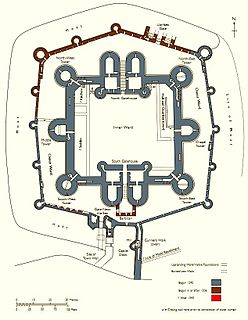
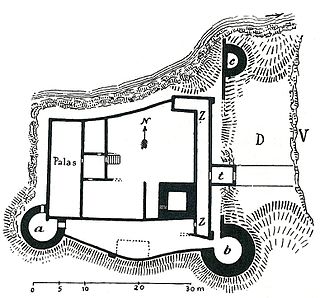
A Zingel (lat. cingulum = "belt") is part of the outer bailey of a castle. [1] The term is German.

Latin is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. The Latin alphabet is derived from the Etruscan and Greek alphabets, and ultimately from the Phoenician alphabet.

An outer bailey or outer ward is the defended outer enclosure of a castle. It protects the inner bailey and usually contains those ancillary buildings used for the management of the castle or the supply of its occupants. These domestic buildings could include workshops, livestock stalls and stables; storage facilities such as barns, sheds and granaries, as well as quarters for servants such as maids, farm workers, and even the castle governors or castellans. In many cases there was also a brewery, a bakehouse and a kitchen, if the latter was not located in the hall or palas. An outer bailey was often called a base court in England. Depending on topography it could also be referred to as a lower bailey or lower ward, the keep being in the upper bailey or ward. Chepstow Castle has lower, middle and upper baileys.

A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages by predominantly the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word castle, but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Usage of the term has varied over time and has been applied to structures as diverse as hill forts and country houses. Over the approximately 900 years that castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls and arrowslits, were commonplace.
Originally it was taken to be the palisade, the bank on which it stood and the ditch in front of it. In the High and Late Middle Ages the term also included the outer curtain wall or enceinte of a castle or city, otherwise known as the "zingel wall" (Zingelmauer) which conformed to the surrounding terrain.

A palisade—sometimes called a stakewall or a paling—is typically a fence or wall made from iron or wooden stakes, or tree trunks and used as a defensive structure or enclosure.

A ditch in military engineering is an obstacle, designed to slow down or break up an attacking force, while a trench is intended to provide cover to the defenders. In military fortifications the side of a ditch farthest from the enemy and closest to the next line of defence is known as the scarp while the side of a ditch closest to the enemy is known as the counterscarp.
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that commenced around 1000 and lasted until around 1250. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around 1500.
Often also called a "mantle wall" (Mantelmauer) or Bering, the term survives today in German street names, for example, in Eckernförde, Hildesheim, Husum, Meldorf or Salzgitter. Derivative names are found in Bremerhaven (Zingelke), Essen (Zingelpfad) or Niemberg (Zingelrain). In all there are around 30 roads and streets in Germany whose names are derived from this term. In addition, the name has also been used as a surname.

Eckernförde (German pronunciation: [ɛkɐnˈføːɐ̯də] is a German town in Schleswig-Holstein, Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde, on the coast of the Baltic Sea approximately 30 km north-west of Kiel. The population is about 23,000. Eckernförde is a popular tourist destination in northern Germany.

Hildesheim[ˈhɪldəsˌhaɪ̯m](

Husum is the capital of the Kreis (district) Nordfriesland in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. The town was the birthplace of the novelist Theodor Storm, who coined the epithet "the grey town by the sea". It is also the home of the annual international piano festival Raritäten der Klaviermusik founded in 1986.