Related Research Articles
A Byzantine fault is a condition of a system, particularly a distributed computing system, where a fault occurs such that different symptoms are presented to different observers, including imperfect information on whether a system component has failed. The term takes its name from an allegory, the "Byzantine generals problem", developed to describe a situation in which, to avoid catastrophic failure of a system, the system's actors must agree on a strategy, but some of these actors are unreliable in such a way as to cause other (good) actors to disagree on the strategy and they may be unaware of the disagreement.
Ada Programming Support Environment or APSE, was a specification for a programming environment to support software development in the Ada programming language. This represented the second stage of the U.S. military Ada project; once the language was implemented, it was felt necessary to specify and implement a standard set of tools, hence the APSE. CAIS-A, Common APSE Interface Set A, was defined in MIL STD-1838A.
SUPER-UX was a version of the Unix operating system from NEC that is used on its SX series of supercomputers.

Shlomi Dolev is a Rita Altura Trust Chair Professor in Computer Science at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) and the head of the BGU Negev Hi-Tech Faculty Startup Accelerator.

Aircrack-ng is a network software suite consisting of a detector, packet sniffer, WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK cracker and analysis tool for 802.11 wireless LANs. It works with any wireless network interface controller whose driver supports raw monitoring mode and can sniff 802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g traffic. Packages are released for Linux and Windows.

Edge computing is a distributed computing model that brings computation and data storage closer to the sources of data. More broadly, it refers to any design that pushes computation physically closer to a user, so as to reduce the latency compared to when an application runs on a centralized data centre.
A gossip protocol or epidemic protocol is a procedure or process of computer peer-to-peer communication that is based on the way epidemics spread. Some distributed systems use peer-to-peer gossip to ensure that data is disseminated to all members of a group. Some ad-hoc networks have no central registry and the only way to spread common data is to rely on each member to pass it along to their neighbors.
Virgil Dorin Gligor is a Romanian-American professor of electrical and computer engineering who specializes in the research of network security and applied cryptography.

Alexander G. Fraser, also known as A. G. Fraser and Sandy Fraser, was a noted British-American computer scientist and the former Chief Scientist of AT&T.
Social cloud computing, also peer-to-peer social cloud computing, is an area of computer science that generalizes cloud computing to include the sharing, bartering and renting of computing resources across peers whose owners and operators are verified through a social network or reputation system. It expands cloud computing past the confines of formal commercial data centers operated by cloud providers to include anyone interested in participating within the cloud services sharing economy. This in turn leads to more options, greater economies of scale, while bearing additional advantages for hosting data and computing services closer to the edge where they may be needed most.

Jayadev Misra is an Indian-born computer scientist who has spent most of his professional career in the United States. He is the Schlumberger Centennial Chair Emeritus in computer science and a University Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus at the University of Texas at Austin. Professionally he is known for his contributions to the formal aspects of concurrent programming and for jointly spearheading, with Sir Tony Hoare, the project on Verified Software Initiative (VSI).
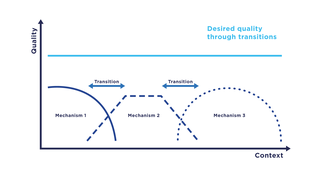
Transition refers to a computer science paradigm in the context of communication systems which describes the change of communication mechanisms, i.e., functions of a communication system, in particular, service and protocol components. In a transition, communication mechanisms within a system are replaced by functionally comparable mechanisms with the aim to ensure the highest possible quality, e.g., as captured by the quality of service.

David Atienza Alonso is a Spanish/Swiss scientist in the disciplines of computer and electrical engineering. His research focuses on hardware‐software co‐design and management for energy‐efficient and thermal-aware computing systems, always starting from a system‐level perspective to the actual electronic design. He is a full professor of electrical and computer engineering at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (EPFL) and the head of the Embedded Systems Laboratory (ESL). He is an IEEE Fellow (2016), and an ACM Fellow (2022).

Ümit V. Çatalyürek is a professor of computer science at the Georgia Institute of Technology, and adjunct professor in department of Biomedical Informatics at the Ohio State University. He is known for his work on graph analytics, parallel algorithms for scientific applications, data-intensive computing, and large scale genomic and biomedical applications. He was the director of the High Performance Computing Lab at the Ohio State University. He was named Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in 2016 for contributions to combinatorial scientific computing and parallel computing.

Richard Vuduc is a tenured professor of computer science at the Georgia Institute of Technology. His research lab, The HPC Garage, studies high-performance computing, scientific computing, parallel algorithms, modeling, and engineering. He is a member of the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM). As of 2022, Vuduc serves as Vice President of the SIAM Activity Group on Supercomputing. He has co-authored over 200 articles in peer-reviewed journals and conferences.

Ujjwal Maulik is an Indian Computer Scientist and a Professor. He is the former Head of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at Jadavpur University, Kolkata, West Bengal, India. He has worked in many countries including India, US, Germany, France, Australia, China, Italy, Poland, Mexico, Slovenia and Hungary. He also held the position of the principal-in-charge and the head of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at Kalyani Government Engineering College.

Hussein S. M. Zedan was a computer scientist of Egyptian descent, mainly based in the United Kingdom.

