
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the north–south position of a point on the Earth's surface. Latitude is an angle which ranges from 0° at the Equator to 90° at the poles. Lines of constant latitude, or parallels, run east–west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude is used together with longitude to specify the precise location of features on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term latitude should be taken to be the geodetic latitude as defined below. Briefly, geodetic latitude at a point is the angle formed by the vector perpendicular to the ellipsoidal surface from that point, and the equatorial plane. Also defined are six auxiliary latitudes which are used in special applications.

Original sin, also called ancestral sin, is a Christian belief in the state of sin in which humanity has existed since the fall of man, stemming from Adam and Eve's rebellion in Eden, namely the sin of disobedience in consuming the forbidden fruit from the tree of the knowledge of good and evil. This condition has been characterized in many ways, ranging from something as insignificant as a slight deficiency, or a tendency toward sin yet without collective guilt, referred to as a "sin nature", to something as drastic as total depravity or automatic guilt of all humans through collective guilt.
In a religious context, sin is an act of transgression against divine law. In Islamic ethics, Muslims see sin as anything that goes against the commands of Allah (God). Judaism regards the violation of any of the 613 commandments as a sin.

In mathematics, a spherical coordinate system is a coordinate system for three-dimensional space where the position of a point is specified by three numbers: the radial distance of that point from a fixed origin, its polar angle measured from a fixed zenith direction, and the azimuth angle of its orthogonal projection on a reference plane that passes through the origin and is orthogonal to the zenith, measured from a fixed reference direction on that plane. It can be seen as the three-dimensional version of the polar coordinate system.

In mathematics, the trigonometric functions are functions of an angle. They relate the angles of a triangle to the lengths of its sides. Trigonometric functions are important in the study of triangles and modeling periodic phenomena, among many other applications.
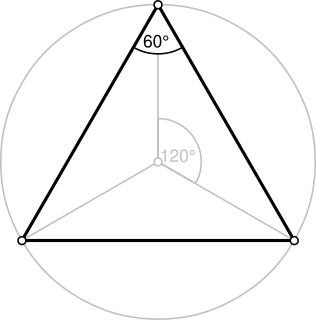
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted .

The seven deadly sins, also known as the capital vices or cardinal sins, is a grouping and classification of vices within Christian teachings. Behaviours or habits are classified under this category if they directly give birth to other immoralities. According to the standard list, they are pride, greed, lust, envy, gluttony, wrath and sloth, which are also contrary to the seven virtues. These sins are often thought to be abuses or excessive versions of one's natural faculties or passions.

A great circle, also known as an orthodrome, of a sphere is the intersection of the sphere and a plane that passes through the center point of the sphere. A great circle is the largest circle that can be drawn on any given sphere. Any diameter of any great circle coincides with a diameter of the sphere, and therefore all great circles have the same center and circumference as each other. This special case of a circle of a sphere is in opposition to a small circle, that is, the intersection of the sphere and a plane that does not pass through the center. Every circle in Euclidean 3-space is a great circle of exactly one sphere.

In astronomy, a celestial coordinate system is a system for specifying positions of celestial objects: satellites, planets, stars, galaxies, and so on. Coordinate systems can specify an object's position in three-dimensional space or plot merely its direction on a celestial sphere, if the object's distance is unknown or trivial.
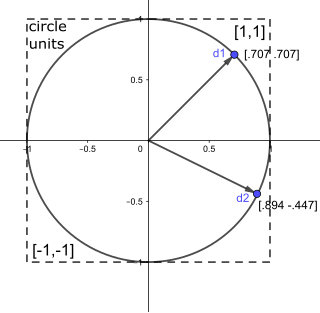
In mathematics, a unit vector in a normed vector space is a vector of length 1. A unit vector is often denoted by a lowercase letter with a circumflex, or "hat": . The term direction vector is used to describe a unit vector being used to represent spatial direction, and such quantities are commonly denoted as d. Two 2D direction vectors, d1 and d2 are illustrated. 2D spatial directions represented this way are numerically equivalent to points on the unit circle.
In vector calculus, the Jacobian matrix is the matrix of all first-order partial derivatives of a vector-valued function. When the matrix is a square matrix, both the matrix and its determinant are referred to as the Jacobian in literature.

A sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical curve that describes a smooth periodic oscillation. A sine wave is a continuous wave. It is named after the function sine, of which it is the graph. It occurs often in pure and applied mathematics, as well as physics, engineering, signal processing and many other fields. Its most basic form as a function of time (t) is:
The plus-minus sign (±) is a mathematical symbol with multiple meanings.
A sub-orbital spaceflight is a spaceflight in which the spacecraft reaches outer space, but its trajectory intersects the atmosphere or surface of the gravitating body from which it was launched, so that it will not complete one orbital revolution.

In mathematics, the sine is a trigonometric function of an angle. The sine of an acute angle is defined in the context of a right triangle: for the specified angle, it is the ratio of the length of the side that is opposite that angle to the length of the longest side of the triangle.
The Sacrament of Penance and Reconciliation is one of the seven sacraments of the Catholic Church, in which the faithful obtain absolution for the sins committed against God and neighbour and are reconciled with the community of the Church. By this sacrament Catholics believe they are freed from sins committed after baptism. The sacrament of Penance is considered the normal way to be absolved from mortal sin, by which one would otherwise possibly condemn oneself to Hell. Catholic theology regarding the forgiveness of sins debates whether Christ at the judgment of the individual after their death would allow those with unconfessed mortal sins a chance to repent and save themselves – especially those who had not made plans to confess, or were not mentally ill, coerced, or suicidal. While persons with certain unconfessed mortal sins that were under some form of censure still at their death might not be allowed a Catholic Funeral Mass and burial rites, and while Catholics with unconfessed mortal sins may not receive Communion, these matters, though related, are not the same as whether an individual with unconfessed serious sins is condemned to Hell.

Jorge Arias is a Mexican-American professional wrestler currently signed to WWE, where he performs on the SmackDown brand under the ring name Sin Cara.

Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships involving lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies.

The Seven Deadly Sins is a Japanese fantasy manga series written and illustrated by Nakaba Suzuki. It has been serialized in Kodansha's Weekly Shōnen Magazine since October 2012, with the chapters collected into thirty-one tankōbon volumes as of April 17, 2018. The manga features a setting similar to the European Middle Ages, with its titular group of knights representing the seven deadly sins.















