
The Palestine Liberation Organization is a Palestinian nationalist coalition that is internationally recognized as the official representative of the Palestinian people in both the Palestinian territories and the diaspora. It is currently represented by the Palestinian Authority based in the West Bank city of Al-Bireh.
Palestinians hold a diverse range of views on the peace process with Israel, though the goal that unites them is the end of the Israeli occupation of the West Bank. Some Palestinians accept a two-state solution, with the West Bank and the Gaza Strip forming a distinct Palestinian state, whereas other Palestinians insist on a one-state solution with equal rights for all citizens whether they are Muslims, Christians or Jews. In this scenario, Palestinian refugees may be allowed to resettle the land they were forced to flee in the 1948 Palestinian expulsion and flight. However, widespread anti-Semitic sentiments in Palestinian society and Palestinian militancy have hindered the peace process.

The Israeli–Palestinian conflict is an ongoing military and political conflict about land and self-determination within the territory of the former Mandatory Palestine. Key aspects of the conflict include the Israeli occupation of the West Bank and Gaza Strip, the status of Jerusalem, Israeli settlements, borders, security, water rights, the permit regime, Palestinian freedom of movement, and the Palestinian right of return.

The history of the State of Palestine describes the creation and evolution of the State of Palestine in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. During the British mandate period, numerous plans of partition of Palestine were proposed but without the agreement of all parties. In 1947, the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was voted for. The leaders of the Jewish Agency for Palestine accepted parts of the plan, while Arab leaders refused it. This triggered the 1947–1949 Palestine war and led, in 1948, to the establishment of the state of Israel on a part of Mandate Palestine as the Mandate came to an end.

The Oslo I Accord or Oslo I, officially called the Declaration of Principles on Interim Self-Government Arrangements or short Declaration of Principles (DOP), was an attempt in 1993 to set up a framework that would lead to the resolution of the ongoing Israeli–Palestinian conflict. It was the first face-to-face agreement between the government of Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO).

The Interim Agreement on the West Bank and the Gaza Strip commonly known as Oslo II or Oslo 2, was a key and complex agreement in the Israeli–Palestinian peace process. Because it was signed in Taba, Egypt, it is sometimes called the Taba Agreement. The Oslo Accords envisioned the establishment of a Palestinian interim self-government in the Palestinian territories. Oslo II created the Areas A, B and C in the West Bank. The Palestinian Authority was given some limited powers and responsibilities in the Areas A and B and a prospect of negotiations on a final settlement based on Security Council Resolutions 242 and 338. The Accord was officially signed on 28 September 1995.
The Economic Cooperation Foundation was founded by Dr. Yair Hirschfeld, together with former Minister of Justice, Dr. Yossi Beilin at the end of 1990 as a non-profit, non-governmental track II think tank, whose objectives are to build, maintain and support Israeli-Palestinian and Israeli-Arab cooperation in the political, economic, and civil society spheres in support of creating a sustainable Permanent Status based on a two-state solution. Based in Tel-Aviv, the ECF is led today by Hirschfeld, Beilin and its Treasurer Mr. Boaz Karni. Dr. Nimrod Novik is Chairman of the ECF Executive Board.

Joseph "Yossi" Beilin is an Israeli politician who has served in multiple ministerial and leadership positions in the Israeli government. Much of his political career was in the Labour Party. He also served as chairman of the Meretz-Yachad political party. After retiring from political life, Beilin founded 'Beilink', a business consultancy company. He also writes opinion pieces in Israeli papers Haaretz and Israel Hayom.

Intermittent discussions are held by various parties and proposals put forward in an attempt to resolve the ongoing Israeli–Palestinian conflict through a peace process. Since the 1970s, there has been a parallel effort made to find terms upon which peace can be agreed to in both the Arab–Israeli conflict and in the Palestinian–Israeli conflict. Notably the Camp David Accords between Egypt and Israel, which included discussions on plans for "Palestinian autonomy", but did not include any Palestinian representatives. The autonomy plan would not be implemented, but its stipulations would to a large extent be represented in the Oslo Accords.

