Aripiprazole, sold under the brand names Abilify and Aristada, among others, is an atypical antipsychotic. It is primarily used in the treatment of schizophrenia, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), and bipolar disorder; other uses include as an add-on treatment in major depressive disorder, tic disorders, and irritability associated with autism. Aripiprazole is taken by mouth or via injection into a muscle. A Cochrane review found low-quality evidence of effectiveness in treating schizophrenia.

3,4-Methylenedioxyamphetamine is an empathogen-entactogen, psychostimulant, and psychedelic drug of the amphetamine family that is encountered mainly as a recreational drug. In its pharmacology, MDA is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). In most countries, the drug is a controlled substance and its possession and sale are illegal.

The dopamine receptor D4 is a dopamine D2-like G protein-coupled receptor encoded by the DRD4 gene on chromosome 11 at 11p15.5.

Vanoxerine is a piperazine derivative which is a potent and selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI). Vanoxerine binds to the target site on the dopamine transporter (DAT) ~ 50 times more strongly than cocaine, but simultaneously inhibits the release of dopamine. This combined effect only slightly elevates dopamine levels, giving vanoxerine only mild stimulant effects. Vanoxerine has also been observed to be a potent blocker of the IKr (hERG) channel. Vanoxerine also binds with nanomolar affinity to the serotonin transporter.

Prenalterol is a cardiac stimulant which acts as a β1 adrenoreceptor agonist.
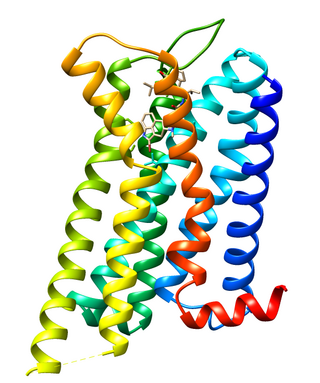
Dopamine receptor D2, also known as D2R, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the DRD2 gene. After work from Paul Greengard's lab had suggested that dopamine receptors were the site of action of antipsychotic drugs, several groups, including those of Solomon Snyder and Philip Seeman used a radiolabeled antipsychotic drug to identify what is now known as the dopamine D2 receptor. The dopamine D2 receptor is the main receptor for most antipsychotic drugs. The structure of DRD2 in complex with the atypical antipsychotic risperidone has been determined.

Dopamine receptor D1, also known as DRD1. It is one of the two types of D1-like receptor family — receptors D1 and D5. It is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD1 gene.

Dopamine receptor D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD3 gene.

RTI-126 is a phenyltropane derivative which acts as a potent monoamine reuptake inhibitor and stimulant drug, and has been sold as a designer drug. It is around 5 times more potent than cocaine at inhibiting monoamine reuptake in vitro, but is relatively unselective. It binds to all three monoamine transporters, although still with some selectivity for the dopamine transporter. RTI-126 has a fast onset of effects and short duration of action, and its pharmacological profile in animals is among the closest to cocaine itself out of all the drugs in the RTI series. Its main application in scientific research has been in studies investigating the influence of pharmacokinetics on the abuse potential of stimulant drugs, with its rapid entry into the brain thought to be a key factor in producing its high propensity for development of dependence in animals.

GBR-12935 is a piperazine derivative which is a potent and selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor. It was originally developed in its 3H radiolabelled form for the purpose of mapping the distribution of dopaminergic neurons in the brain by selective labelling of dopamine transporter proteins. This has led to potential clinical uses in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease, although selective radioligands such as Ioflupane (¹²³I) are now available for this application. GBR-12935 is now widely used in animal research into Parkinson's disease and the dopamine pathways in the brain.

Doxanthrine is a synthetic compound which is a potent and selective full agonist for the dopamine D1 receptor. Doxanthrine has been shown to be orally active in producing contralateral rotation in the 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson's disease.

1-(2-Pyrimidinyl)piperazine (1-PP, 1-PmP) is a chemical compound and piperazine derivative. It is known to act as an antagonist of the α2-adrenergic receptor (Ki = 7.3–40 nM) and, to a much lesser extent, as a partial agonist of the 5-HT1A receptor (Ki = 414 nM; Emax = 54%). It has negligible affinity for the dopamine D2, D3, and D4 receptors (Ki > 10,000 nM) and does not appear to have significant affinity for the α1-adrenergic receptors. Its crystal structure has been determined.

Sunifiram is an experimental drug which has antiamnesic effects in animal studies and with significantly higher potency than piracetam. Sunifiram is a molecular simplification of unifiram (DM-232). Another analogue is sapunifiram (MN-19). As of 2016, sunifiram had not been subjected to toxicology testing, nor to any human clinical trials, and is not approved for use anywhere in the world.
1-(1-Naphthyl)piperazine (1-NP) is a drug which is a phenylpiperazine derivative. It acts as a non-selective, mixed serotonergic agent, exerting partial agonism at the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1E, and 5-HT1F receptors, while antagonizing the 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptors. It has also been shown to possess high affinity for the 5-HT3, 5-HT5A, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors, and may bind to 5-HT4 and the SERT as well. In animals it produces effects including hyperphagia, hyperactivity, and anxiolysis, of which are all likely mediated predominantly or fully by blockade of the 5-HT2C receptor.
Clorotepine, also known as octoclothepin or octoclothepine, is an antipsychotic of the tricyclic group which was derived from perathiepin in 1965 and marketed in the Czech Republic by Spofa in or around 1971 for the treatment of schizophrenic psychosis.

Mazapertine (RWJ-37796) is an antipsychotic agent that was developed by Johnson & Johnson but never marketed. It exerts its pharmacological effect through affinity for dopamine D2, serotonin 5-HT1A, and α1-adrenergic receptors.

Substituted phenylmorpholines, or substituted phenmetrazines alternatively, are chemical derivatives of phenylmorpholine or of the psychostimulant drug phenmetrazine. Most such compounds act as releasers of monoamine neurotransmitters, and have stimulant effects. Some also act as agonists at serotonin receptors, and compounds with an N-propyl substitution act as dopamine receptor agonists. A number of derivatives from this class have been investigated for medical applications, such as for use as anorectics or medications for the treatment of ADHD. Some compounds have also become subject to illicit use as designer drugs.

Enciprazine is an anxiolytic and antipsychotic of the phenylpiperazine class which was never marketed. It shows high affinity for the α1-adrenergic receptor and 5-HT1A receptor, among other sites. The drug was initially anticipated to produce ortho-methoxyphenylpiperazine (oMeOPP), a serotonin receptor agonist with high affinity for the 5-HT1A receptor, as a significant active metabolite, but subsequent research found this not to be the case.

CPD-1 (LS-193743) is a drug with a benzofuranyl piperazine structure, which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT2 receptor family, with highest affinity and full agonist efficacy at the 5-HT2C subtype, and lower affinity and partial agonist action at the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B subtypes.




















