
Chittoor is a city and district headquarters in Chittoor district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is also the mandal and divisional headquarters of Chittoor mandal and Chittoor revenue division respectively. The city has a population of 153,756 and that of the agglomeration is 175,647.

Rayalaseema is a geographic region in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It comprises four southern districts of the State, from prior to the districts reorganisation in 2022, namely Kurnool, Anantapur, YSR and Chittoor. Four new districts were created from these, namely Sri Sathya Sai, Nandyal, Annamayya and Tirupati. As of 2011 census of India, the western four districts of the region had a population of 15,184,908 and cover an area of 71,060 km2 (27,440 sq mi).

The Union Public Service Commission, commonly abbreviated as UPSC, is India's premier central recruitment agency for recruitment of all the Group 'A' officers under Government of India. It is responsible for appointments to and examinations for the Group 'A' posts of several central government establishments which also includes the central public sector undertakings and the central autonomous bodies. While Department of Personnel and Training is the central personnel agency in India.
In Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan, a Tehsildar, Talukdar, or Mamlatdar is a land revenue officer accompanied by revenue inspectors. They are in charge of obtaining taxes from a tehsil with regard to land revenue. A tehsildar is also known as an executive magistrate of the relevant tehsil. The immediate subordinate of a tehsildar is known as a naib tehsildar.

Boianapalli Vinod Kumar is an Indian politician and former Member of Parliament, presently serving as Vice-chairman of Telangana State Planning Board. He represented the Karimnagar constituency of Telangana State in the 16th Lok Sabha (2014-2019) and Hanamkonda constituency in the 14th Lok Sabha (2004-2009). He is one of the founding members of the Telangana Rashtra Samithi (TRS) party and is presently a politburo member and served as party's deputy Floor Leader in the 16th Lok Sabha.

Kailasa Venkata Ramiah was an educationist from Andhra Pradesh, India. He was born in Pegallapadu village of Khammam district. He stood first-in-first in both B.Sc and M.Sc from Osmania University and grew to head the Physics Department of Osmania University. He is recipient of the Sir Akbar Hyderi Gold medal and several awards during his career both as student and later as an academician. He finished his PhD in record time and later his research was in quantum mechanics and Raman effect. He published about 100 papers in both national and international journals. He served to become the first Vice-Chancellor of Kakatiya University (1976–79). He founded the University from its inception. It was his vision and efforts that led to the development of Kakatiya University in a short period of time.

Prof. Ghanta Chakrapani is a distinguished Academician and the first (founder) Chairman(2014-2020) of Telangana State Public Service Commission. At Present he is working as a professor of Sociology and Dean of Social Sciences at Dr. B. R. Ambedkar Open University, Hyderabad. Associated with peoples movements, democratic and rights movements he became a public intellectual in the region. Since 1997, Bhuvanagiri meeting he was directly associated with the Telangana separate statehood movement, and emerged as one of the protagonists of the Telangana agitation, as a writer, public speaker, columnist, and Television analyst he played multiple roles in the spread of Telangana ideology. He is one of the founders of the Peace Initiative Committee which negotiated with the government and Maoist Naxalites for peace talks in 2004-05. During the talks, the Government of Andhra Pradesh (AP) appointed him as the convenor for the Cease-fire Monitoring Committee. After the formation of a separate State for Telangana, the Government of Telangana appointed Dr.Chakrapani as the first Chairman of TSPSC. After assuming the Charge as Chairman, TSPSC in December 2014, Prof. Chakrapani has introduced several path-breaking reforms and introduced IT initiatives to modernize the conduct of examinations and processing of recruitments.The Hans India, thereby transforming the youngest State PSC in the country into a modern Public Service Commission.The Hindu.

