| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 233 seats in the Andra kammaren of the Riksdag 117 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
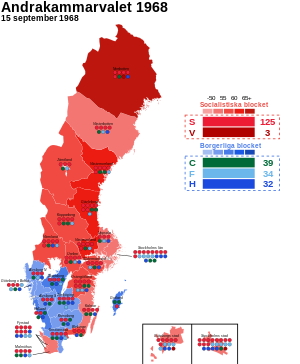 Largest bloc and seats won by constituency | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
General elections were held in Sweden on 15 September 1968. [1] Held in the wake of the crushing of the Prague Spring, it resulted in a landslide victory for the Social Democratic government and Prime Minister Tage Erlander. It is one of two general elections in Swedish history where a single party received more than half of the vote (the other being the election of 1940). Erlander would resign the following year after an uninterrupted tenure of 23 years as head of government.
Contents
The Social Democrats had held the office of Prime Minister since 1932 except a three-month "holiday cabinet" in 1936. This was due to the Social Democrats' absolute majority in the upper house of the Swedish parliament, the First Chamber, and a steady majority for them in general elections and also at large in municipality and county council elections. The latter gave them the majority in the upper house, the First Chamber. When they did not have an absolute majority, the Social Democrats could rely on a passive support from the Communists as the Social Democrats almost always nearly had half of the seats. The two socialist parties in the Riksdag did not however win a majority in the general elections of 1952 and 1956.




