
Barnaviridae is a family of non-enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses. Cultivated mushrooms serve as natural hosts. The family has one genus, Barnavirus, which contains one species: Mushroom bacilliform virus. Diseases associated with this family includes La France disease.

Bromoviridae is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are six genera in the family.

Closteroviridae is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four genera and 59 species in this family, seven of which are unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this family include: yellowing and necrosis, particularly affecting the phloem.

Comovirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae; its genera were formerly classified in the family Comoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 62 species in this subfamily, assigned to 3 genera.
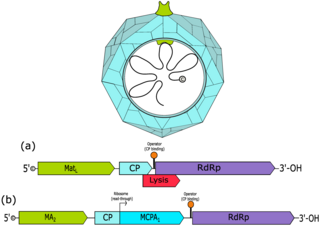
Fiersviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect prokaryotes. Bacteria serve as the natural host. They are small viruses with linear, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genomes that encode four proteins. All phages of this family require bacterial pili to attach to and infect cells. The family has 185 genera, most discovered by metagenomics. In 2020, the family was renamed from Leviviridae to its current name.

Nodaviridae is a family of nonenveloped positive-strand RNA viruses. Vertebrates and invertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family include: viral encephalopathy and retinopathy in fish. There are nine species in the family, assigned to two genera.

Tymoviridae is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 42 species in this family, assigned to three genera, with two species unassigned to a genus.

Alphaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 65 species in this family, assigned to six genera. Diseases associated with this family include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Betaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 108 species in this family, assigned to 13 genera in two subfamilies. Diseases associated with this family include mosaic and ringspot symptoms.
Gammaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Fungi serve as natural hosts. There is only one genus in the family, Mycoflexivirus, which has one species: Botrytis virus F.

Secoviridae is a family of viruses in the order Picornavirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 8 genera and 86 species in this family, one of which is unassigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of families Sequiviridae, now dissolved, and Comoviridae, now subfamily Comovirinae, along with the then unassigned genera Cheravirus, Sadwavirus, and Torradovirus.

Virgaviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. The name of the family is derived from the Latin word virga (rod), as all viruses in this family are rod-shaped. There are currently 59 species in this family, divided among seven genera.
Macluravirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Potyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are ten species in this genus.
Betatetravirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Alphatetraviridae. Moths and butterflies serve as natural hosts. There are seven species in this genus. Infection outcome varies from unapparent to lethal.
Brambyvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Potyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Blackberry virus Y.
Maculavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Tymoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Grapevine fleck virus.
Omegatetravirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Alphatetraviridae. Moths and butterflies serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Infection outcome varies from unapparent to lethal.
Sclerodarnavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Alphaflexiviridae. Fungi serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Sclerotinia sclerotiorum debilitation-associated RNA virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: hypovirulence or debilitation.

Carmotetraviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses. There is only one genus in this family, Alphacarmotetravirus, which has one species: Providence virus. Lepidopteran insects serve as natural hosts.
Permutotetraviridae is a family of viruses. Lepidopteran insects serve as natural hosts. The family contains one genus that has two species. Diseases associated with this family include: infection outcome varies from unapparent to lethal.










