
Marie Byrd Land is the portion of West Antarctica lying east of the Ross Ice Shelf and the Ross Sea and south of the Pacific Ocean, extending eastward approximately to a line between the head of the Ross Ice Shelf and Eights Coast. It stretches between 158°W and 103°24'W. The inclusion of the area between the Rockefeller Plateau and Eights Coast is based upon the leading role of the American Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd in the exploration of this area. The name was originally applied by Admiral Byrd in 1929, in honor of his wife, to the northwestern part of the area, the part that was explored in that year.

Dundee Island is an ice-covered island lying east of the northeastern tip of Antarctic Peninsula and south of Joinville Island.
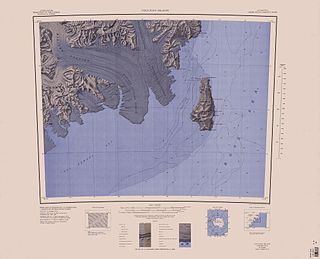
Borchgrevink Glacier is a large glacier in the Victory Mountains, Victoria Land, draining south between Malta Plateau and Daniell Peninsula, and thence projecting into Glacier Strait, Ross Sea, as a floating glacier tongue, the Borchgrevink Glacier Tongue, just south of Cape Jones. It was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1957–58, for Carsten Borchgrevink, leader of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1898–1900. Borchgrevink visited the area in February 1900 and first observed the seaward portion of the glacier.

HMNZS Endeavour was a Royal New Zealand Navy Antarctic support vessel. She was the first of three ships in the Royal New Zealand Navy to bear that name.
Prospect Point is a headland at the west extremity of Velingrad Peninsula on Graham Coast in Graham Land, nearly 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) south of Ferin Head and immediately east of the Fish Islands. Roughly charted by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill, 1934-37. Photographed by Hunting Aerosurveys Ltd. in 1956-57. The name was suggested in 1957 by E. P. Arrowsmith, Governor of the Falkland Islands.

Wonsey Rock is a small rock north of Cameron Island in the Swain Islands. This region was photographed by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump (1946–47), ANARE (1956), and the Soviet expedition (1956). It was included in a 1957 survey of the islands north of Wilkes Station by C.R. Eklund. He named the rock for construction mechanic Duane J. Wonsey, U.S. Navy, of the Wilkes Station party, 1957.
Belding Island is an island 3 nautical miles (6 km) long, lying west of the south end of Watkins Island, Biscoe Islands. It was mapped from air photos taken by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition (1956–57), and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Harwood S. Belding, an American physiologist who was Director of the Quartermaster at the Climatic Research Laboratory, Department of the Army, Lawrence, Massachusetts, and initiated considerable research on cold climate clothing.

Buromskiy Island is a small island lying 0.6 km (0.37 mi) south of Haswell Island in the Haswell Islands of Antarctica. About 200 m long and 100 m wide, it was discovered and mapped by the Australasian Antarctic Expedition under Douglas Mawson, 1911–14. It was photographed by the Soviet expedition of 1958 and named for N.I. Buromskiy, expedition hydrographer who lost his life in the Antarctic in 1957. It lies 2.7 km north of Mabus Point, the site of Russia's Mirny Station.

Chërnyy Island is a small island lying 0.9 kilometres (0.5 nmi) south of the eastern tip of Thomas Island in the Highjump Archipelago. It was mapped from air photos taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump (1946–47). It was rephotographed by the Soviet expedition (1956) and named Ostrov Chërnyy.

Dewart Island is the central island in the Frazier Islands, in Vincennes Bay, Wilkes Land, East Antarctica.
Patterson Rock is an insular rock 0.5 nautical miles (0.9 km) west of Cameron Island, in the Swain Islands. This region was photographed from the air by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump (1946–47), ANARE (1956) and the Soviet expedition (1956). The rock was included in a 1957 ground survey by C.R. Eklund, who named it for Acy H. Patterson, U.S. Navy, electrician at Wilkes Station, 1957.
The Géologie Archipelago, also known as the Geology Archipelago or Cape Geology Archipelago, is a small archipelago of rocky islands and rocks close to the north of Cape Géodésie and Astrolabe Glacier Tongue, extending from Helene Island on the west to the Dumoulin Islands on the east, in Adélie Land, Antarctica.
Magee Rock is an insular rock lying 0.2 nautical miles (0.4 km) northeast of Cameron Island, in the Swain Islands of Antarctica. This region was photographed from the air by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump (1946–47), Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (1956) and the Soviet expedition (1956). The rock was included in a 1957 ground survey by Carl R. Eklund, who named it for George E. Magee, U.S. Navy, a carpenter at Wilkes Station, 1957.

Savage Glacier is a glacier at the east end of Thurston Island, lying south of Tierney Peninsula and flowing east to Seraph Bay. The glacier was discovered on helicopter flights from the USS Glacier and Burton Island by personnel of the U.S. Navy Bellingshausen Sea Expedition in February 1960. The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names named the glacier for Lieutenant John Savage, U.S. Navy, dental officer aboard the Glacier, who assisted in establishing geodetic control points in the area.

Soldat Island is an elongated rocky island, 4.6 kilometres (2.5 nmi) long, lying south of Partizan Island in the south part of the entrance to Langnes Fjord, Vestfold Hills. This feature was photographed by the Lars Christensen Expedition (1936–37), but was plotted on the subsequent maps as a peninsula. It was first shown to be an island by John Roscoe's 1952 study of aerial photographs of the area taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump (1946–47). The area was photographed by ANARE (1954–58) and the Soviet Antarctic Expedition (1956), the latter applying the name Ostrov Soldat.

Kartografov Island is a small coastal island lying in the western part of the mouth of Harald Bay, Oates Land, Antarctica. It was photographed by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump (1946–47), the Soviet Antarctic Expedition (1957–58) and the Australian National Antarctic Research Expedition (1959). The island was named "Ostrov Kartografov" by the Soviet expedition.

Khmara Island is a small island lying 2 kilometres (1 nmi) south of Haswell Island, Queen Mary Coast, Antarctica. It was mapped from aerial photos taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47. It was remapped by the Soviet Antarctic Expedition, 1956, and named after tractor driver Ivan F. Khmara.

Cameron Island is a small island just north of Hailstorm Island, in the Swain Islands, Antarctica. This region was photographed from the air by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump (1946–47), ANARE (1956), and the Soviet expedition (1956). The island was included in a 1957 ground survey by C.R. Eklund, who named it for Richard L. Cameron, chief glaciologist at Wilkes Station, 1957.