The Sharm El Sheikh Memorandum, full name: The Sharm El Sheikh Memorandum on Implementation Timeline of Outstanding Commitments of Agreements Signed and the Resumption of Permanent Status Negotiations, was a memorandum signed on September 4, 1999, by Prime Minister of Israel Ehud Barak and PLO Chairman Yasser Arafat at Sharm el Sheikh in Egypt, overseen by the United States represented by Secretary of State Madeleine Albright. The memorandum was witnessed and co-signed by President Hosni Mubarak of Egypt and King Abdullah of Jordan.
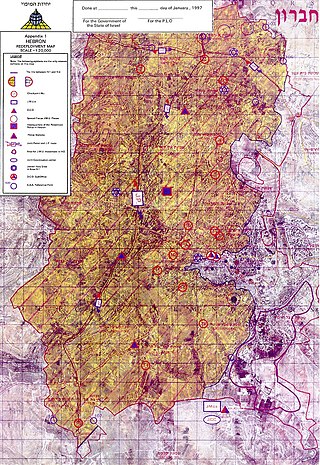
The Protocol Concerning the Redeployment in Hebron, also known as the Hebron Protocol or Hebron Agreement, was signed on 17 January 1997 by Israel, represented by Prime Minister of Israel Benjamin Netanyahu, and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), represented by PLO Chairman Yasser Arafat, under the supervision of U.S. Secretary of State, Warren Christopher. It concerned the partial redeployment of Israeli military forces from Hebron in accordance with the 1995 Interim Agreement on the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. According to the Protocol, Area H-1 would come under Palestinian control, while Area H-2 would remain under Israeli control. A large Palestinian majority still lives in both Area H-1 and Area H-2. The redeployment started on 16 January 1997. The protocol has never been ratified by either of the contracting parties.
The Letters of Mutual Recognition were exchanged between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization on 9 September 1993. In their correspondence, Israeli prime minister Yitzhak Rabin and Palestinian political leader Yasser Arafat agreed to begin cooperating towards a peaceful solution to the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. The PLO recognized Israel's right to exist in peace, renounced Palestinian militancy and terrorism, and accepted UNSC Resolution 242 and UNSC Resolution 338. Israel recognized the PLO as a legitimate authority representing the Palestinian people and agreed to commence comprehensive negotiations for the Israeli–Palestinian peace process. These initial agreements between Rabin and Arafat laid the groundwork for the Oslo I Accord on 13 September 1993, effectively serving as its preamble.
The Arab–Israeli conflict began in the 20th century, evolving from earlier Intercommunal violence in Mandatory Palestine. The conflict became a major international issue with the birth of Israel in 1948. The Arab–Israeli conflict has resulted in at least five major wars and a number of minor conflicts. It has also been the source of two major Palestinian uprisings (intifadas).

Rabbi Menachem Froman was an Israeli Orthodox rabbi, and a peacemaker and negotiator with close ties to Palestinian religious leaders. A founding member of Gush Emunim, he served as the chief rabbi of Tekoa in the West Bank. He was well known for promoting and leading interfaith dialogue between Jews, Christians and Muslims, focusing on using religion as a tool and source for recognizing the humanity and dignity of all people. Together with a Palestinian journalist close to Hamas, Rabbi Froman drafted a ceasefire agreement between Israel and the Hamas government in the Gaza Strip, known as the Froman-Amayreh Agreement. The agreement was endorsed by Hamas government, but it did not receive any official response from the Israeli government.
Hilde Henriksen Waage is a Norwegian historian and peace researcher. She is Professor of History at the University of Oslo and was acting Director of Peace Research Institute Oslo from 1992 to 1993. Waage is an expert on the Israeli–Palestinian conflict and Norway–Israel relations.

Political relations between the State of Palestine and the United States have been complex and strained since the 1960s. While the U.S. does not recognize the State of Palestine, it recognizes the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) as the legitimate representative entity for the Palestinian people; following the Oslo Accords, it recognized the Palestinian National Authority as the legitimate Palestinian government of the Palestinian territories.

The Oslo Accords are a pair of interim agreements between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO): the Oslo I Accord, signed in Washington, D.C., in 1993; and the Oslo II Accord, signed in Taba, Egypt, in 1995. They marked the start of the Oslo process, a peace process aimed at achieving a peace treaty based on Resolution 242 and Resolution 338 of the United Nations Security Council. The Oslo process began after secret negotiations in Oslo, Norway, resulting in both the recognition of Israel by the PLO and the recognition by Israel of the PLO as the representative of the Palestinian people and as a partner in bilateral negotiations.

The Madrid Conference of 1991 was a peace conference, held from 30 October to 1 November 1991 in Madrid, hosted by Spain and co-sponsored by the United States and the Soviet Union. It was an attempt by the international community to revive the Israeli–Palestinian peace process through negotiations, involving Israel and the Palestinians as well as Arab countries, including Jordan, Lebanon and Syria.

Ahmed Ali Mohammad Qurei, also known by his kunyaAbu Alaa, was a Palestinian politician who served as the second prime minister of the Palestinian National Authority.

Oslo is a 2021 American political drama television film about the secret negotiation of the Oslo Accords. The film was directed by Bartlett Sher and written by J. T. Rogers, based on Rogers' play of the same name. It stars Andrew Scott, Ruth Wilson, and Jeff Wilbusch. It was released on May 29, 2021, on HBO.











