
Orogeny is a mountain-building process that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An orogenic belt or orogen develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere. A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny.
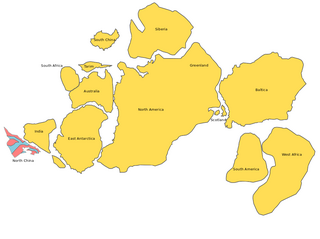
Nena, an acronym for Northern Europe–North America, was the Early Proterozoic amalgamation of Baltica and Laurentia into a single "cratonic landmass", a name first proposed in 1990. Since then several similar Proterozoic supercontinents have been proposed, including Nuna and Arctica, that include other Archaean cratons, such as Siberia and East Antarctica. In the original concept Nena formed c.1,900 million years ago in the Penokean, Makkovikan, Ketilidian, and Svecofennian orogenies. However, because Nena excludes several known Archaean cratons, including those in India and Australia, it is strictly speaking not a supercontinent. Although Nena and Nuna share many similarities, Nena accounted for a larger landmass than Nuna. This extended landmass included the Angara, Antarctica, Baltica, Laurentia, and Siberia bodies. Nena, or Nuna, can, nevertheless be thought of as the core of Columbia, another supercontinent concept with several proposed configurations.

The Grenville orogeny was a long-lived Mesoproterozoic mountain-building event associated with the assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia. Its record is a prominent orogenic belt which spans a significant portion of the North American continent, from Labrador to Mexico, as well as to Scotland.

The Yilgarn Craton is a large craton that constitutes a major part of the Western Australian land mass. It is bounded by a mixture of sedimentary basins and Proterozoic fold and thrust belts. Zircon grains in the Jack Hills, Narryer Terrane have been dated at ~4.27 Ga, with one detrital zircon dated as old as 4.4 Ga.

The geology of Australia includes virtually all known rock types, spanning a geological time period of over 3.8 billion years, including some of the oldest rocks on earth. Australia is a continent situated on the Indo-Australian Plate.

The Petermann Orogeny was an Australian intracontinental event that affected basement rocks of the northern Musgrave Province and Ediacaran (Proterozoic) sediments of the (now) southern Amadeus Basin between ~550-535 Ma. The remains are seen today in the Petermann Ranges.

The Gascoyne Complex is a terrane of Proterozoic granite and metamorphic rock in the central-western part of Western Australia. The complex outcrops at the exposed western end of the Capricorn Orogen, a 1,000 km-long arcuate belt of folded, faulted and metamorphosed rocks between two Archean cratons; the Pilbara craton to the north and the Yilgarn craton to the south. The Gascoyne Complex is thought to record the collision of these two different Archean continental fragments during the Capricorn Orogeny at 1830–1780 Ma.
The Centralian Superbasin is a large intracratonic sedimentary basin which occupied a large area of central, southern and western Australia during much of the Neoproterozoic Era.

The Trans-Hudson orogeny or Trans-Hudsonian orogeny was the major mountain building event (orogeny) that formed the Precambrian Canadian Shield and the North American Craton, forging the initial North American continent. It gave rise to the Trans-Hudson orogen (THO), or Trans-Hudson Orogen Transect (THOT), which is the largest Paleoproterozoic orogenic belt in the world. It consists of a network of belts that were formed by Proterozoic crustal accretion and the collision of pre-existing Archean continents. The event occurred 2.0–1.8 billion years ago.

The Wyoming Craton is a craton in the west-central United States and western Canada – more specifically, in Montana, Wyoming, southern Alberta, southern Saskatchewan, and parts of northern Utah. Also called the Wyoming Province, it is the initial core of the continental crust of North America.

The East Antarctic Shield or Craton is a cratonic rock body that covers 10.2 million square kilometers or roughly 73% of the continent of Antarctica. The shield is almost entirely buried by the East Antarctic Ice Sheet that has an average thickness of 2200 meters but reaches up to 4700 meters in some locations. East Antarctica is separated from West Antarctica by the 100–300 kilometer wide Transantarctic Mountains, which span nearly 3,500 kilometers from the Weddell Sea to the Ross Sea. The East Antarctic Shield is then divided into an extensive central craton that occupies most of the continental interior and various other marginal cratons that are exposed along the coast.
The Damara orogeny was part of the Pan-African orogeny. The Damara orogeny occurred late in the creation of Gondwana, at the intersection of the Congo and the Kalahari cratons.

