Related Research Articles

Reelin (RELN) is a large secreted extracellular matrix glycoprotein that helps regulate processes of neuronal migration and positioning in the developing brain by controlling cell–cell interactions. Besides this important role in early development, reelin continues to work in the adult brain. It modulates synaptic plasticity by enhancing the induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation. It also stimulates dendrite and dendritic spine development and regulates the continuing migration of neuroblasts generated in adult neurogenesis sites like the subventricular and subgranular zones. It is found not only in the brain but also in the liver, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, Fallopian tube, breast and in comparatively lower levels across a range of anatomical regions.
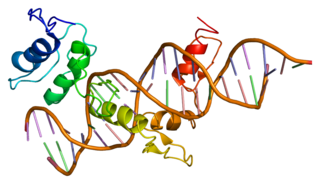
Zinc finger protein GLI1 also known as glioma-associated oncogene is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLI1 gene. It was originally isolated from human glioblastoma cells.

Zinc finger protein GLI2 also known as GLI family zinc finger 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLI2 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a transcription factor.

Zinc finger protein GLI3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLI3 gene.

The Disabled-1 (Dab1) gene encodes a key regulator of Reelin signaling. Reelin is a large glycoprotein secreted by neurons of the developing brain, particularly Cajal-Retzius cells. DAB1 functions downstream of Reln in a signaling pathway that controls cell positioning in the developing brain and during adult neurogenesis. It docks to the intracellular part of the Reelin very low density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) and apoE receptor type 2 (ApoER2) and becomes tyrosine-phosphorylated following binding of Reelin to cortical neurons. In mice, mutations of Dab1 and Reelin generate identical phenotypes. In humans, Reelin mutations are associated with brain malformations and mental retardation. In mice, Dab1 mutation results in the scrambler mouse phenotype.

A reeler is a mouse mutant, so named because of its characteristic "reeling" gait. This is caused by the profound underdevelopment of the mouse's cerebellum, a segment of the brain responsible for locomotion. The mutation is autosomal and recessive, and prevents the typical cerebellar folia from forming.

CLOCK or Clock is a gene encoding a basic helix-loop-helix-PAS transcription factor that is believed to affect both the persistence and period of circadian rhythms.

ABCD1 is a protein that transfers fatty acids into peroxisomes.

Myosin VIIA is protein that in humans is encoded by the MYO7A gene. Myosin VIIA is a member of the unconventional myosin superfamily of proteins. Myosins are actin binding molecular motors that use the enzymatic conversion of ATP - ADP + inorganic phosphate (Pi) to provide the energy for movement.
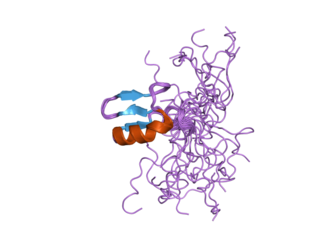
Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 7 also known as ATP-dependent helicase CHD7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CHD7 gene.

Alsin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ALS2 gene. ALS2 orthologs have been identified in all mammals for which complete genome data are available.

E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RAD18 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RAD18 gene.
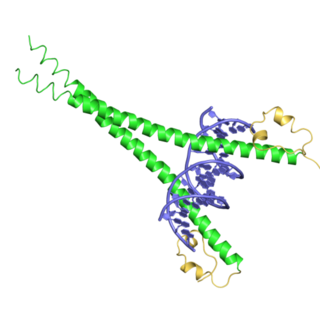
Transcription factor MafG is a bZip Maf transcription factor protein that in humans is encoded by the MAFG gene.

Homeobox protein Hox-A3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HOXA3 gene.

Carbonic anhydrase-related protein is an protein that in humans is encoded by the CA8 gene. The CA8 protein lacks the catalytic activity of other carbonic anhydrase enzymes. A rare, autosomal recessive form of cerebellar ataxia known as "cerebellar ataxia, mental retardation, and dysequilibrium syndrome 3" (CAMRQ3) is caused by mutations in the CA8 gene.

Protein Jumonji is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JARID2 gene. JARID2 is a member of the alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylase superfamily.

Krueppel-like factor 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF17 gene.
Scrambler is a spontaneous mouse mutant lacking a functional DAB1 gene, resulting in a phenotype resembling that seen in the reeler mouse. The strain was first described by Sweet et al. in 1996.
Reeler domain is a protein domain.
Cajal–Retzius cells are a heterogeneous population of morphologically and molecularly distinct reelin-producing cell types in the marginal zone/layer I of the developmental cerebral cortex and in the immature hippocampus of different species and at different times during embryogenesis and postnatal life.
References
- ↑ Yoneshima, H; Nagata, E; Matsumoto, M; Yamada, M; Nakajima, K; Miyata, T; Ogawa, M; Mikoshiba, K (1997). "A novel neurological mutant mouse, yotari, which exhibits reeler-like phenotype but expresses CR-50 antigen/reelin". Neuroscience Research. 29 (3): 217–23. doi:10.1016/S0168-0102(97)00088-6. PMID 9436647. S2CID 14374275.
- ↑ Sheldon, M; Rice, DS; D'arcangelo, G; Yoneshima, H; Nakajima, K; Mikoshiba, K; Howell, BW; Cooper, JA; et al. (1997). "Scrambler and yotari disrupt the disabled gene and produce a reeler-like phenotype in mice". Nature. 389 (6652): 730–3. Bibcode:1997Natur.389..730S. doi:10.1038/39601. PMID 9338784. S2CID 4414738.