Zygmunt J. Haas is a professor and distinguished chair in computer science, University of Texas at Dallas (UTD) also the professor emeritus in electrical and computer engineering, Cornell University. His research interests include ad hoc networks, wireless networks, sensor networks, and zone routing protocols.
A Network Coordinate System is a system for predicting characteristics such as the latency or bandwidth of connections between nodes in a network by assigning coordinates to nodes. More formally, It assigns a coordinate embedding to each node in a network using an optimization algorithm such that a predefined operation estimates some directional characteristic of the connection between node and .
References
- 1 2 Babaoglu, O.; Joy, W. (December 1981). "Converting a Swap-Based System to do Paging in an Architecture Lacking Page-Reference Bits" (PDF). ACM SIGOPS Operating Systems Review. 15 (5): 78–86. doi:10.1145/1067627.806595. hdl:1813/6314 . Retrieved February 10, 2022.
- ↑ Babaoglu, O.; Ferrari, D. (1983). "Two-Level Replacement Decisions in Paging Stores" (PDF). IEEE Transactions on Computers. C-32 (12). IEEE: 1151–1159. doi:10.1109/tc.1983.1676176. S2CID 9451830.
- ↑ Babaoglu, O.; Bartoli, A.; Dini, G. (1997). "Enriched view synchrony: a programming paradigm for partitionable asynchronous distributed systems" (PDF). IEEE Transactions on Computers. 46 (6): 642–658. doi:10.1109/12.600823. ISSN 0018-9340.
- ↑ Babaoglu, O.; Drummond, R. (1985). "Streets of Byzantium: Network Architectures for Fast Reliable Broadcasts" (PDF). IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering. SE-11 (6): 546–554. doi:10.1109/tse.1985.232247. ISSN 0098-5589. S2CID 1426166.
- ↑ Davoli, R.; Giachini, L.-A.; Babaoglu, O.; Amoroso, A.; Alvisi, L. (1996). "Parallel computing in networks of workstations with Paralex" (PDF). IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems. 7 (4): 371–384. doi:10.1109/71.494632. ISSN 1045-9219.
- ↑ Babaoglu, O.; Davoli, R.; Montresor, A. (2001). "Group communication in partitionable systems: specification and algorithms" (PDF). IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering. 27 (4): 308–336. doi:10.1109/32.917522. ISSN 0098-5589.
- ↑ Jelasity, Márk; Montresor, Alberto; Babaoglu, Ozalp (2004), "A Modular Paradigm for Building Self-Organizing Peer-to-Peer Applications", Engineering Self-Organising Systems, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 2977, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 265–282, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-24701-2_18, ISBN 978-3-540-21201-0 , retrieved 2023-08-21
- ↑ Babaoglu, O.; Meling, H.; Montresor, A. (2002). "Anthill: A framework for the development of agent-based peer-to-peer systems" (PDF). Proceedings 22nd International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems. IEEE Comput. Soc. pp. 15–22. doi:10.1109/icdcs.2002.1022238. ISBN 0-7695-1585-1. S2CID 6042644.
- ↑ Sîrbu, A.; Babaoglu, O. (2016). "Towards operator-less data centers through data-driven, predictive, proactive autonomics" (PDF). Cluster Computing. 19 (2): 865–878. arXiv: 1606.04456 . doi:10.1007/s10586-016-0564-y. ISSN 1386-7857. S2CID 254377566.
- ↑ Jelasity, Márk; Montresor, Alberto; Babaoglu, Ozalp (August 2005). "Gossip-based aggregation in large dynamic networks" (PDF). ACM Transactions on Computer Systems. 23 (3): 219–252. doi:10.1145/1082469.1082470. ISSN 0734-2071. S2CID 2608879.
- ↑ Jelasity, Márk; Montresor, Alberto; Babaoglu, Ozalp (August 2009). "T-Man: Gossip-based fast overlay topology construction" (PDF). Computer Networks. 53 (13): 2321–2339. doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2009.03.013. ISSN 1389-1286.
- ↑ Babaoglu, O.; Jelasity, M. (2008). "Self-* properties through gossiping" (PDF). Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 366 (1881): 3747–3757. Bibcode:2008RSPTA.366.3747B. doi:10.1098/rsta.2008.0122. ISSN 1364-503X. PMID 18672459. S2CID 7710850.
- ↑ Babaoglu; Canright; Deutsch; Caro; Ducatelle; Gambardella; Ganguly; Jelasity; Montemanni; Montresor; Urnes (2006). "Design Patterns from Biology for Distributed Computing" (PDF). ACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive Systems. 1 (1): 26–66. doi:10.1145/1152934.1152937. S2CID 1024220.
- ↑ Arteconi, Stefano; Hales, David; Babaoglu, Ozalp (2007), "Greedy Cheating Liars and the Fools Who Believe Them", Engineering Self-Organising Systems, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4335, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp. 161–175, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-69868-5_11, ISBN 978-3-540-69867-8 , retrieved 2023-08-21
- ↑ Babaoglu, O.; Marzolla, M. (2014). "The people's cloud" (PDF). IEEE Spectrum. 51 (10): 50–55. doi:10.1109/MSPEC.2014.6905491. ISSN 0018-9235. S2CID 10784456.
- ↑ Sîrbu, Alina; Babaoglu, Ozalp (2015), "A Holistic Approach to Log Data Analysis in High-Performance Computing Systems: The Case of IBM Blue Gene/Q", Euro-Par 2015: Parallel Processing Workshops, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 9523, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 631–643, arXiv: 1410.4449 , doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-27308-2_51 , ISBN 978-3-319-27307-5
- ↑ Marshall Kirk McKusick (1999–2001). Twenty Years of Berkeley Unix : From AT&T-Owned to Freely Redistributable. From the book Open Sources: Voices from the Open Source Revolution. O'Reilly. ISBN 1-56592-582-3 . Retrieved February 10, 2022.