
Continuous track or tracked treads are a system of vehicle propulsion used in tracked vehicles, running on a continuous band of treads or track plates driven by two or more wheels. The large surface area of the tracks distributes the weight of the vehicle better than steel or rubber tyres on an equivalent vehicle, enabling continuous tracked vehicles to traverse soft ground with less likelihood of becoming stuck due to sinking.

A railcar is a self-propelled railway vehicle designed to transport passengers. The term "railcar" is usually used in reference to a train consisting of a single coach, with a driver's cab at one or both ends. Some railway companies, such as the Great Western, termed such vehicles "railmotors".

A traction engine is a steam-powered tractor used to move heavy loads on roads, plough ground or to provide power at a chosen location. The name derives from the Latin tractus, meaning 'drawn', since the prime function of any traction engine is to draw a load behind it. They are sometimes called road locomotives to distinguish them from railway locomotives – that is, steam engines that run on rails.

A steamroller is a form of road roller – a type of heavy construction machinery used for leveling surfaces, such as roads or airfields – that is powered by a steam engine. The leveling/flattening action is achieved through a combination of the size and weight of the vehicle and the rolls: the smooth wheels and the large cylinder or drum fitted in place of treaded road wheels.

A high pressure watertube boiler is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. In smaller boilers, additional generating tubes are separate in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on the water-filled tubes that make up the walls of the furnace to generate steam.

Sentinel Waggon Works Ltd was a British company based in Shrewsbury, Shropshire that made steam-powered lorries, railway locomotives, and later, diesel engined lorries, buses and locomotives.

Mann's Patent Steam Cart and Wagon Company manufactured steam powered road vehicles in Leeds, England.

Straker-Squire was a British automobile manufacturer based in Bristol, and later Edmonton in North London.

A steam wagon is a steam-powered truck for carrying freight. It was the earliest form of lorry (truck) and came in two basic forms: overtype and undertype, the distinction being the position of the engine relative to the boiler. Manufacturers tended to concentrate on one form or the other.
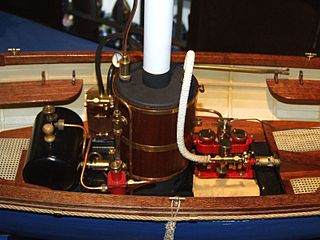
A vertical boiler is a type of fire-tube or water-tube boiler where the boiler barrel is oriented vertically instead of the more common horizontal orientation. Vertical boilers were used for a variety of steam-powered vehicles and other mobile machines, including early steam locomotives.
The Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (L&YR) operated two classes of twenty steam railmotors in total.

A vertical boiler with horizontal fire-tubes is a type of small vertical boiler, used to generate steam for small machinery. It is characterised by having many narrow fire-tubes, running horizontally.

The Sentinel boiler was a design of vertical boiler, fitted to the numerous steam wagons built by the Sentinel Waggon Works.

A transverse boiler is a boiler used to generate steam to power a vehicle. Unlike other boilers, its external drum is mounted transversely across the vehicle.

A vertical fire-tube boiler or vertical multitubular boiler is a vertical boiler where the heating surface is composed of multiple small fire-tubes, arranged vertically.
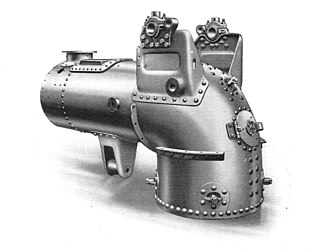
A pistol boiler is a design of steam boiler used in light steam tractors and overtype steam wagons. It is noted for the unusual shape of the firebox, a circular design intended to be self-supporting without the use of firebox stays.

A steam motor is a form of steam engine used for light locomotives and light self-propelled motor cars used on railways. The origins of steam motor cars for railways go back to at least the 1850s, if not earlier, as experimental economizations for railways or railroads with marginal budgets. These first examples, at least in North America, appear to have been fitted with light reciprocating engines, and either direct or geared drives, or geared-endless chain drives. Most incorporated a passenger carrying coach attached to the engine and its boiler. Boiler types varied in these earlier examples, with vertical boilers dominant in the first decade and then with very small diameter horizontal boilers. Other examples of steam motor cars incorporated an express-baggage or luggage type car body, with coupling apparatus provided to allow the steam motor car to draw a light passenger coach.

A steam railcar is a rail vehicle that does not require a locomotive as it contains its own steam engine. The first steam railcar was an experimental unit designed and built in 1847 by James Samuel and William Bridges Adams. In 1848, they made the Fairfield steam carriage that they sold to the Bristol and Exeter Railway, who used it for two years on a branch line.

The South African Railways Dutton road-rail tractors of 1923 were road-rail steam tractors.




















