A Ziegler–Natta catalyst, named after Karl Ziegler and Giulio Natta, is a catalyst used in the synthesis of polymers of 1-alkenes (alpha-olefins). Two broad classes of Ziegler–Natta catalysts are employed, distinguished by their solubility:

Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl4. It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. TiCl4 is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as “tickle” or “tickle 4”, as a phonetic representation of the symbols of its molecular formula.

Hafnium(IV) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula HfCl4. This colourless solid is the precursor to most hafnium organometallic compounds. It has a variety of highly specialized applications, mainly in materials science and as a catalyst.

Titanocene dichloride is the organotitanium compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2TiCl2, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiCl2. This metallocene is a common reagent in organometallic and organic synthesis. It exists as a bright red solid that slowly hydrolyzes in air. It shows antitumour activity and was the first non-platinum complex to undergo clinical trials as a chemotherapy drug.

Zirconium(IV) chloride, also known as zirconium tetrachloride, is an inorganic compound frequently used as a precursor to other compounds of zirconium. This white high-melting solid hydrolyzes rapidly in humid air.

In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by haptic, covalent bonds to two arene (ring) ligands. The arenes have the formula CnHn, substituted derivatives and heterocyclic derivatives. Because the metal is usually situated between the two rings, it is said to be "sandwiched". A special class of sandwich complexes are the metallocenes.

Organoactinide chemistry is the science exploring the properties, structure, and reactivity of organoactinide compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to actinide chemical bond.

Organotitanium chemistry is the science of organotitanium compounds describing their physical properties, synthesis, and reactions. Organotitanium compounds in organometallic chemistry contain carbon-titanium chemical bonds. They are reagents in organic chemistry and are involved in major industrial processes.

Dicarbonylbis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium is the chemical compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2Ti(CO)2, abbreviated Cp2Ti(CO)2. This maroon-coloured, air-sensitive species is soluble in aliphatic and aromatic solvents. It has been used for the deoxygenation of sulfoxides, reductive coupling of aromatic aldehydes and reduction of aldehydes.

Organozirconium chemistry is the science of exploring the properties, structure, and reactivity of organozirconium compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing chemical bonds between carbon and zirconium. Organozirconium compounds have been widely studied, in part because they are useful catalysts in Ziegler-Natta polymerization.

2,2′-Bis(2-indenyl) biphenyl is an organic compound with the formula [C6H4C9H7]2. The compound is the precursor, upon deprotonation, to ansa-metallocene complexes within the area of transition metal indenyl complexes.
In organometallic chemistry, a transition metal indenyl complex is a coordination compound that contains one or more indenyl ligands. The indenyl ligand is formally the anion derived from deprotonation of indene. The η5-indenyl ligand is related to the η5cyclopentadienyl anion (Cp), thus indenyl analogues of many cyclopentadienyl complexes are known. Indenyl ligands lack the 5-fold symmetry of Cp, so they exhibit more complicated geometries. Furthermore, some indenyl complexes also exist with only η3-bonding mode. The η5- and η3-bonding modes sometimes interconvert.
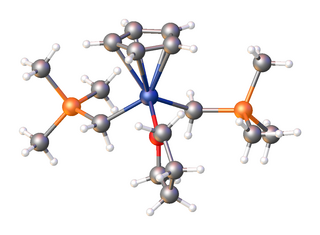
Organoscandium chemistry is an area with organometallic compounds focused on compounds with at least one carbon to scandium chemical bond. The interest in organoscandium compounds is mostly academic but motivated by potential practical applications in catalysis, especially in polymerization. A common precursor is scandium chloride, especially its THF complex.
In organometallic chemistry, bent metallocenes are a subset of metallocenes. In bent metallocenes, the ring systems coordinated to the metal are not parallel, but are tilted at an angle. A common example of a bent metallocene is Cp2TiCl2. Several reagents and much research is based on bent metallocenes.
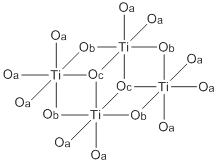
Titanium ethoxide is a chemical compound with the formula Ti4(OCH2CH3)16. It is a commercially available colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents but hydrolyzes readily. Its structure is more complex than suggested by its empirical formula. Like other alkoxides of titanium(IV) and zirconium(IV), it finds used in organic synthesis and materials science.

Titanocene pentasulfide is the organotitanium compound with the formula (C5H5)2TiS5, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiS5. This metallocene exists as a bright red solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is of academic interest as a precursor to unusual allotropes of elemental sulfur as well as some related inorganic rings.
Magnesocene, also known as bis(cyclopentadienyl)magnesium(II) and sometimes abbreviated as MgCp2, is an organometallic compound with the formula Mg(η5-C5H5)2. It is an example of an s-block main group sandwich compound, structurally related to the d-block element metallocenes, and consists of a central magnesium atom sandwiched between two cyclopentadienyl rings.

(Cyclopentadienyl)titanium trichloride is an organotitanium compound with the formula (C5H5)TiCl3. It is a moisture sensitive orange solid. The compound adopts a piano stool geometry.

(Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)titanium trichloride is an organotitanium compound with the formula Cp*TiCl3 (Cp* = C5(CH3)5). It is an orange solid. The compound adopts a piano stool geometry. An early synthesis involve the combination of lithium pentamethylcyclopentadienide and titanium tetrachloride.

Hafnocene dichloride is the organohafnium compound with the formula (C5H5)2HfCl2. It is a white solid that is sparingly soluble in some organic solvents. The lighter homologues zirconacene dichloride and titanocene dichloride have received much more attention. While hafnocene is only of academic interest, some more soluble derivatives are precatalysts for olefin polymerization. Moreso than the Zr analogue, this compound is highly resistant to reduction.















