
Zucchius is a prominent lunar impact crater located near the southwestern limb. Because of its location the crater appears oblong-shaped due to foreshortening. It lies just to the south-southwest of the crater Segner, and northeast of the much larger walled plain Bailly. To the southeast is Bettinus, a formation only slightly larger than Zucchius.

Rutherfurd is a lunar impact crater located entirely within the southern rim of the much larger crater Clavius. The crater Porter is located to the north-northeast of Rutherfurd, on the northeastern rim of Clavius. Rutherfurd forms the larger member in an arcing chain of craters of decreasing size that curves across the floor of Clavius. The craters in this chain do not appear to be the same age, so this formation is most likely random in nature.

Petavius is a large lunar impact crater located to the southeast of the Mare Fecunditatis, near the southeastern lunar limb. Attached to the northwest rim is the smaller crater Wrottesley. To the southeast are Palitzsch, Vallis Palitzsch, and Hase. Farther to the north is the large crater Vendelinus. Petavius appears oblong when viewed from the Earth due to foreshortening. Petavius is Imbrian in age.

Taruntius is a lunar impact crater on the northwestern edge of Mare Fecunditatis. It was named after ancient Roman philosopher, mathematician and astrologer Lucius Tarutius Firmanus. To the northwest is the lava-flooded crater Lawrence, and to the north lie the craters Watts and da Vinci.

Faraday is a lunar impact crater in the southern highlands of the Moon. It was named after British chemist and physicist Michael Faraday. It lies across the southeast rim of the larger crater Stöfler, and the northwest rim of Faraday forms a wide rampart across the otherwise flat floor of Stöfler. To the east of Faraday is Maurolycus.

Gassendi is a large lunar impact crater feature located at the northern edge of Mare Humorum. It was named after French astronomer Pierre Gassendi. The formation has been inundated by lava during the formation of the mare, so only the rim and the multiple central peaks remain above the surface. The outer rim is worn and eroded, although it retains a generally circular form. A smaller crater – Gassendi A – intrudes into the northern rim, and joins a rough uplift at the northwest part of the floor. The crater pair bear a curious resemblance to a diamond ring.

Eudoxus is a prominent lunar impact crater that lies to the east of the northern tip of the Montes Caucasus range. It is named after the Greek astronomer Eudoxus of Cnidus. It is located to the south of the prominent crater Aristoteles in the northern regions of the visible Moon. To the south is the ruined formation of Alexander, and the small crater Lamèch lies to the southwest.

Römer is a lunar impact crater that is located to the north of the Sinus Amoris in the northeast section of the Moon. It was named after Danish astronomer Ole Rømer. It lies in the southwestern part of the mountainous region named the Montes Taurus. It was unofficially named as Atatürk by astronomer Hugh Percy Wilkins in his lunar map, possibly due to the fact that the Montes Taurus are located in Turkey. To the west-northwest is the crater-bay Le Monnier, on the eastern edge of Mare Serenitatis.
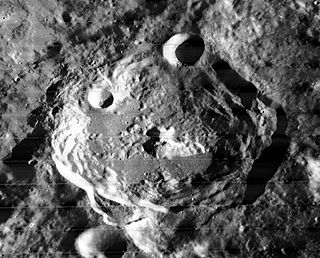
O'Day is a prominent lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It intrudes into the northwestern edge of Mare Ingenii, and the rim is lower on that side. To the northwest is the crater pair of Holetschek and Sierpinski. Southwest of O'Day lies the crater Seidel. It is named in honour of the American physicist Marcus O'Day.

Godin is a lunar impact crater located just to the south of the crater Agrippa, on a rough upland region to the east of Sinus Medii. Its diameter is 34 km. The crater was named after 18th century French astronomer Louis Godin. The ruined crater Tempel lies to the northeast, on the east side of Agrippa. Due south is the flooded remains of Lade.

Harpalus is a young lunar impact crater that lies on the Mare Frigoris, at the eastern edge of the Sinus Roris. To the southeast at the edge of the mare is the small crater Foucault, and to the northwest on the opposite edge is the walled plain named South.

Palitzsch is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southeast part of the Moon, near the southeast rim of the crater Petavius. Just to the southwest of Palitzsch is Hase, while to the east-southeast is Legendre.

Milne is a large lunar crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon, named after the British mathematician and astrophysicist Edward Arthur Milne. It lies to the northeast of the Mare Australe, and southeast of Lacus Solitudinis.

Schomberger is a prominent lunar impact crater that lies in the southern part of the Moon, in the area near the limb. It is located to the southwest of the crater Boguslawsky, and southeast of Simpelius. The relatively young satellite crater Schomberger A is nearly attached to the southern rim, and the much-aged Schomberger C lies just off the western rim.

Carpenter is a lunar impact crater in the northern part of the Moon, relatively close to the limb. At this position the crater is foreshortened and appears oval in shape. It is, however, very nearly circular in outline. The outer rampart to the south is adjoined to the old crater Anaximander, and the satellite formation Anaximander B lies along the western rim. To the northeast is Anaximenes.

Philolaus is a lunar impact crater that is located in the northern part of the Moon's near side. It lies within one crater diameter to the east-southeast of the flooded crater Anaximenes, and to the west of the smaller Anaxagoras. It overlies the older and heavily worn Philolaus C to the south.

Crookes is a lunar impact crater that lies on the Moon's far side as seen from the Earth. It lies just to the southwest of the giant crater Korolev. To the southwest of Crookes is McKellar.

Hayn is a lunar impact crater that lies next to the northeast limb of the Moon. This location restricts the amount of detail that can be viewed from the Earth, as the western inner side is permanently hidden from sight. Observation of this crater can also be affected by libration, which can completely hide this crater from sight.

Das is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located to the north-west of the walled plain Chebyshev. To the south-west of Das is the irregular crater Mariotte, and Von der Pahlen lies to the east-northeast. The crater was named after Indian astronomer Anil Kumar Das.

Kohlschütter is a lunar impact crater that cannot be viewed directly from the Earth as it lies on the Moon's far side. It is located a couple of hundred kilometers to the southeast of the Mare Moscoviense, and due south of the smaller crater Nagaoka. It is a relatively isolated formation surrounded by a multitude of smaller impacts typical of the battered far side.























