
The Altai Mountains, also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia and Eastern Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob have their headwaters. The massif merges with the Sayan Mountains in the northeast, and gradually becomes lower in the southeast, where it merges into the high plateau of the Gobi Desert. It spans from about 45° to 52° N and from about 84° to 99° E.

The bearded vulture, also known as the lammergeier and ossifrage, is a very large bird of prey in the monotypic genus Gypaetus. Traditionally considered an Old World vulture, it actually forms a separate minor lineage of Accipitridae together with the Egyptian vulture, its closest living relative. It is not much more closely related to the Old World vultures proper than to, for example, hawks, and differs from the former by its feathered neck. Although dissimilar, the Egyptian and bearded vulture each have a lozenge-shaped tail—unusual among birds of prey. It is vernacularly known as Homa, a bird in Iranian mythology.

The cinereous vulture is a large raptor in the family Accipitridae and distributed through much of temperate Eurasia. It is also known as the black vulture, monk vulture and Eurasian black vulture. With a body length of 1.2 m, 3.1 m (10 ft) across the wings and a maximum weight of 14 kg (31 lb), it is the largest Old World vulture and largest member of the Accipitridae family.

Kryptobaatar, also known as Gobibaatar or Tugrigbaatar, is an extinct mammalian genus dating from the Upper Cretaceous Period and identified in Central Asia. This animal was a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta, and was a member of the family Djadochtatheriidae. It lived contemporaneously with some of the dinosaurs. Its skull had a length of perhaps 3 cm.

The Eastern Gobi desert steppe is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in Mongolia and northern China. It is the easternmost of the ecoregions that make up the larger Gobi Desert. It lies between the more humid Mongolian–Manchurian grassland on the north, east, and southeast, and the drier Alashan Plateau semi-desert to the west.
Articles related to Mongolia include:

The Bayankhongor Province or Bayanhongor Aimag is one of the 21 aimags (provinces) of Mongolia. It is located in the southwest of the country and, at 116,000 square kilometers, it is one of the largest aimags. The capital of the aimag shares the provincial name, Bayankhongor.

Zavkhan, also spelt Zaukhan or Zabhkhan, is one of the 21 aimags (provinces) of Mongolia, located in the west of the country, 1,104 km from Ulaanbaatar. Its capital is Uliastai. The aimag is named after the Zavkhan River, which forms the border between Zavkhan and Gobi-Altai aimag.

Dalanzadgad is the capital of Ömnögovi Aimag in Mongolia. It is located 540 kilometers (340 mi) south of the national capital Ulaanbaatar. The altitude of the city center is 1,470 meters.

An ice field is a mass of interconnected valley glaciers on a mountain mass with protruding rock ridges or summits. They are often found in the colder climates and higher altitudes of the world where there is sufficient precipitation for them to form. The higher peaks of the underlying mountain rock that protrude through the icefields are known as nunataks. Ice fields are larger than alpine glaciers, but smaller than ice caps and ice sheets. The topography of ice fields is determined by the shape of the surrounding landforms, while ice caps have their own forms overriding underlying shapes.
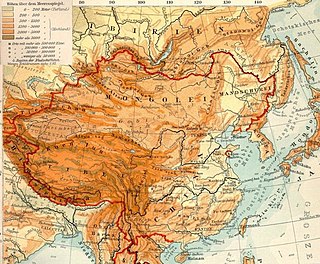
The Mongolian Plateau is an inland plateau in Asia that lies between 37°46′-53°08′N and 87°40′-122°15′E and has an area of approximately 3,200,000 square kilometers (1,200,000 sq mi). It is bounded by the Greater Hinggan Mountains in the east, the Yin Mountains to the south, the Altai Mountains to the west, and the Sayan and Khentii mountains to the north. The plateau includes the Gobi Desert as well as dry steppe regions. It has an elevation of roughly 1,000 to 1,500 meters, with the lowest point in Hulunbuir and the highest point in the Altai.

The saxaul sparrow is a passerine bird of the sparrow family Passeridae, found in parts of Central Asia. At 14–16 centimetres (5.5–6.3 in) and 25–32 grams (0.88–1.13 oz), it is among the larger sparrows. Both sexes have plumage ranging from dull grey to sandy brown, and pale brown legs. Females have less boldly coloured plumage and bills, lacking the pattern of black stripes on the male's head. The head markings of both sexes make the saxaul sparrow distinctive, and unlikely to be confused with any other bird. Vocalisations include a comparatively soft and musical chirping call, a song, and a flight call.

The Kourtaliotiko Gorge, also known as the Asomatos Gorge (Greek: Φαράγγι Ασώματου), is a gorge on the southern side of the western part of the island of Crete. It is situated where the Kourtaliotiko River flows southwards between the mountains of Kouroupa and Xiron.

The Gurvan Saikhan, is a mountain range in the Ömnögovi Province of southern Mongolia. It is named for three subranges: Baruun Saikhany Nuruu, Dund Saikhany Nuruu and Zuun Saikhany Nuruu.

Gobi Gurvansaikhan National Park is a national park in southern Mongolia. The park was established in 1993, and expanded to its current size in 2000. The park, at nearly 27,000 square kilometers, is the largest national park in Mongolia, stretching 380 km from east to west and 80 km from north to south.

The Mongolian-Manchurian grassland, also known as the Mongolian-Manchurian steppe or Gobi-Manchurian steppe, in the temperate grassland biome, is an ecoregion in East Asia covering parts of Mongolia, the Chinese Autonomous region of Inner Mongolia, and Northeast China.

Dulduityn Danzanravjaa was a prominent Mongolian writer, composer, painter, Buddhist scholar, physician and the fifth Noyon Khutagt, the Lama of the Gobi. His name is a Mongolian adaptation of the last part of the Tibetan name Lobsang Tenzin Rabgye given to Danzanravjaa by the fourth Bogd Gegeen on his visit to the Mongolian capital, Urga, in 1812 – where Danzanravjaa was also recognized as an Incarnate Lama. There are several versions concerning the origins and use of "Dulduityn". He was the fifth incarnation of the Gobi Noyon Khutagt, which is the title of a prominent line of tulkus of the Nyingmapa lineage of Tibetan Buddhism in Mongolia and was found by the personal attendant of the fourth Noyon Khutagt in 1809. It was not possible to enthrone Danzanravjaa as the fifth Noyon Hutagt because of the ban from the ruling Manchu (Qing) dynasty on recognition of this line of incarnations. Mongolia at the time was under Manchurian Qing control. He was enthroned as the Avshaa Gegeen in Ongiin Gol Monastery by Ishdonilhudev Rinpoche. He is primarily famous for his poetry, but is also known for his prophecies, and treatises on medicine, philosophy, and astrology.

The Gobi Desert is a large, cold desert and grassland region located in northern China and southern Mongolia. It is the sixth largest desert in the world. The name of the desert comes from the Mongolian word Gobi, used to refer to all of the waterless regions in the Mongolian Plateau; in Chinese, Gobi is used to refer to rocky, semi-deserts such as the Gobi itself rather than sandy deserts.

The wildlife of Mongolia consists of flora, fauna and funga found in the harsh habitats dictated by the diverse climatic conditions found throughout the country. In the north, there are salty marshes and fresh-water sources. The centre has desert steppes. In the south, there are semi deserts as well as the hot Gobi desert in the south, the fifth-largest desert in the world.

The Uvac Special Nature Reserve is a special nature reserve of the category I in Serbia. It is known for the successful project of the preservation of the griffon vulture.



















