
George II was King of Greece from September 1922 to March 1924 and from November 1935 to his death in April 1947.
The abolition of monarchy and anti-royalism is a legislative or revolutionary movement to abolish monarchical elements in government, usually hereditary.

Ioannis Metaxas was a Greek military officer and politician who served as the Prime Minister of Greece from 1936 until his death in 1941. He governed constitutionally for the first four months of his tenure, and thereafter as the strongman leader of the 4th of August Regime following his appointment by King George II.

Alexandros Zaimis was a Greek politician who served as Greece's Prime Minister, Minister of the Interior, Minister of Justice, and High Commissioner of Crete. He served as Prime Minister six times, and although a leader of the monarchist faction was the third and last President of the Second Hellenic Republic.

Georgios Kondylis DSO was a Greek general, politician and prime minister of Greece. He was nicknamed Keravnos, Greek for "thunder" or "thunderbolt".
Parliamentary elections were held in Greece on 17 November 1974. They were the first after the end of the military junta of 1967–1974, and took place during the metapolitefsi era. The winner was Konstantinos Karamanlis and his newly formed conservative party, New Democracy. Karamanlis had already formed a government of national unity just after the fall of the dictatorship. The second-largest party was the centrist Center Union – New Forces. The third party in the Parliament became the newly-formed PASOK, a radical socialist party led by Andreas Papandreou, son of the former Prime Minister Georgios Papandreou.

A referendum on maintaining the monarchy was held in Greece on 1 September 1946. The proposal was approved by 68.4% of voters with a turnout of 88.6%.
A referendum on becoming a republic was held in Greece on 13 April 1924. It followed the catastrophic outcome of the Asia Minor Campaign. As a result of the military defeat, King Constantine I was forced to abdicate in favor of his son, King George II. King George himself later went into exile in the Kingdom of Romania, the home of his wife Elisabeth of Romania, while the government debated the fate of the monarchy. Ultimately, a plebiscite was called. This referendum, following the restoration of Constantine I in 1920, reflected the see-saw nature of the Greek electorate and the then-present dominance of the Liberal and Republican Venizelists in Greek politics and abolished the Crown.

Panagis Tsaldaris was a Greek politician and the 48th Prime Minister of Greece. He was a revered conservative politician and leader for many years (1922–1936) of the conservative People's Party in the period before World War II. He was the husband of Lina Tsaldari, a Greek suffragist, member of Parliament, and the Minister for Social Welfare.

The currently deposed Greek royal family was the ruling family for the Kingdom of Greece from 1863 to 1924 and again from 1935 to 1973.

The history of the Hellenic Republic constitutes three republican periods in the modern history of Greece: from 1822 until 1832; from 1924 until 1935; and from 1974 through to the present. See also the constitutional history of Greece.
Parliamentary elections were held in Greece on 16 December 1923. The result was a victory for the Liberal Party, which won 250 of the 398 seats.
A referendum on retaining the monarchy or becoming a republic was held in Norway on 12 and 13 November 1905. Voters were asked whether they approved of the Storting's decision to authorise the government to make the offer of the throne of the newly self-ruling country. The Storting had wanted to offer the throne to Prince Carl of Denmark, but the prince insisted that the Norwegian people have a chance to decide whether they wanted to retain a monarchy.
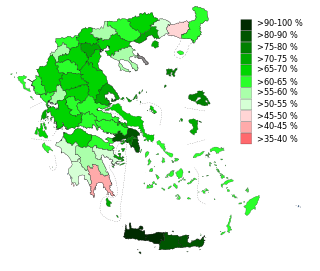
A referendum on retaining the republic was held in Greece on 8 December 1974. After the collapse of the military junta that ruled the country since 1967, the issue of the form of government remained unsolved. The Junta had already staged a referendum held on 29 July 1973, which resulted in the establishment of the Republic. However, after the fall of the military regime, the new government, under Prime Minister Constantine Karamanlis, decided to hold another one, as Junta constituent acts were considered void. Constantine II, the former king, was banned by the new government from returning to Greece to campaign in the referendum, but the Karamanlis government allowed him to make a televised address to the nation. A total of 69.2% of voters favoured retaining the republic with a turnout of 75.6%.

General elections were held in Belgium on 4 June 1950. The result was a victory for the Christian Social Party, which won 108 of the 212 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 54 of the 106 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 92.6%. This election was the last one in Belgian history where a single party achieved an absolute majority. Elections for the nine provincial councils were also held.

A constitutional referendum was held in Greece on 29 July 1973. The amendments would confirm the abolition of the monarchy by the military junta and establish a republic. The proposal was approved by 78.6% of voters with a turnout of 75%.
A constitutional referendum was held in Greece on 15 November 1968. Voters were asked whether they wished to ratify a new constitution prepared by the dictatorial regime. It was approved by 92.1% of voters, with a voter turnout of 77.7%.
A referendum on restoring the monarchy was held in Albania on 29 June 1997 alongside parliamentary elections. The proposal was rejected by 66.7% of voters. However, former Crown Prince Leka claimed that 65.7% voted in favour.











