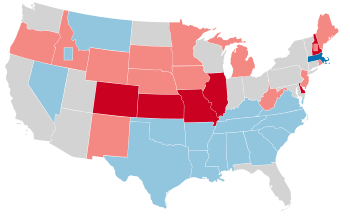
The 1978 United States Senate elections were held on November 7, in the middle of Democratic President Jimmy Carter's term. The 33 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies.

The 1976 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate. Held on November 2, the 33 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections. They coincided with Democrat Jimmy Carter's presidential election and the United States Bicentennial celebration. Although almost half of the seats decided in this election changed parties, Carter's narrow victory did not provide coattails for the Democratic Party. Each party flipped seven Senate seats, although, one of the seats flipped by Democrats was previously held by a Conservative.

The 1964 United States Senate elections were held on November 3. The 33 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. They coincided with the election of President Lyndon B. Johnson by an overwhelming majority, to a full term. His Democratic Party picked up a net two seats from the Republicans. As of 2023, this was the last time either party has had a two-thirds majority in the Senate, which allowed the Senate Democrats to override a veto, propose constitutional amendments, or convict and expel certain officials without any votes from Senate Republicans. However, internal divisions would have prevented the Democrats from having done so. The Senate election cycle coincided with Democratic gains in the House in the same year.

The 1954 United States Senate elections was a midterm election in the first term of Dwight D. Eisenhower's presidency. The 32 Senate seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and six special elections were held to fill vacancies. Eisenhower's Republican party lost a net of two seats to the Democratic opposition. This small change was just enough to give Democrats control of the chamber with the support of an Independent who agreed to caucus with them, he later officially joined the party in April 1955.

The 1952 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate which coincided with the election of Dwight D. Eisenhower to the presidency by a large margin. The 32 Senate seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and three special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republicans took control of the Senate by managing to make a net gain of two seats. However, Wayne Morse (R-OR) became an independent forcing Republicans to rely on Vice President Richard Nixon's tie-breaking vote, although Republicans maintained a 48–47–1 plurality. Throughout the next Congress, Republicans were able to restore their 49–46–1 majority. This was the third time, as well as second consecutive, in which a sitting Senate leader lost his seat.

The 1948 United States Senate elections were elections which coincided with the election of Democratic President Harry S. Truman for a full term. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and one special election was held to fill a vacancy. Truman had campaigned against an "obstructionist" Congress that had blocked many of his initiatives, and in addition the U.S. economy recovered from the postwar recession of 1946–1947 by election day. Thus Truman was rewarded with a Democratic gain of nine seats in the Senate, enough to give them control of the chamber. This was the last time until 2020 that Democrats flipped a chamber of Congress in a presidential election cycle.

The 1944 United States Senate elections coincided with the re-election of Franklin D. Roosevelt to his fourth term as president. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and three special elections were held to fill vacancies.
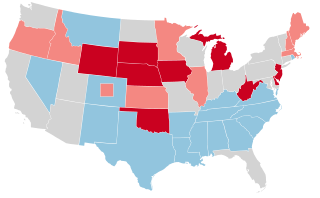
The 1942 United States Senate elections were held November 3, 1942, midway through Franklin D. Roosevelt's third term as president. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and two special elections were held to fill vacancies.

The 1940 United States Senate elections coincided with the election of Franklin D. Roosevelt to his third term as president. The 32 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies.

The 1938 United States Senate elections occurred in the middle of Franklin D. Roosevelt's second term. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republicans gained eight seats from the Democrats, though this occurred after multiple Democratic gains since the 1932 election, leading to the Democrats retaining a commanding lead over the Republicans with more than two-thirds of the legislative chamber.

The 1936 United States Senate elections coincided with the reelection of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Great Depression continued and voters backed progressive candidates favoring Roosevelt's New Deal in races across the country. The Democrats gained 5 net seats during the election, and in combination with Democratic and Farmer–Labor interim appointments and the defection of George W. Norris from the Republican Party to become independent, the Republicans were reduced to 16 seats. Democrats gained a further two seats due to mid-term vacancies. The Democrats' 77 seats and their 62-seat majority remain their largest in history.

The 1934 United States Senate elections were held in the middle of Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt's first term. The 32 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. During the Great Depression, voters strongly backed Roosevelt's New Deal and his allies in the Senate, with Democrats picking up a net of nine seats, giving them a supermajority. Republicans later lost three more seats due to mid-term vacancies ; however, a Democrat in Iowa died and the seat remained vacant until the next election. The Democrats entered the next election with a 70-22-2-1 majority.

The 1930 United States Senate elections occurred in the middle of Republican President Herbert Hoover's term. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. With the Great Depression beginning to take hold, Republican incumbents became unpopular, and Democrats picked up a net of eight seats, erasing the Republican gains from the previous election cycle, however, Republicans retained control of the chamber. This was the first of four consecutive Senate elections during the Depression in which Democrats made enormous gains, achieving a cumulative pick-up of 34 seats.
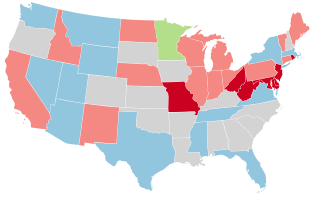
The 1928 United States Senate elections were elections that coincided with the presidential election of Republican Herbert Hoover. The 32 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The strong economy helped the Republicans to gain seven seats from the Democrats.

The 1926 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate that occurred in the middle of Republican President Calvin Coolidge's second term. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republican majority was reduced by seven seats.

The 1924 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate which coincided with the election of Republican President Calvin Coolidge to a full term. The 32 seats of Class 2 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. The strong economy and Coolidge's popularity helped Republican candidates increase their majority by three. Republicans would gain a further two seats through mid-term vacancies bringing their seat share to 56-39-1.

The 1922 United States Senate elections were elections that occurred in the middle of Republican President Warren G. Harding's term. The 32 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. With the Republicans divided between conservative and progressive factions, the Democrats gained six net seats from the Republicans while the Farmer–Labor party gained one. The Republicans retained their Senate majority.

The 1920 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate that coincided with the presidential election of Warren G. Harding. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections, and special elections were held to fill vacancies. Democrat Woodrow Wilson's unpopularity allowed Republicans to win races across the country, winning ten seats from the Democrats and providing them with an overwhelming 59-to-37 majority. The Republican landslide was so vast that Democrats lost over half of the seats that were contested this year and failed to win a single race outside the South.

The 1914 United States Senate elections were held on November 3, 1914. These were the first regularly scheduled elections held following the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment to the United States Constitution in 1913, which required that all seats up for election be popularly elected, rather than chosen by their state legislatures. Thus, it was the first time that elections were generally scheduled on Election Day to coincide with the U.S. House elections. The 32 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections in 1914. Special elections were also held to fill vacancies. These elections occurred in the middle of Democratic President Woodrow Wilson's first term.

The 1912–13 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. They were the last U.S. Senate elections before the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, establishing direct elections for all Senate seats. Senators had been primarily chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1912 and 1913, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. Some states elected their senators directly even before passage of Seventeenth Amendment. Oregon pioneered direct election and experimented with different measures over several years until it succeeded in 1907. Soon after, Nebraska followed suit and laid the foundation for other states to adopt measures reflecting the people's will. By 1912, as many as 29 states elected senators either as nominees of their party's primary or in conjunction with a general election.