
Origami is the Japanese art of paper folding. In modern usage, the word "origami" is often used as an inclusive term for all folding practices, regardless of their culture of origin. The goal is to transform a flat square sheet of paper into a finished sculpture through folding and sculpting techniques. Modern origami practitioners generally discourage the use of cuts, glue, or markings on the paper. Origami folders often use the Japanese word kirigami to refer to designs which use cuts.
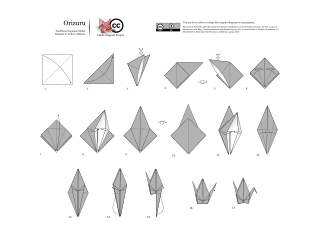
The Yoshizawa–Randlett system is a diagramming system used to describe the folds of origami models. Many origami books begin with a description of basic origami techniques which are used to construct the models. There are also a number of standard bases which are commonly used as a first step in construction. Models are typically classified as requiring low, intermediate or high skill depending on the complexity of the techniques involved in the construction.

The discipline of origami or paper folding has received a considerable amount of mathematical study. Fields of interest include a given paper model's flat-foldability, and the use of paper folds to solve up-to cubic mathematical equations.
Peter Engel is an American origami artist and theorist, science writer, graphic designer, and architect. He has written several books on Origami, including Origami from Angelfish to Zen, 10-Fold Origami: Fabulous Paperfolds You Can Make in Just 10 Steps!, and Origami Odyssey.

Robert Harbin was a South African-born magician and author. He is noted as the inventor of a number of classic illusions, including the Zig Zag Girl. He also became an authority on origami.

Chinese paper folding, or zhezhi, is the art of paper folding that originated in medieval China.

Robert James Lang is an American physicist who is also one of the foremost origami artists and theorists in the world. He is known for his complex and elegant designs, most notably of insects and animals. He has studied the mathematics of origami and used computers to study the theories behind origami. He has made great advances in making real-world applications of origami to engineering problems.

Akira Yoshizawa was a Japanese origamist, considered to be the grandmaster of origami. He is credited with raising origami from a craft to a living art. According to his own estimation made in 1989, he created more than 50,000 models, of which only a few hundred designs were presented as diagrams in his 18 books. Yoshizawa acted as an international cultural ambassador for Japan throughout his career. In 1983, Emperor Hirohito awarded him the Order of the Rising Sun, 5th class, one of the highest honors bestowed in Japan.

Wet-folding is an origami technique developed by Akira Yoshizawa that employs water to dampen the paper so that it can be manipulated more easily. This process adds an element of sculpture to origami, which is otherwise purely geometric. Wet-folding is used very often by professional folders for non-geometric origami, such as animals. Wet-folders usually employ thicker paper than what would usually be used for normal origami, to ensure that the paper does not tear.

A fortune teller is a form of origami used in children's games. Parts of the fortune teller are labelled with colors or numbers that serve as options for a player to choose from, and on the inside are eight flaps, each concealing a message. The person operating the fortune teller manipulates the device based on the choices made by the player, and finally one of the hidden messages is revealed. These messages may purport to answer questions, or they may be activities that the player must perform.
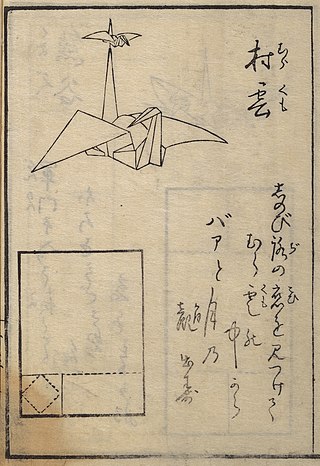
The history of origami followed after the invention of paper and was a result of paper's use in society. In the detailed Japanese classification, origami is divided into stylized ceremonial origami and recreational origami, and only recreational origami is generally recognized as origami. However, this page describes the history of both ceremonial and recreational origami.
Lillian Vorhaus Oppenheimer was an origami pioneer from New York City. Becoming a leading figure in the art form in her later years, Oppenheimer is credited with popularizing it in the United States. She adopted the Japanese word origami instead of the English paper folding, and the foreign term became established in the English language due to her efforts.

Three Musicians, also known as Musicians with Masks or Musicians in Masks, is a large oil painting created by Spanish artist Pablo Picasso. He painted two versions of Three Musicians. Both versions were completed in the summer of 1921 in Fontainebleau near Paris, France, in the garage of a villa that Picasso was using as his studio. They exemplify the Synthetic Cubist style; the flat planes of color and "intricate puzzle-like composition" giving the appearance of cutout paper with which the style originated. These paintings each colorfully represent three figures wearing masks. The two figures in the center and left are wearing the costumes of Pierrot and Harlequin from the popular Italian theater Commedia dell'arte, and the figure on the right is dressed as a monk. In one version, there also is a dog underneath the table.

Kawasaki's theorem or Kawasaki–Justin theorem is a theorem in the mathematics of paper folding that describes the crease patterns with a single vertex that may be folded to form a flat figure. It states that the pattern is flat-foldable if and only if alternatingly adding and subtracting the angles of consecutive folds around the vertex gives an alternating sum of zero. Crease patterns with more than one vertex do not obey such a simple criterion, and are NP-hard to fold.
Paper toys are constructed in several ways, by folding, as in paper airplanes, paper fortune tellers or Origami, or by cutting, decorating or assembling pieces of paper with glue or tape to create a paper doll or paper model.
Ligia Montoya was an Argentinian paper-folding artist, who played an important role in all aspects of the 'golden age' of the international origami movement from the 1950s, from which developed modern artistic origami—that is, innovative paper-folding exploring a variety of different approaches, rather than repeating limited traditional figures.
Samuel L Randlett is an American origami artist who helped develop the modern system for diagramming origami folds. Together with Robert Harbin he developed the notation introduced by Akira Yoshizawa to form what is now called the Yoshizawa-Randlett system. This was first described in Samuel Randlett's Art of Origami in 1961.

George Rhoads was a contemporary American painter, sculptor and origami master. He was best known for his whimsical audiokinetic sculptures in airports, science museums, shopping malls, children's hospitals, and other public places throughout the world.
Tomohiro Tachi is a Japanese academic who studies origami from an interdisciplinary perspective, combining approaches from the mathematics of paper folding, structural rigidity, computational geometry, architecture, and materials science. His work was profiled in "The Origami Revolution" (2017), part of the Nova series of US science documentaries. He is a professor at the University of Tokyo.

















