Related Research Articles

Hemoglobin is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transport of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin in the blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs to the other tissues of the body, where it releases the oxygen to enable aerobic respiration which powers the animal's metabolism. A healthy human has 12 to 20 grams of hemoglobin in every 100 mL of blood. Hemoglobin is a metalloprotein, a chromoprotein, and globulin.

Protein biosynthesis is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences.

Succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit C, also known as succinate dehydrogenase cytochrome b560 subunit, mitochondrial, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SDHC gene. This gene encodes one of four nuclear-encoded subunits that comprise succinate dehydrogenase, also known as mitochondrial complex II, a key enzyme complex of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and aerobic respiratory chains of mitochondria. The encoded protein is one of two integral membrane proteins that anchor other subunits of the complex, which form the catalytic core, to the inner mitochondrial membrane. There are several related pseudogenes for this gene on different chromosomes. Mutations in this gene have been associated with pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described.
Macroglobulins are large globular proteins and are found in the blood and other body fluids. Various physiological processes, including immunity, coagulation, and chemical transport, rely on these proteins. A macroglobulin is a plasma globulin of high molecular weight. Elevated levels of macroglobulins (macroglobulinemia) may cause manifestations of excess blood viscosity and/or precipitate within blood vessels when temperature drops. Other macroglobulins include α2-macroglobulin, which is elevated in nephrotic syndrome, diabetes, severe burns, and other conditions, while a deficiency is associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
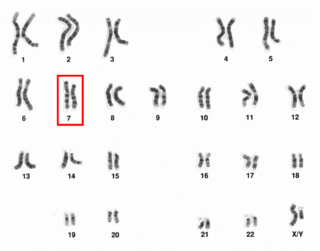
Chromosome 7 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, who normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 7 spans about 160 million base pairs and represents between 5 and 5.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
Chromosome 8 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 8 spans about 146 million base pairs and represents between 4.5 and 5.0% of the total DNA in cells.
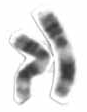
Chromosome 11 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Humans normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 11 spans about 135 million base pairs and represents between 4 and 4.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. The shorter arm is termed 11p while the longer arm is 11q. At about 21.5 genes per megabase, chromosome 11 is one of the most gene-rich, and disease-rich, chromosomes in the human genome.

Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur subunit, mitochondrial (SDHB) also known as iron-sulfur subunit of complex II (Ip) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SDHB gene.
The Kell antigen system is a human blood group system, that is, a group of antigens on the human red blood cell surface which are important determinants of blood type and are targets for autoimmune or alloimmune diseases which destroy red blood cells. The Kell antigens are K, k, Kpa, Kpb, Jsa and Jsb. The Kell antigens are peptides found within the Kell protein, a 93-kilodalton transmembrane zinc-dependent endopeptidase which is responsible for cleaving endothelin-3.
XK is a protein found on human red blood cells and other tissues which is responsible for the Kx antigen which helps determine a person's blood type.

McLeod syndrome is an X-linked recessive genetic disorder that may affect the blood, brain, peripheral nerves, muscle, and heart. It is caused by a variety of recessively inherited mutations in the XK gene on the X chromosome. The gene is responsible for producing the Kx protein, a secondary supportive protein for the Kell antigen on the red blood cell surface.

The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor, also known as CD116, is a receptor for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, which stimulates the production of white blood cells. In contrast to M-CSF and G-CSF which are lineage specific, GM-CSF and its receptor play a role in earlier stages of development. The receptor is primarily located on neutrophils, eosinophils and monocytes/macrophages, it is also on CD34+ progenitor cells (myeloblasts) and precursors for erythroid and megakaryocytic lineages, but only in the beginning of their development.

The Gs alpha subunit is a subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein Gs that stimulates the cAMP-dependent pathway by activating adenylyl cyclase. Gsα is a GTPase that functions as a cellular signaling protein. Gsα is the founding member of one of the four families of heterotrimeric G proteins, defined by the alpha subunits they contain: the Gαs family, Gαi/Gαo family, Gαq family, and Gα12/Gα13 family. The Gs-family has only two members: the other member is Golf, named for its predominant expression in the olfactory system. In humans, Gsα is encoded by the GNAS complex locus, while Golfα is encoded by the GNAL gene.
Gi protein alpha subunit is a family of heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunits. This family is also commonly called the Gi/o family or Gi/o/z/t family to include closely related family members. G alpha subunits may be referred to as Gi alpha, Gαi, or Giα.
The IκB kinase is an enzyme complex that is involved in propagating the cellular response to inflammation, specifically the regulation of lymphocytes.

AP-1 complex subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP1B1 gene.

AP-3 complex subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP3B1 gene.

40S ribosomal protein S29 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPS29 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNG11 gene.
The KX Blood-group Antigen (KXA) Family (TC# 2.A.112) consists of transport proteins that are part of the TOG superfamily. The KX gene codes for a novel protein with characteristics of membrane transporters that has been proposed to be a Na+ -dependent neutral amine and/or oligopeptide transporter. It is predicted to be 444 amino acyl residues in length and exhibits 10 putative transmembrane α-helical segments. The KX blood group antigen mRNA expression pattern correlates with McLeod syndrome.
References
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: XK, Kell blood group complex subunit-related family, member 5" . Retrieved 2014-06-05.