![Stereo, skeletal formula of saccharopine ((2S)-2-{[(5S)-5-aminopentyl]amino}) Saccharopine.svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6b/Saccharopine.svg/250px-Saccharopine.svg.png) | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
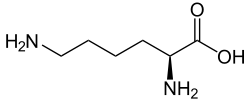
| IUPAC name 2-[(5-Amino-5-carboxypentyl)amino]pentanedioic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | saccharopine |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H20N2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 276.289 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanoic acids | |
Related compounds | Palmitoylethanolamide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Saccharopine is an intermediate in the metabolism of amino acid lysine. It is a precursor of lysine in the alpha-aminoadipate pathway which occurs in fungi and euglenids. In mammals and seed plants saccharopine is an intermediate in the degradation of lysine, formed by condensation of lysine and alpha-ketoglutarate.