Related Research Articles

A xanthoma is a deposition of yellowish cholesterol-rich material that can appear anywhere in the body in various disease states. They are cutaneous manifestations of lipidosis in which lipids accumulate in large foam cells within the skin. They are associated with hyperlipidemias, both primary and secondary types.

Xanthelasma is a sharply demarcated yellowish deposit of cholesterol underneath the skin. It usually occurs on or around the eyelids. While they are neither harmful to the skin nor painful, these minor growths may be disfiguring and can be removed. There is a growing body of evidence for the association between xanthelasma deposits and blood low-density lipoprotein levels and increased risk of atherosclerosis.

A papule is a small, well-defined bump in the skin. It may have a rounded, pointed or flat top, and may have a dip. It can appear with a stalk, be thread-like or look warty. It can be soft or firm and its surface may be rough or smooth. Some have crusts or scales. A papule can be flesh colored, yellow, white, brown, red, blue or purplish. There may be just one or many, and they may occur irregularly in different parts of the body or appear in clusters. It does not contain fluid but may progress to a pustule or vesicle. A papule is smaller than a nodule; it can be as tiny as a pinhead and is typically less than 1 cm in width, according to some sources, and 0.5 cm according to others. When merged together, it appears as a plaque.
Diabetic dermopathy is a type of skin lesion usually seen in people with diabetes mellitus. It is characterized by dull-red papules that progress to well-circumscribed, small, round, atrophic hyperpigmented skin lesions usually on the shins. It is the most common of several diabetic skin conditions, being found in up to 30% of diabetics. Similar lesions can occasionally be found in non-diabetics usually following trauma or injury to the area; however, more than 4 lesions strongly suggests diabetes.
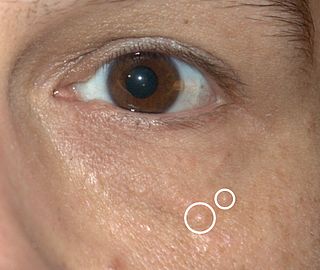
Syringomas are benign eccrine sweat duct tumors, typically found clustered on eyelids, although they may also be found in the armpits, abdomen, chest, neck, scalp, or groin area, including genitals, in a symmetric pattern. They are skin-colored or yellowish firm, rounded bumps, 1–3 mm in diameter, and may be confused with xanthoma, milia, hidrocystoma, trichoepithelioma, and xanthelasma. They are more common in women and are most commonly found in middle-aged Asian women. While they can present at any time in life, they typically present during adolescence. They are usually not associated with any other symptoms, although can sometimes cause itchiness or irritation.

The Koebner phenomenon or Köbner phenomenon, also called the Koebner response or the isomorphic response, attributed to Heinrich Köbner, is the appearance of skin lesions on lines of trauma. The Koebner phenomenon may result from either a linear exposure or irritation. Conditions demonstrating linear lesions after a linear exposure to a causative agent include: molluscum contagiosum, warts and toxicodendron dermatitis. Warts and molluscum contagiosum lesions can be spread in linear patterns by self-scratching ("auto-inoculation"). Toxicodendron dermatitis lesions are often linear from brushing up against the plant. Causes of the Koebner phenomenon that are secondary to scratching rather than an infective or chemical cause include vitiligo, psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen nitidus, pityriasis rubra pilaris, and keratosis follicularis.
Verruciform xanthoma is an uncommon benign lesion that has a verruciform (wart-like) appearance, but it may appear polypoid, papillomatous, or sessile. The verruciform was first described by Shafer in 1971 on the oral mucosa. Usually found on the oral mucosa of middle-aged persons, verruciform xanthomas have also been reported on the scrotum and penis of middle-aged to elderly Japanese males. While the most common site is the oral mucosa, lesions that occur elsewhere usually arise on the perineum or on the skin with some predisposing factor, such as lymphedema or an epidermal nevus.
Familial partial lipodystrophy, also known as Köbberling–Dunnigan syndrome, is a rare genetic metabolic condition characterized by the loss of subcutaneous fat.
Non-X histiocytoses are a clinically well-defined group of cutaneous syndromes characterized by infiltrates of monocytes/macrophages, as opposed to X-type histiocytoses in which the infiltrates contain Langerhans cells. Conditions included in this group are:
Xanthoma disseminatum is a rare cutaneous condition that preferentially affects males in childhood, characterized by the insidious onset of small, yellow-red to brown papules and nodules that are discrete and disseminated.
Papular xanthoma is a cutaneous condition that is a rare form of non-X histiocytosis.

Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia or type III hyperlipoproteinemia is a condition characterized by increased total cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and decreased HDL levels.
Xanthoma diabeticorum is a cutaneous condition that may result in young persons who are unresponsive to insulin.
Normolipoproteinemic xanthomatosis is a cutaneous condition characterized by a xanthoma in the presence of normal cholesterol and lipoprotein levels.
Wende–Bauckus syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by tiny white macules on the trunk with confluence within flexures.
Localized heat contact urticaria is a cutaneous condition, one of the rarest forms of urticaria, where within minutes of contact with heat from any source, itching and wheals occur at the precise site of contact, lasting up to 1 hour.
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 1416. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.