Greyhounds is a police special forces unit of the Andhra Pradesh and Telangana Police departments in India. Greyhounds specialises in counter-insurgency operations against Naxalite and Maoist terrorists.
The State Police Services (SPS), also simply known as State Police, are the police services under the control of respective state governments of the States and union territories of India.
Raja Bahadur Venkatarama Reddy Telangana State Police Academy (TSPA), formerly Andhra Pradesh Police Academy, is a government institution in the state of Telangana, India that prepares candidates for service in the police and other law enforcement agencies, forensic scientists, and criminal justice.
Muthyala Stephen Raveendra is the present Inspector General of Police of Home Guards, Telangana w.e.f. 19 December 2023. In the past, he was Police commissioner of Cyberabad Metropolitan Police from 25 August 2021 through 12 December 2023, and Inspector General of Police of West Zone also holding full additional charge as Deputy Inspector General of Police
Rachel Chatterjee is a retired Indian Administrative Service (IAS) Officer and the first women to be appointed as the Chairperson of Andhra Pradesh Public Service Commission.

The Bihar Public Service Commission (BPSC) is a body created by the Constitution of India to select applicants for civil services in the Indian state of Bihar according to the merits of the applicants.
V. Dinesh Reddy is an Indian police officer from the state of Andhra Pradesh serving as the Director General of Andhra Pradesh Police. He is an Indian Police Service (IPS) officer from the 1977 batch of the Andhra Pradesh cadre. He completed his schooling from Hyderabad public school (HPS) and college from Madras Christian College (MCC) and St.Stephens Delhi. Dinesh Reddy joined the Indian Police Service on 30 July 1977 from the Andhra Pradesh Cadre and he retired serving as the Director General of Andhra Pradesh Police in 2013.
The Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act of 2014, commonly known as the Telangana Act, is an Act of Indian Parliament that split the state of Andhra Pradesh into Telangana and the residuary Andhra Pradesh state, as an outcome of the Telangana movement. The Act defined the boundaries of the two states, determined how the assets and liabilities were to be divided, and laid out the status of Hyderabad as the permanent capital of new Telangana state and temporary capital of the Andhra Pradesh state.

The Telangana State Public Service Commission, chiefly, TSPSC is a body created by the Constitution of India to select applicants for civil service jobs in the Indian state of Telangana according to the merits of the applicants and the rules of reservation.
Damodar Gautam Sawang is the chairman of Andhra Pradesh Public Service Commission and a former Director General of Police, Andhra Pradesh.
Dr. C. V. S. K. Sarma is an economist and a retired IAS officer with exceptional public service record. He served as an IAS officer from 1980 to 2013, and retired as the Agriculture Production Commissioner & Spl. Chief Secretary to Government, Agriculture & Coop. Department, Government of Andhra Pradesh. He was also the Vice Chancellor, A.P. Horticulture University before he retired.
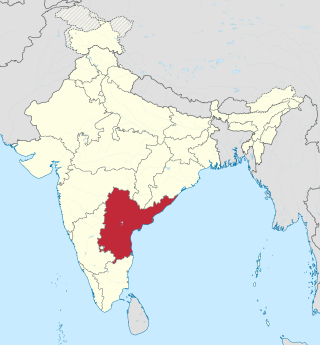
Andhra Pradesh, retrospectively referred to as United Andhra Pradesh, Undivided Andhra Pradesh or Ummadi Andhra Pradesh, was a state in India formed by States Reorganisation Act, 1956 with Hyderabad as its capital and was reorganised by Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014. The state was made up of three distinct cultural regions of Telangana, Rayalaseema, and Coastal Andhra. Before the 1956 reorganisation, Telangana had been part of Hyderabad State ruled by Nizam of Hyderabad, whereas Rayalaseema and Coastal Andhra had been part of Andhra State, formerly a part of Madras Presidency ruled by British India.
Nidigattu Sanjay, better known as N. Sanjay, is a Silver jubilee 1996-batch Regular Recruit (RR) Indian Police Service Officer belonging to Andhra Pradesh cadre. At present, Sanjay is the Chief of AP Criminal Investigation Department. He also holds full additional charges as Director-General of AP Disaster Response and Fire Services and as Director, AP Police Personnel and Training.









