Related Research Articles

Nevada is the only U.S. state where prostitution is legally permitted in some form. Prostitution is legal in 10 of Nevada's 17 counties, although only six allow it in every municipality. Six counties have at least one active brothel, which mainly operate in isolated, rural areas. The state's most populated counties, Clark and Washoe, are among those that do not permit prostitution. It is also illegal in Nevada's capital, Carson City, an independent city.

A brothel, bordello, bawdy house, ranch, house of ill repute, house of ill fame, or whorehouse is a place where people engage in sexual activity with prostitutes. However, for legal or cultural reasons, establishments often describe themselves as massage parlors, bars, strip clubs, body rub parlours, studios, or by some other description. Sex work in a brothel is considered safer than street prostitution.

A sex doll is an anthropomorphic sex toy in the size and shape of a sexual partner. The sex doll may consist of an entire body, or just a head, pelvis, or other body part intended for sexual stimulation. Sex dolls are made from various materials like silicone, TPE, or rubber to replicate a lifelike feel. These materials are chosen for their durability and realistic texture, enhancing the overall experience for users. The parts sometimes vibrate and may be moveable and interchangeable. Sex dolls exist in many forms, but are usually distinguished from sex robots, which are anthropomorphic creations designed to be able to engage in more complex interactions.

Street prostitution is a form of prostitution in which a prostitute solicits customers from a public place, most commonly a street, while waiting at street corners or walking alongside a street, but also other public places such as parks, benches, etc. The street prostitute is often dressed in a provocative manner. The sex act may be performed in the customer's car, in a nearby secluded street location, or at the prostitute's residence or in a rented motel room.

Prostitution in Germany is legal, as are other aspects of the sex industry, including brothels, advertisement, and job offers through HR companies. Full-service sex work is widespread and regulated by the German government, which levies taxes on it. In 2016, the government adopted a new law, the Prostitutes Protection Act, in an effort to improve the legal situation of sex workers, while also now enacting a legal requirement for registration of prostitution activity and banning prostitution which involves no use of condoms. The social stigmatization of sex work persists and many workers continue to lead a double life. Human rights organizations consider the resulting common exploitation of women from Eastern and Southeastern Europe to be the main problem associated with the profession.
Prostitution in Hong Kong is itself legal, but organised prostitution is illegal, as there are laws against keeping a vice establishment, causing or procuring another to be a prostitute, living on the prostitution of others, or public solicitation.
Forced prostitution, also known as involuntary prostitution or compulsory prostitution, is prostitution or sexual slavery that takes place as a result of coercion by a third party. The terms "forced prostitution" or "enforced prostitution" appear in international and humanitarian conventions, such as the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, but have been inconsistently applied. "Forced prostitution" refers to conditions of control over a person who is coerced by another to engage in sexual activity.

Prostitution in France was legal until April 2016, but several surrounding activities were illegal, like operating a brothel, living off the avails (pimping), and paying for sex with someone under the age of 18.
Prostitution in Rhode Island was outlawed in 2009. On November 3, 2009, Republican Governor Donald Carcieri signed into law a bill which makes the buying and selling of sexual services a crime.
Prostitution in Austria is legal and regulated.

Le Chabanais was one of the best known and most luxurious brothels in Paris, operating near the Louvre at 12 rue Chabanais from 1878 until 1946, when brothels were outlawed in France. It was founded by the Irish-born Madame Kelly, who was closely acquainted with several members at the Jockey-Club de Paris. Among the habitués were Albert, Prince of Wales ; Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec; Cary Grant; Humphrey Bogart, Mae West and diplomatic guests of the French government.
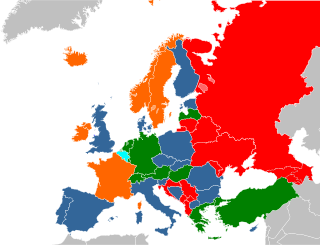
The legality of prostitution in Europe varies by country.

Prostitution laws varies widely from country to country, and between jurisdictions within a country. At one extreme, prostitution or sex work is legal in some places and regarded as a profession, while at the other extreme, it is considered a severe crime punishable by death in some other places. A variety of different legal models exist around the world, including total bans, bans that only target the customer, and laws permitting prostitution but prohibiting organized groups, an example being brothels.

Justine Paris, real name Bienfait, was a French courtesan and madam. She hosted several of the most famous brothels in mid-18th-century Paris and was one of the most known and successful of her trade. She and her brothel are portrayed in the memoirs of Casanova. She has been suggested to be the role model for the title character in Juliette by the Marquis de Sade.
Loi Marthe Richard of 13 April 1946 abolished the regime of regulated prostitution in France that had been in force since 1804. It required the closure of brothels. The law bears the name of Marthe Richard, who was a municipal councillor of Paris but not a parliamentary representative.
Le Fourcy was the most famous mass brothel of Paris, a so-called Maison d'abattage. It was located in the Saint-Paul district in the 4th arrondissement at 10 rue de Fourcy, and was notorious for treating its women very badly. In his book Le Petit Simonin, novelist Albert Simonin wrote:
"The Fourcy in the district of Saint-Paul, the most famous of the Paris slaughter houses, demanded 5.50 francs per session. "Five francs per lady and room," as if it were a chorus's chorus, who goes to the room? "The ten sous, which were asked for as a supplement to the five francs, is not a tip, but a tariff for the towel attracted so many customers on working days that some ladies who were not too bad, were anything but unemployed and able to cope with seventy sessions."
The authorities of medieval Paris attempted to confine prostitution to a particular district. Louis IX (1226–1270) designated nine streets in the Beaubourg Quartier where it would be permitted. In the early part of the 19th century, state-controlled legal brothels started to appear in several French cities. By law, they had to be run by a woman, and their external appearance had to be discreet. The maisons were required to light a red lantern when they were open, and the prostitutes were only permitted to leave the maisons on certain days and only if accompanied by its head. By 1810, Paris alone had 180 officially approved brothels.
Prostitution in Paris, both in street form and in dedicated facilities has had a long history and remains present to this day.

The history of prostitution in France has similarities with the history of prostitution in other countries in Europe, namely a succession of periods of tolerance and repression, but with certain distinct features such as a relatively long period of tolerance of brothels.
Tanbazar, or Tanbazaar was a 2,000-room brothel complex in Narayanganj, central Bangladesh. Until its closure in 1999, it was the largest brothel in the country, with 3,500 prostitutes working there.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Victor Castanet, "Xdolls: la maison de poupées sexuelles", Paris Match , March 8, 2018 (in French).
- 1 2 3 "Sex doll 'brothel': Xdolls escapes Paris council censure", BBC News, March 22, 2018.
- 1 2 3 David Chazan, "Calls for Paris sex-doll 'brothel' to be closed down over rape fantasy claims", The Telegraph , March 17, 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 Leslie Katz, "Paris sex doll 'brothel' to stay open despite protests", CNET, March 23, 2018.
- 1 2 3 Céline Carez, "Paris: la 'maison close' aux poupées sexuelles fait polémique", Le Parisien , March 16, 2018 (in French).
- ↑ "Paris: ouverture d'une maison close exploitant des poupées en silicone", 24matins, February 6, 2018 (in French).
- ↑ Simonetta Caminiti, "L'ultima frontiera del sesso? Le "Bocca di Rosa" in plastica", Il Giornale , March 18, 2018 (in Italian).