The Sveconorwegian orogeny was an orogenic system active 1140 to 960 million years ago and currently exposed as the Sveconorwegian orogenic belt in southwestern Sweden and southern Norway. In Norway the orogenic belt is exposed southeast of the front of the Caledonian nappe system and in nappe windows. The Sveconorwegian orogen is commonly grouped within the Grenvillian Mesoproterozoic orogens. Contrary to many other known orogenic belts the Sveconorwegian orogens eastern border does not have any known suture zone with ophiolites.
The Albany-Fraser orogeny was an orogenic event which created the Albany-Fraser Orogen in what is now Australia between 2.63 and 1.16 billion years ago, during the late Archean and Proterozoic. Tectonic history developed from isotope dating suggests that the orogeny occurred as the combined North Australia Craton-West Australia Craton collided with the East Antarctic-South Australian Craton. The Kepa Kurl Booya Province, including its component zones, the Fraser Zone, Nornalup Zone and Biranup Zone represents the crystalline basement of the orogen. Numerous theories and hypotheses have been presented about the orogeny. For example, in 2011 geochronology dating of 1.71 to 1.65 billion year old granite and gabbro intrusions in the Biranup Zone suggested craton margin rocks rather than a previously interrupted small terrane wedged against the Yilgarn Craton. In other cases, researchers attempting to reconstruct the supercontinent Rodinia suggested a possible connection between Australia-Antarctica and the proto-North American continent Laurentia, but in 2003 paleomagnetic data from the Albany-Fraser orogeny suggested that Australia and Laurentia were at different latitudes.
The Mangaroon orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now Western Australia between 1.68 and 1.62 billion years ago in the Proterozoic, preserved in the rocks of the large Gascoyne Province.

The Mazatzal orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1650 to 1600 Mya in the Statherian Period of the Paleoproterozoic. Preserved in the rocks of New Mexico and Arizona, it is interpreted as the collision of the 1700-1600 Mya age Mazatzal island arc terrane with the proto-North American continent. This was the second in a series of orogenies within a long-lived convergent boundary along southern Laurentia that ended with the ca. 1200–1000 Mya Grenville orogeny during the final assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia, which ended an 800-million-year episode of convergent boundary tectonism.

The Yavapai orogeny was an orogenic (mountain-building) event in what is now the Southwestern United States that occurred between 1710 and 1680 million years ago (Mya), in the Statherian Period of the Paleoproterozoic. Recorded in the rocks of New Mexico and Arizona, it is interpreted as the collision of the 1800-1700 Mya age Yavapai island arc terrane with the proto-North American continent. This was the first in a series of orogenies within a long-lived convergent boundary along southern Laurentia that ended with the ca. 1200–1000 Mya Grenville orogeny during the final assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia, which ended an 800-million-year episode of convergent boundary tectonism.

The Picuris orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1.43 to 1.3 billion years ago in the Calymmian Period of the Mesoproterozoic. The event is named for the Picuris Mountains in northern New Mexico and interpreted either as the suturing of the Granite-Rhyolite crustal province to the southern margin of the proto-North American continent Laurentia or as the final suturing of the Mazatzal crustal province onto Laurentia. According to the former hypothesis, this was the second in a series of orogenies within a long-lived convergent boundary along southern Laurentia that ended with the ca. 1200–1000 Mya Grenville orogeny during the final assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia, which ended an 800-million-year episode of convergent boundary tectonism.

The geology of the Kimberley, a region of Western Australia, is a rock record of the early Proterozoic eon that includes tectonic plate collision, mountain-building (orogeny) and the joining (suturing) of the Kimberley and Northern Australia cratons, followed by sedimentary basin formation.











