
Wine is a free and open-source compatibility layer to allow application software and computer games developed for Microsoft Windows to run on Unix-like operating systems. Developers can compile Windows applications against WineLib to help port them to Unix-like systems. Wine is predominantly written using black-box testing reverse-engineering, to avoid copyright issues. No code emulation or virtualization occurs. Wine is primarily developed for Linux and macOS.

Liberty BASIC (LB) is a commercial computer programming language and integrated development environment (IDE). It has an interpreter, developed in Smalltalk, which recognizes its own dialect of the BASIC programming language. It runs on 16- and 32-bit Windows and OS/2.

PureBasic is a commercially distributed procedural computer programming language and integrated development environment based on BASIC and developed by Fantaisie Software for Windows, Linux, and macOS. An Amiga version is available, although it has been discontinued and some parts of it are released as open-source. The first public release of PureBasic for Windows was on 17 December 2000. It has been continually updated ever since.
XBasic is a variant of the BASIC programming language that was developed in the late 1980s for the Motorola 88000 CPU and Unix by Max Reason. In the early 1990s it was ported to Windows and Linux, and since 1999 it has been available as open source software with its runtime library under the LGPL license.

The Windows API, informally WinAPI, is the foundational application programming interface (API) that allows a computer program to access the features of the Microsoft Windows operating system in which the program is running.

Delphi is a general-purpose programming language and a software product that uses the Delphi dialect of the Object Pascal programming language and provides an integrated development environment (IDE) for rapid application development of desktop, mobile, web, and console software, currently developed and maintained by Embarcadero Technologies.
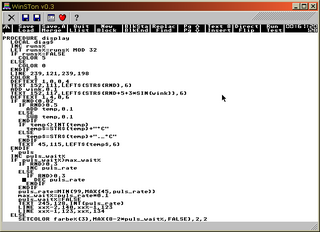
GFA BASIC is a dialect of the BASIC programming language, by Frank Ostrowski. The name is derived from the company, which distributed the software. In the mid-1980s to the 1990s it enjoyed popularity as an advanced BASIC dialect, but has been mostly superseded by several other programming languages. Official support ended in the early 2000s.

PyQt is a Python binding of the cross-platform GUI toolkit Qt, implemented as a Python plug-in. PyQt is free software developed by the British firm Riverbank Computing. It is available under similar terms to Qt versions older than 4.5; this means a variety of licenses including GNU General Public License (GPL) and commercial license, but not the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL). PyQt supports Microsoft Windows as well as various kinds of UNIX, including Linux and MacOS.

PHP-GTK is a set of language bindings for the programming language PHP which allow GTK graphical user interface (GUI) applications to be written in PHP. PHP-GTK provides an object-oriented programming interface to GTK classes and functions. PHP-GTK partly supports GTK2, but GTK3 is unsupported.
A dynamic-link library (DLL) is a shared library in the Microsoft Windows or OS/2 operating system.
In computer programming, the term hooking covers a range of techniques used to alter or augment the behaviour of an operating system, of applications, or of other software components by intercepting function calls or messages or events passed between software components. Code that handles such intercepted function calls, events or messages is called a hook.

Code::Blocks is a free, open-source, cross-platform IDE that supports multiple compilers including GCC, Clang and Visual C++. It is developed in C++ using wxWidgets as the GUI toolkit. Using a plugin architecture, its capabilities and features are defined by the provided plugins. Currently, Code::Blocks is oriented towards C, C++, and Fortran. It has a custom build system and optional Make support.
J/Direct was a technology included in some versions of Microsoft Java Virtual Machine, which allowed direct calls into the Windows API. J/Direct was specific of Microsoft's Virtual Machine, in replacement of the standard Java Native Interface (JNI).
Platform Invocation Services, commonly referred to as P/Invoke, is a feature of Common Language Infrastructure implementations, like Microsoft's Common Language Runtime, that enables managed code to call native code.
The Microsoft Windows operating system supports a form of shared libraries known as "dynamic-link libraries", which are code libraries that can be used by multiple processes while only one copy is loaded into memory. This article provides an overview of the core libraries that are included with every modern Windows installation, on top of which most Windows applications are built.

Visual Basic (VB) before .NET, sometimes referred to as Classic Visual Basic, is a third-generation programming language, based on BASIC, and an integrated development environment (IDE), from Microsoft for Windows known for supporting rapid application development (RAD) of graphical user interface (GUI) applications, event-driven programming and both consumption and development of components via the Component Object Model (COM) technology.

Geany is a free and open-source lightweight GUI text editor using Scintilla and GTK, including basic IDE features. It is designed to have short load times, with limited dependency on separate packages or external libraries on Linux. It has been ported to a wide range of operating systems, such as BSD, Linux, macOS, Solaris and Windows. The Windows port lacks an embedded terminal window; also missing from the Windows version are the external development tools present under Unix, unless installed separately by the user. Among the supported programming languages and markup languages are C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, PHP, HTML, LaTeX, CSS, Python, Perl, Ruby, Pascal, Haskell, Erlang, Vala and many others.
GLBasic is a commercial BASIC programming language that can compile to various platforms including Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, and some handheld devices. The language is designed to be simple and intuitive.
Basic4ppc is a programming language originally for Pocket PC handheld computers running Windows Mobile operating system, by Anywhere Software. Since 2014, B4x was renamed, and currently, 2023, supports multiple devices and their OS, including desktop and mobile solutions with development adaptions for these environments. The language is based on a BASIC-like syntax, taking advantage of Microsoft's .NET technology, to allow additional libraries, graphical user interface design of windows forms, rapid application development (RAD), and .NET framework compatible compilation. The language implements a unique way of adding objects to a program without being object-oriented. Its advantages are simplicity, development pace and the integration with .NET framework. A special version of the integrated development environment (IDE) allows developing straight onto the Windows Mobile device or. With the demise of Windows Mobile operating system and the devices running it Basic4PPC came to the end of its life in about 2012. For owners of Basic4PPC it remains a useful Windows-desktop BASIC compiler as it runs code directly in the Windows environment and it can compile a project to a Windows 'exe' file for use as a Windows program.

The Windows 9x series of operating systems refers to the monolithic kernel which powers these operating systems. The basic code is similar in function to MS-DOS. As a 16-/32-bit hybrid, it requires support from MS-DOS to operate.













