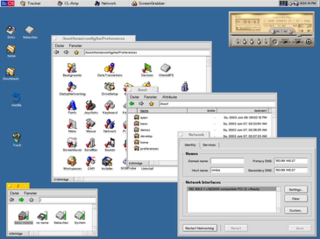
BeOS was an operating system for personal computers first developed by Be Inc. in 1990. It was first written to run on BeBox hardware.

OpenGL is a cross-language, cross-platform application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D and 3D vector graphics. The API is typically used to interact with a graphics processing unit (GPU), to achieve hardware-accelerated rendering.
Darwin is an open-source Unix-like operating system first released by Apple Inc. in 2000. It is composed of code derived from NeXTSTEP, BSD, Mach, and other free software projects' code, as well as code developed by Apple.

ReactOS is a free and open-source operating system for amd64/i686 personal computers intended to be binary-compatible with computer programs and device drivers made for Windows Server 2003 and later versions of Windows. ReactOS has been noted as a potential open-source drop-in replacement for Windows and for its information on undocumented Windows APIs.

Haiku is a free and open-source operating system compatible with the now discontinued BeOS. Its development began in 2001, and the operating system became self-hosting in 2008. The first alpha release was made in September 2009, and the last was November 2012; the first beta was released in September 2018, followed by beta 2 in June 2020 and beta 3 in July 2021.
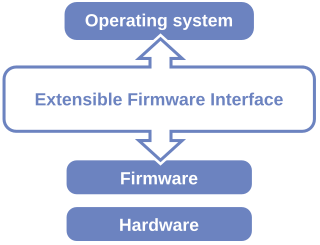
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a publicly available specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware. UEFI replaces the legacy Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) firmware interface originally present in all IBM PC-compatible personal computers, with most UEFI firmware implementations providing support for legacy BIOS services. UEFI can support remote diagnostics and repair of computers, even with no operating system installed.
BeGeistert is an annual users' and developers' conference for the open source operating system Haiku.
magnussoft ZETA, earlier yellowTAB ZETA, was an operating system formerly developed by yellowTAB of Germany based on the Be Operating System developed by Be Inc.; because of yellowTAB's insolvency, ZETA was later being developed by an independent team of which little was known, and distributed by magnussoft. As of February 28, 2007 the current version of ZETA is 1.5. On March 28, 2007, magnussoft announced that it has discontinued funding the development of ZETA by March 16, because the sales figures had fallen far short of the company's expectations, so that the project was no longer economically viable. A few days later, the company also stopped the distribution of ZETA in reaction to allegations that ZETA constituted an illegal unlicensed derivative of the BeOS source code and binaries.

OpenTracker is the open-source version of the Tracker file manager for BeOS-compatible operating systems.
The Software Freedom Law Center (SFLC) is an organization that provides pro bono legal representation and related services to not-for-profit developers of free software/open source software. It was launched in February 2005 with Eben Moglen as chairman. Initial funding of US$4 million was pledged by Open Source Development Labs.

Mac OS X Leopard is the sixth major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Macintosh computers. Leopard was released on October 26, 2007 as the successor of Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger, and is available in two editions: a desktop version suitable for personal computers, and a server version, Mac OS X Server. It retailed for $129 for the desktop version and $499 for Server. Leopard was superseded by Snow Leopard in 2009. Leopard is the final version of macOS to support the PowerPC architecture as Snow Leopard functions solely on Intel based Macs.

A free and open-source graphics device driver is a software stack which controls computer-graphics hardware and supports graphics-rendering application programming interfaces (APIs) and is released under a free and open-source software license. Graphics device drivers are written for specific hardware to work within a specific operating system kernel and to support a range of APIs used by applications to access the graphics hardware. They may also control output to the display if the display driver is part of the graphics hardware. Most free and open-source graphics device drivers are developed by the Mesa project. The driver is made up of a compiler, a rendering API, and software which manages access to the graphics hardware.

Gnash is a media player for playing SWF files. Gnash is available both as a standalone player for desktop computers and embedded devices, as well as a plugin for the browsers still supporting NPAPI. It is part of the GNU Project and is a free and open-source alternative to Adobe Flash Player. It was developed from the gameswf project.
The Visual Component Framework (VCF) is an abandoned open source project for development under Microsoft Windows and Apple Macintosh that is distributed under the BSD license. It is an advanced C++ application framework that makes it easier to produce GUI-based C++ applications. The framework is C++ design and has built in support for rapid application development. The framework is designed to be portable over multiple platforms and compilers.

Oracle VM VirtualBox is a type-2 hypervisor for x86 virtualization developed by Oracle Corporation.
SciTech SNAP is an operating system portable, dynamically loadable, native-size 32-bit/64-bit device driver architecture. SciTech SNAP defines the architecture for loading an operating system neutral binary device driver for any type of hardware device, be it a graphics controller, audio controller, SCSI controller or network controller. SciTech SNAP drivers are source code portable between different microprocessor platforms, and the binary drivers are operating system portable within a particular microprocessor family.
Linux began in 1991 as a personal project by Finnish student Linus Torvalds: to create a new free operating system kernel. The resulting Linux kernel has been marked by constant growth throughout its history. Since the initial release of its source code in 1991, it has grown from a small number of C files under a license prohibiting commercial distribution to the 4.15 version in 2018 with more than 23.3 million lines of source code, not counting comments, under the GNU General Public License v2.
The history of Haiku, a free, open-source operating system, began in 2001. As of January 2016, as refactoring FLOSS effort of BeOS named initially "OpenBeOS". It used open sourced code of a Tracker file browser and NewOS kernel. Today, after 4 alpha and 3 beta versions, work on Haiku continues with a fourth beta planned and 'Nightly' builds available between releases.

NetBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was forked. It continues to be actively developed and is available for many platforms, including servers, desktops, handheld devices, and embedded systems.
Vulkan is a low-overhead, cross-platform API, open standard for 3D graphics and computing. Vulkan targets high-performance real-time 3D graphics applications, such as video games and interactive media. Vulkan is intended to offer higher performance and more efficient CPU and GPU usage compared to older OpenGL and Direct3D 11 APIs. It provides a considerably lower-level API for the application than the older APIs, making Vulkan comparable to Apple's Metal API and Microsoft's Direct3D 12. In addition to its lower CPU usage, Vulkan is designed to allow developers to better distribute work among multiple CPU cores.









