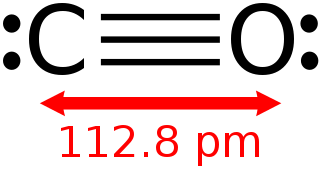Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a sovereign state largely situated in the northwest of South America, with territories in Central America. Colombia shares a border to the northwest with Panama, to the east with Venezuela and Brazil and to the south with Ecuador and Peru. It shares its maritime limits with Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, Jamaica, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic. Colombia is a unitary, constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments, with the capital in Bogota.

Carbon dioxide (chemical formula CO2) is a colorless gas with a density about 60% higher than that of dry air. Carbon dioxide consists of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It occurs naturally in Earth's atmosphere as a trace gas. The current concentration is about 0.04% (410 ppm) by volume, having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Natural sources include volcanoes, hot springs and geysers, and it is freed from carbonate rocks by dissolution in water and acids. Because carbon dioxide is soluble in water, it occurs naturally in groundwater, rivers and lakes, ice caps, glaciers and seawater. It is present in deposits of petroleum and natural gas. Carbon dioxide is odorless at normally encountered concentrations. However, at high concentrations, it has a sharp and acidic odor.
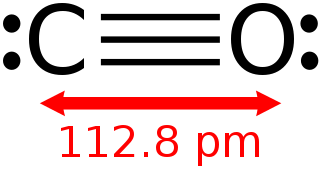
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly less dense than air. It is toxic to animals that use hemoglobin as an oxygen carrier when encountered in concentrations above about 35 ppm, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal biological functions. In the atmosphere, it is spatially variable and short lived, having a role in the formation of ground-level ozone.

The citric acid cycle (CAC) – also known as the TCA cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and carbon dioxide. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically. Even though it is branded as a 'cycle', it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized.

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that can later be released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, "light", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, "putting together". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.

Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the formula CaCO3. It is a common substance found in rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite (most notably as limestone, which is a type of sedimentary rock consisting mainly of calcite) and is the main component of pearls and the shells of marine organisms, snails, and eggs. Calcium carbonate is the active ingredient in agricultural lime and is created when calcium ions in hard water react with carbonate ions to create limescale. It is medicinally used as a calcium supplement or as an antacid, but excessive consumption can be hazardous.

PepsiCo, Inc. is an American multinational food, snack, and beverage corporation headquartered in Harrison, New York, in the hamlet of Purchase. PepsiCo has interests in the manufacturing, marketing, and distribution of grain-based snack foods, beverages, and other products. PepsiCo was formed in 1965 with the merger of the Pepsi-Cola Company and Frito-Lay, Inc. PepsiCo has since expanded from its namesake product Pepsi to a broader range of food and beverage brands, the largest of which included an acquisition of Tropicana Products in 1998 and the Quaker Oats Company in 2001, which added the Gatorade brand to its portfolio.

Global warming is a long-term rise in the average temperature of the Earth's climate system, an aspect of climate change shown by temperature measurements and by multiple effects of the warming. The term commonly refers to the mainly human-caused observed warming since pre-industrial times and its projected continuation, though there were also much earlier periods of global warming. In the modern context the terms global warming and climate change are commonly used interchangeably, but climate change includes both global warming and its effects, such as changes to precipitation and impacts that differ by region. Many of the observed warming changes since the 1950s are unprecedented in the instrumental temperature record, and in historical and paleoclimate proxy records of climate change over thousands to millions of years.
2-Methylbutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, also called 2-Methylbutyryl glycinuria or short/branched-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (SBCADD), is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder. It causes the body to be unable to process the amino acid isoleucine properly. Initial case reports identified individuals with developmental delay and epilepsy, however most cases identified through newborn screening have been asymptomatic.

β-Hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), also known as 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA, is an intermediate in the mevalonate and ketogenesis pathways. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase. The research of Minor J. Coon and Bimal Kumar Bachhawat in the 1950s at University of Illinois led to its discovery.
Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Most of the acetyl-CoA which is converted into fatty acids is derived from carbohydrates via the glycolytic pathway. The glycolytic pathway also provides the glycerol with which three fatty acids can combine to form triglycerides, the final product of the lipogenic process. When only two fatty acids combine with glycerol and the third alcohol group is phosphorylated with a group such as phosphatidylcholine, a phospholipid is formed. Phospholipids form the bulk of the lipid bilayers that make up cell membranes and surround the organelles within the cells

ACADSB is a human gene that encodes short/branched chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (SBCAD), an enzyme in the acyl CoA dehydrogenase family.

Barringtonia acutangula is a species of Barringtonia native to coastal wetlands in southern Asia and northern Australasia, from Afghanistan east to the Philippines and Queensland. Common names include freshwater mangrove, itchytree and mango-pine.
In enzymology, a 3-hydroxy-2-methylbutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.178) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
2-Methylacetoacetyl-CoA is an intermediate in the metabolism of isoleucine.
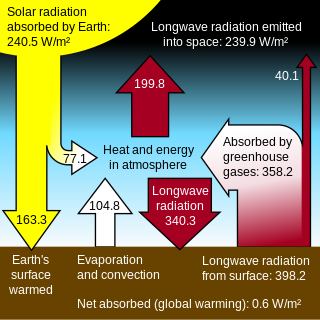
A greenhouse gas is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range. Greenhouse gases cause the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and ozone. Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about −18 °C (0 °F), rather than the present average of 15 °C (59 °F). The atmospheres of Venus, Mars and Titan also contain greenhouse gases.

Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. Like nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal.

Germicidins are a groups of natural products arising from Streptomyces species that acts as autoregulatory inhibitor of spore germination. In Streptomyces viriochromogenes, low concentrations inhibit germination of its own arthrospores, and higher concentrations inhibit porcine Na+/K+ -activated ATPase. Inhibitory effects on germination are also observed when germicidin from Streptomyces is applied to Lepidium sativum. Germicidins and other natural products present potential use as pharmaceuticals, and in this case, those with possible antibiotic or antifungal activity.

β-Hydroxy β-methylbutyryl-coenzyme A (HMB-CoA), also known as 3-hydroxyisovaleryl-CoA, is a metabolite of L-leucine that is produced in the human body. Its immediate precursors are β-hydroxy β-methylbutyric acid (HMB) and β-methylcrotonoyl-CoA (MC-CoA). It can be metabolized into HMB, MC-CoA, and HMG-CoA in humans.