
ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines alpha codes and numeric codes for the representation of currencies and provides information about the relationships between individual currencies and their minor units. This data is published in three tables:

Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. Based on the PostScript language, each PDF file encapsulates a complete description of a fixed-layout flat document, including the text, fonts, vector graphics, raster images and other information needed to display it. PDF has its roots in "The Camelot Project" initiated by Adobe co-founder John Warnock in 1991.

A parabolic antenna is an antenna that uses a parabolic reflector, a curved surface with the cross-sectional shape of a parabola, to direct the radio waves. The most common form is shaped like a dish and is popularly called a dish antenna or parabolic dish. The main advantage of a parabolic antenna is that it has high directivity. It functions similarly to a searchlight or flashlight reflector to direct radio waves in a narrow beam, or receive radio waves from one particular direction only. Parabolic antennas have some of the highest gains, meaning that they can produce the narrowest beamwidths, of any antenna type. In order to achieve narrow beamwidths, the parabolic reflector must be much larger than the wavelength of the radio waves used, so parabolic antennas are used in the high frequency part of the radio spectrum, at UHF and microwave (SHF) frequencies, at which the wavelengths are small enough that conveniently-sized reflectors can be used.
The C standard library or libc is the standard library for the C programming language, as specified in the ISO C standard. Starting from the original ANSI C standard, it was developed at the same time as the C library POSIX specification, which is a superset of it. Since ANSI C was adopted by the International Organization for Standardization, the C standard library is also called the ISO C library.
BAT or B.A.T. may refer to:
SQ, Sq, or sq may stand for:

An orthomode transducer (OMT) is a waveguide component that is commonly referred to as a polarisation duplexer. Orthomode is a contraction of orthoganal mode. Orthomode transducers serve either to combine or to separate two orthogonally polarized microwave signal paths. One of the paths forms the uplink, which is transmitted over the same waveguide as the received signal path, or downlink path. Such a device may be part of a very small aperture terminal (VSAT) antenna feed or a terrestrial microwave radio feed; for example, OMTs are often used with a feed horn to isolate orthogonal polarizations of a signal and to transfer transmit and receive signals to different ports.
Several binary representations of 8-bit character sets for common Western European languages are compared in this article. These encodings were designed for representation of Italian, Spanish, Portuguese, French, German, Dutch, English, Danish, Swedish, Norwegian, and Icelandic, which use the Latin alphabet, a few additional letters and ones with precomposed diacritics, some punctuation, and various symbols. Although they're called "Western European" many of these languages are spoken all over the world. Also, these character sets happen to support many other languages such as Malay, Swahili, and Classical Latin.
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.

ERCC2, or XPD is a protein involved in transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair.
The Open Packaging Conventions (OPC) is a container-file technology initially created by Microsoft to store a combination of XML and non-XML files that together form a single entity such as an Open XML Paper Specification (OpenXPS) document. OPC-based file formats combine the advantages of leaving the independent file entities embedded in the document intact and resulting in much smaller files compared to normal use of XML.

Polarization-division multiplexing (PDM) is a physical layer method for multiplexing signals carried on electromagnetic waves, allowing two channels of information to be transmitted on the same carrier frequency by using waves of two orthogonal polarization states. It is used in microwave links such as satellite television downlinks to double the bandwidth by using two orthogonally polarized feed antennas in satellite dishes. It is also used in fiber optic communication by transmitting separate left and right circularly polarized light beams through the same optical fiber.
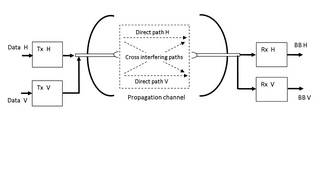
XPIC, or cross-polarization interference cancelling technology, is an algorithm to suppress mutual interference between two received streams in a Polarization-division multiplexing communication system.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.





