrows was one of the two major peasant rebellion movements against Wang Mang's short-lived Xin dynasty, the other being Lülin. It was so named because the rebels painted their eyebrows red.
Liu Penzi was a puppet emperor placed on the Han dynasty throne temporarily by the Red Eyebrows (Chimei) rebels after the collapse of the Xin dynasty, from 25 to 27 AD. Liu Penzi and his two brothers were forced into the Red Eyebrows as child soldiers. When the Red Eyebrows submitted to the new Gengshi Emperor, his older brother Liu Gong fled to support the new emperor. Later, the Red Eyebrows rose again in rebellion and chose Liu Penzi as emperor. When they took Chang'an, Liu Penzi was officially Emperor of China, but he never had actual powers. When Liu Xiu definitively defeated the Red Eyebrows, he spared the 17-year-old puppet emperor.
Guo Shengtong was an empress during the Eastern Han dynasty. She was the second wife and first empress of Emperor Guangwu, the founder of Eastern Han. She eventually lost her husband's favor and was deposed in 41 in favor of his first wife, Yin Lihua. However, both she and her family continued to be respected and honored even after she was deposed.

Yin Lihua, formally Empress Guanglie (光烈皇后), was an empress during the Eastern Han dynasty. She was the second empress of her husband Emperor Guangwu, even though she was his first wife and married him before his first empress, Guo Shengtong, did. She was famed for her beauty and meekness.
Liu Yan, courtesy name Bosheng (伯升), was a Chinese general of one of the major uprisings against the Xin dynasty and its emperor, Wang Mang. Although he was militarily successful, he died early as a victim of political intrigue. His younger brother Liu Xiu, however, would eventually found the Eastern Han dynasty.

Deng Yu, courtesy name Zhonghua, was a Chinese statesman and military commander of the early Eastern Han dynasty who was instrumental in Emperor Guangwu's reunification of China. Although acquainted during his childhood with Liu Xiu, the future Emperor Guangwu, Deng remained aloof from the rebellions that toppled the Xin dynasty, in which Liu had played a leading role. He rejoined Liu as an advisor when the latter was a general under the Gengshi Emperor's short-lived Han restoration, and earned recognition for his skill in recommending talented personnel. When Liu himself claimed the Han imperial title, Deng was appointed Excellency over the Masses, a prime ministerial office, at the age of 24 and further rewarded with a marquisate. Deng spent much of his time as Excellency on campaign, with mixed results. He subsequently resigned as Excellency but remained a senior military commander until his voluntary demobilization in 37 CE, at a time when Emperor Guangwu sought to reduce the military power of his key subordinates.

The Han dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China. It followed the Qin dynasty, which had unified the Warring States of China by conquest. It was founded by Liu Bang. The dynasty is divided into two periods: the Western Han and the Eastern Han, interrupted briefly by the Xin dynasty of Wang Mang. These appellations are derived from the locations of the capital cities Chang'an and Luoyang, respectively. The third and final capital of the dynasty was Xuchang, where the court moved in 196 CE during a period of political turmoil and civil war.
Zhao Xi, courtesy name Boyang, was a Chinese politician who lived in the early Eastern Han dynasty.
Gongsun Shu was the founder and only emperor of Chengjia, a state that controlled China's Sichuan Basin from 25 to 36. A successful official of the Western Han and short-lived Xin dynasties, Gongsun was the Administrator of Daojiang Commandery when the Xin regime fell in 23, amid rebellions aimed at restoring the Han dynasty. Through a series of political and military maneuvers, Gongsun secured control of Yi Province and in 24 proclaimed himself king of Shu. In the following year, he assumed imperial title and founded the Cheng dynasty. Under his administration, the Sichuan region experienced a period of peace and economic prosperity, and the city of Chengdu was developed into an imperial capital. But Gongsun adopted a defensive military posture that kept his influence confined within Sichuan while Liu Xiu's revived Eastern Han regime secured the North China Plain. In 36, Gongsun was mortally wounded in battle against an Eastern Han invasion force, and Chengjia capitulated on the following day.

Singing All Along is a 2016 Chinese television series produced by Ruby Lin, starring Lin and Yuan Hong. Set in 1st-century imperial China, the drama is based on Li Xin's (李歆) 2007–2009 romantic novel series Xiuli Jiangshan (秀丽江山) and focuses on the relationship between Liu Xiu, a peasant-turned-Eastern Han dynasty founder, and Yin Lihua, the love of his life. Although the original novel involved time travel, the television series does not contain those parts.
Sun Deng was briefly appointed puppet emperor by a coalition of Chimei "Red Eyebrows" rebels in December of 26 CE, but later that month was killed by his general Yue Xuan 樂玄 when the rebels surrendered to the superior forces of Emperor Guangwu of Han.
Zhang Bu, courtesy name Wengong (文公), was a major warlord in Eastern China during the Xin and early Eastern Han periods. He was from Langya Commandery in Xu Province.
Chengjia, also called the Cheng dynasty or Great Cheng, was a self-proclaimed empire established by Gongsun Shu in 25 AD after the collapse of the Xin dynasty of Chinese history, rivalling the Eastern Han dynasty founded by Emperor Guangwu later in the same year. Based in the Sichuan Basin with its capital at Chengdu, Chengjia covered a large area including modern Sichuan, Chongqing, Guizhou, Yunnan, and southern Shaanxi, and comprised about 7% of China's population at the time. Chengjia was the most dangerous rival to the Eastern Han and was the last separatist regime in China to be conquered by the latter, in 36 AD.
Liu Yong was a general and politician of the Xin dynasty and early Eastern Han dynasty. He was born in Suiyang County, Liang Commandery, Yuzhou. A member of the Han imperial family, he was the son of Liu Li, Prince of Liang, and an 8th-generation descendant of Liu Wu, Prince Xiao of Liang.
Pang Meng was a Chinese general of the Xin dynasty and early period of the Eastern Han dynasty. He was born in Shanyang Commandery, Yanzhou.









